Oracle Database 19c RAC On Oracle Linux 9 Using VirtualBox
Created: 2024-2-13, Updated: 2024-3-18
Table of contents
- Introduction
- Download Software
- VirtualBox Installation
- VirtualBox Network Setup
- Virtual Machine Setup
- Guest Operating System Installation
- Oracle Installation Prerequisites
- Install Guest Additions
- Create Shared Disks
- Clone the Virtual Machine
- Install the Grid Infrastructure
- Install the Database Software
- Create a Database
- Check the Status of the RAC
- Reference
This article describes the installation of Oracle Database 19c RAC on Linux (Oracle Linux 9.3 64-bit) using VirtualBox (7.0.14) with no additional shared disk devices.
Introduction
One of the biggest obstacles preventing people from setting up test RAC environments is the requirement for shared storage. In a production environment, shared storage is often provided by a SAN or high-end NAS device, but both of these options are very expensive when all you want to do is get some experience installing and using RAC. A cheaper alternative is to use a FireWire disk enclosure to allow two machines to access the same disk(s), but that still costs money and requires two servers. A third option is to use virtualization to fake the shared storage.
Using VirtualBox you can run multiple Virtual Machines (VMs) on a single server, allowing you to run both RAC nodes on a single machine. In addition, it allows you to set up shared virtual disks, overcoming the obstacle of expensive shared storage.
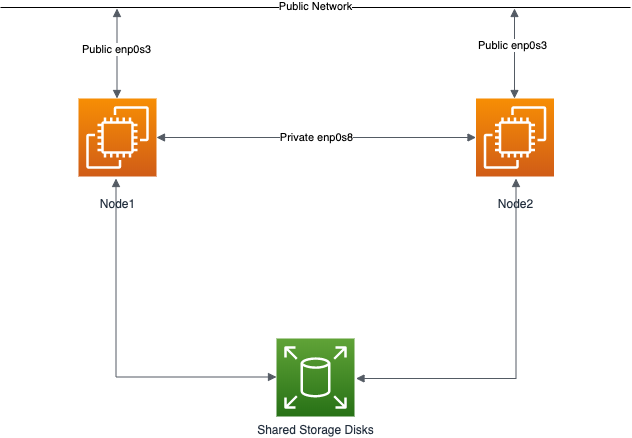
Before you launch into this installation, here are a few things to consider.
- The finished system includes the host operating system, three guest operating systems, two sets of Oracle Grid Infrastructure (Clusterware + ASM) and two Database instances all on a single machine. As you can imagine, this requires a significant amount of disk space, CPU and memory.
- Following on from the last point, the RAC node VMs will each need at least 8G of RAM, but you will see I used 10G for each, and it was still slow. Don’t assume you will be able to run this on a small PC or laptop. You won’t.
- This procedure provides a bare bones installation to get the RAC working. There is no redundancy in the Grid Infrastructure installation or the ASM installation. To add this, simply create double the amount of shared disks and select the “Normal” redundancy option when it is offered. Of course, this will take more disk space.
- This is not, and should not be considered, instructions for a production-ready system. It’s simply to allow you to see what is required to install RAC and give you a system to experiment with.
- The DNS is required to support the scan listener. In previous releases I suggested running the DNS on the host server, but this is easier.
- This article uses the 64-bit versions of Oracle Linux and Oracle 19c.
- When doing this installation on my server, I split the virtual disks on to different physical disks. This is not necessary, but makes things run a bit faster.
- This will probably take over three hours to complete. Maybe a lot longer if you have severe memory or disk speed limitations.
Download Software
Download the following software.
- Oracle Linux 9 (Use the latest spin eg. 9.3)
- VirtualBox (7.0.12)
- Oracle 19c (19.3) Software (64 bit)
- Oracle 19c 19.22 RU from MOS
- OPatch for 19c latest version from MOS
- other necessary patches such as ACFS patch from MOS
This article has been updated for the 19c release and Oracle Linux 9 combination, but the installation is essentially unchanged since 12.2.0.1. Any variations specific for 19c and OL9 will be highlight.
Depending on your minor version of VirtualBox and Oracle Linux, there may be some slight variation in how the screen shots look.
VirtualBox Installation
First, install the VirtualBox software. On RHEL and its clones you do this with the following type of command as the root user.
# rpm -Uvh VirtualBox*.rpm
The package name will vary depending on the host distribution you are using. Once complete, VirtualBox is started from the menu.
VirtualBox Network Setup
We need to make sure a host-only network is configured and check/modify the IP range for that network. This will be the public network for our RAC installation.
- Start VirtualBox from the menu.
- Select the “Tools” option, click “Network” in the pop out menu.
- Click the “Create” button on the right size of the screen. A network called “HostNetwork” will be created.
If you want to use a different subnet for your public addresses you can change the network details here. Just make sure the subnet you choose doesn’t match any real subnets on your network. I’ve decided to stick with the default, which for me is “192.168.56.X”.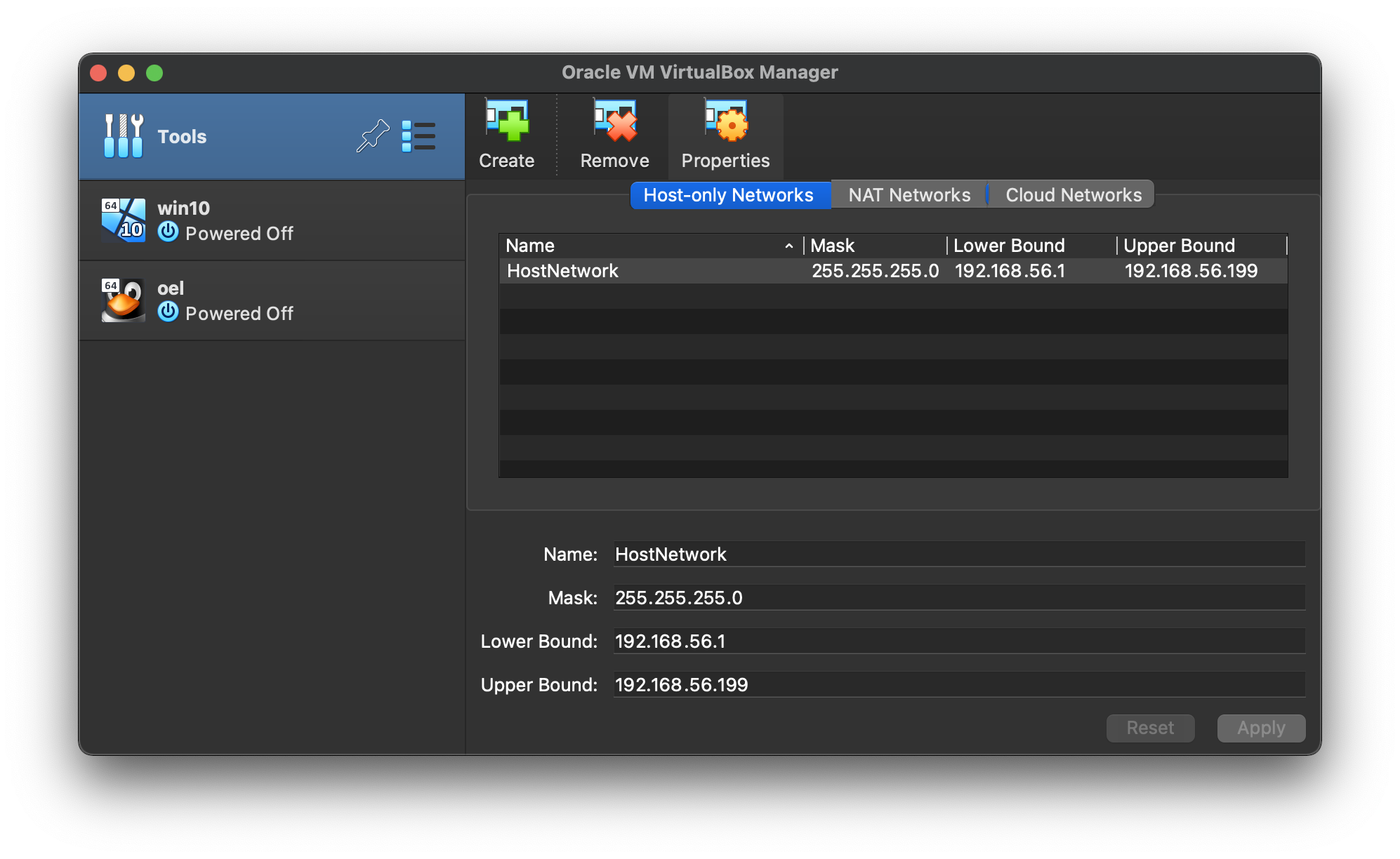
Virtual Machine Setup
Now we must define the two virtual RAC nodes. We can save time by defining one VM, then cloning it when it is installed.
Start VirtualBox and click the “New” button on the toolbar. Enter the name “ol9-19c-rac1”, OS “Linux” and Version “Oracle Linux 9.x (64-bit)”, then click the “Next” button. 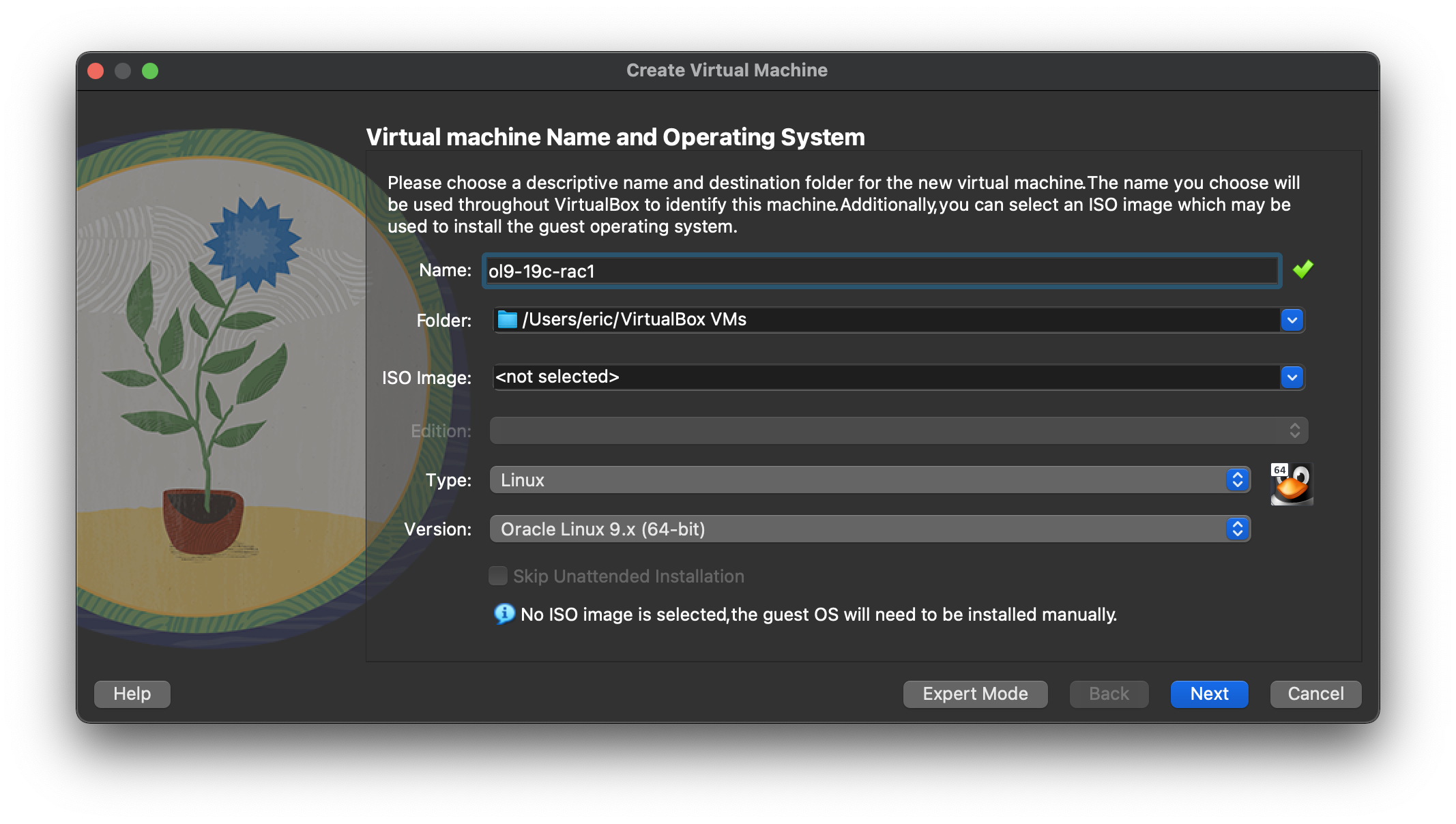 Enter “8192 MB” as the base memory size, then click the “Next” button.
Enter “8192 MB” as the base memory size, then click the “Next” button. 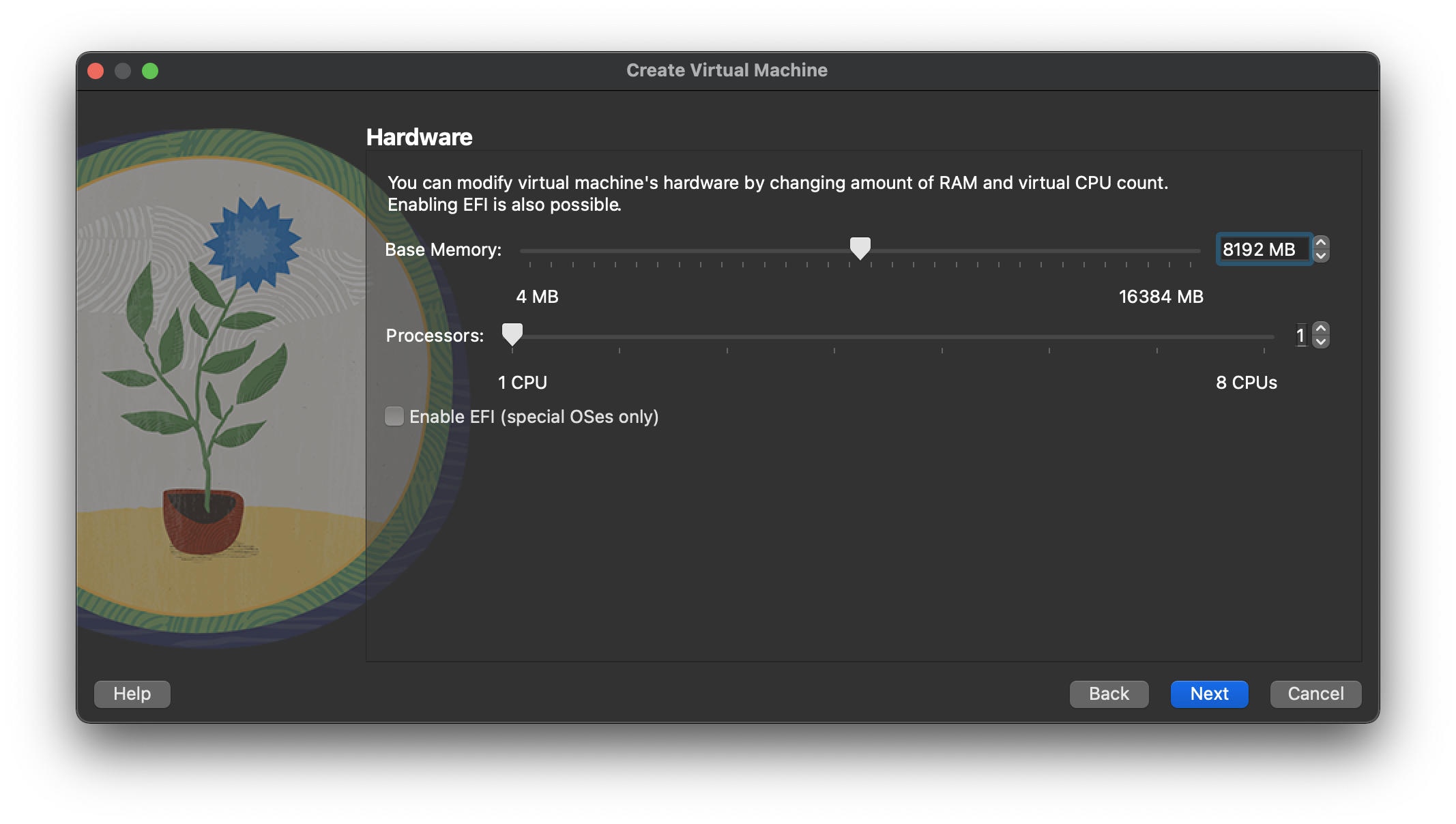 Set the size to “120.00 GB” and accept other default option for a new virtual hard disk and click the “Next” button.
Set the size to “120.00 GB” and accept other default option for a new virtual hard disk and click the “Next” button.
If you can spread the virtual disks onto different physical disks, that will improve performance. 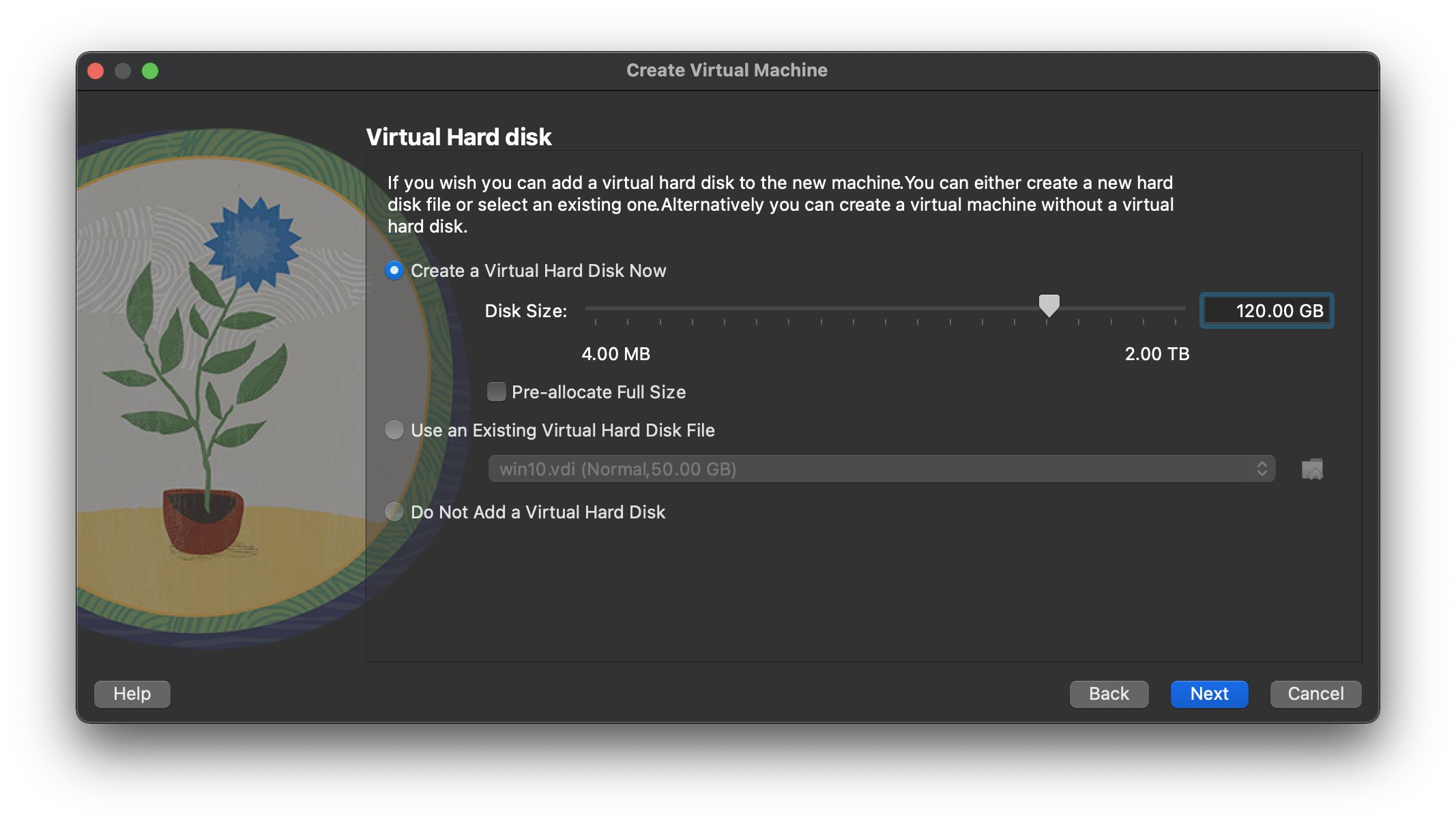 By clicking “Finish” button will complete the wizard of create a new virtual machine.
By clicking “Finish” button will complete the wizard of create a new virtual machine. 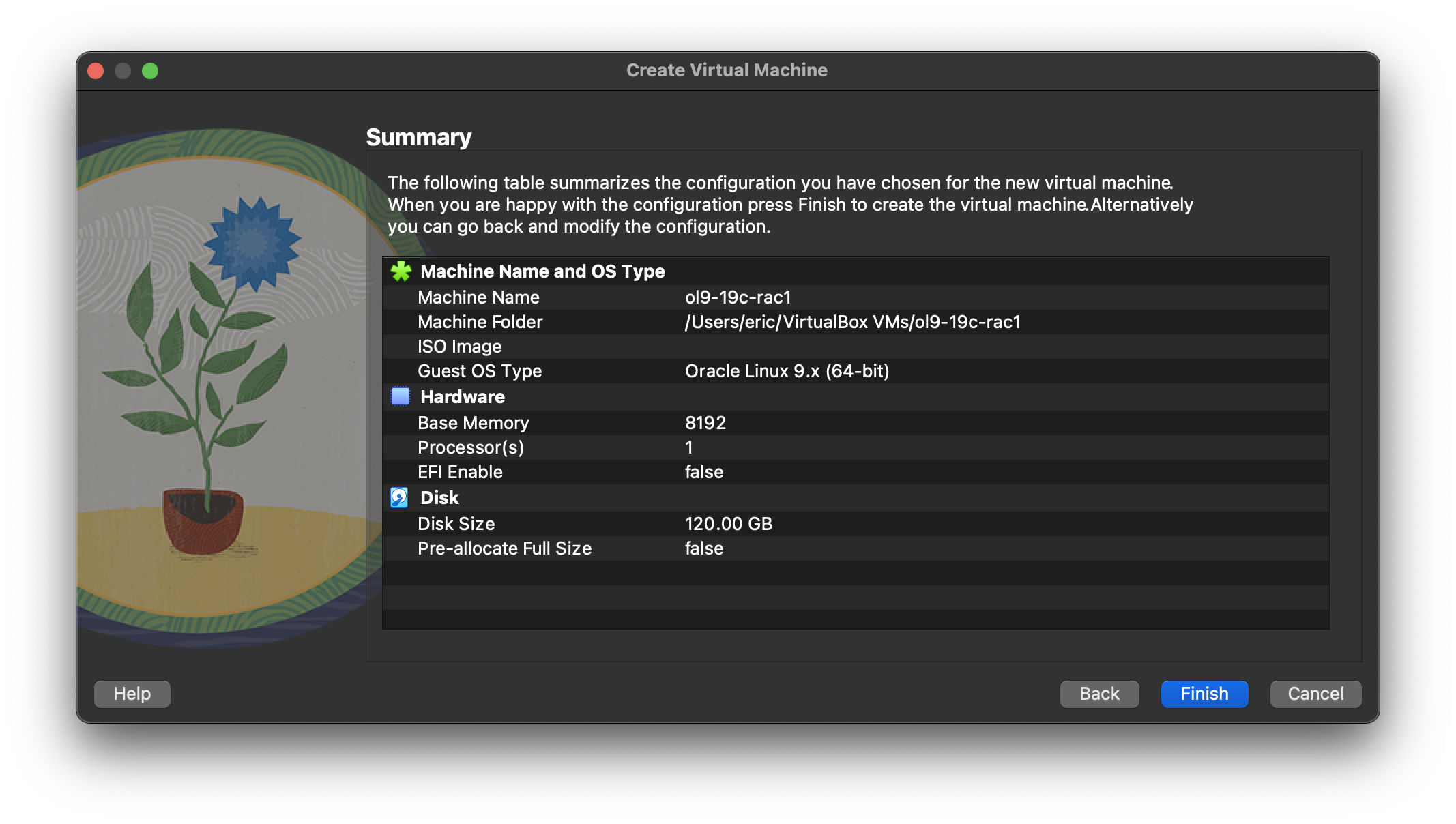 The “ol9-19c-rac1” VM will appear on the left hand pane. Click on the “Settings” on the toolbar.
The “ol9-19c-rac1” VM will appear on the left hand pane. Click on the “Settings” on the toolbar. 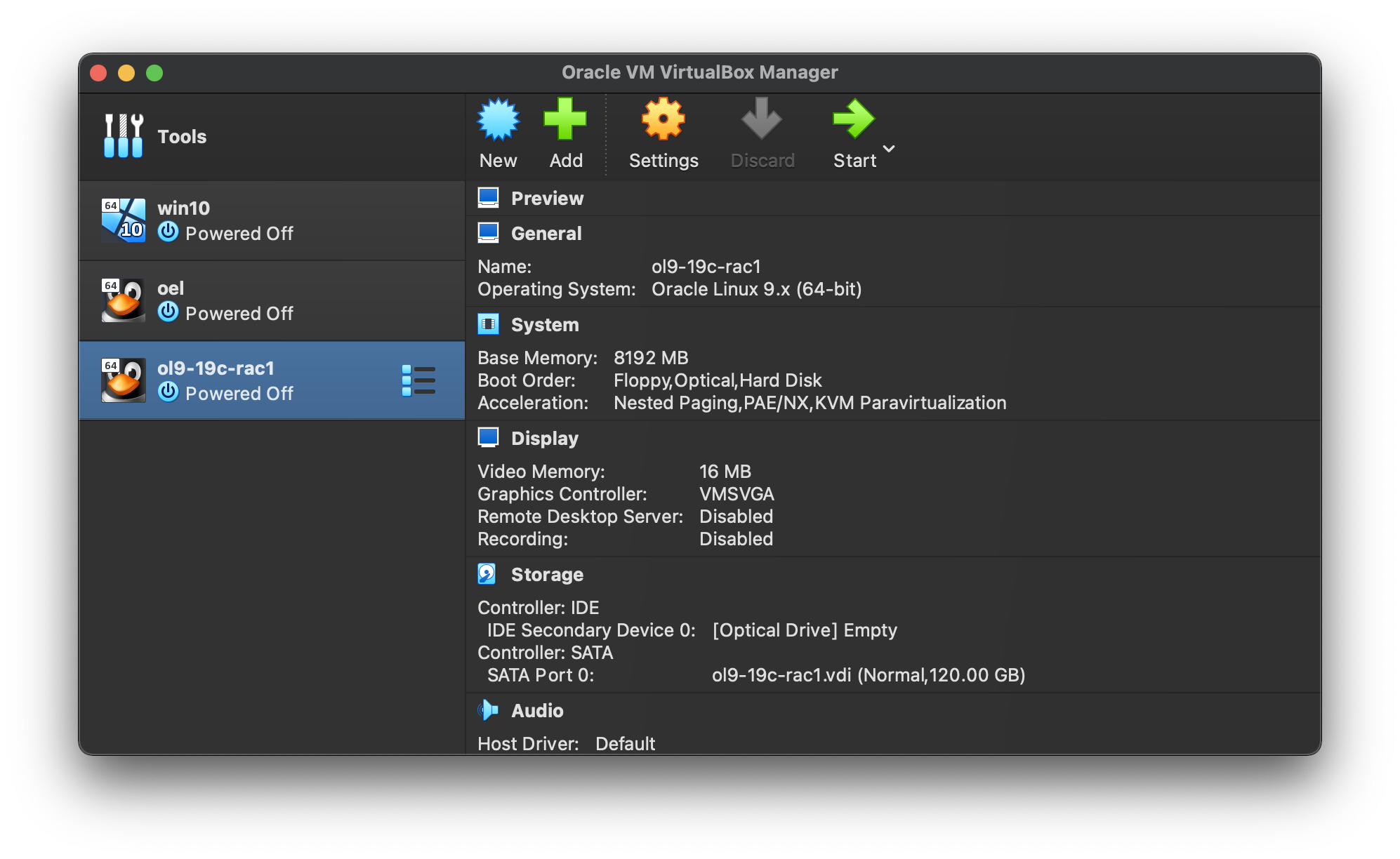 Select “Network” section, and make sure “Adapter 1” is enabled, set to “NAT”, then click on the “Adapter 2” tab.
Select “Network” section, and make sure “Adapter 1” is enabled, set to “NAT”, then click on the “Adapter 2” tab. 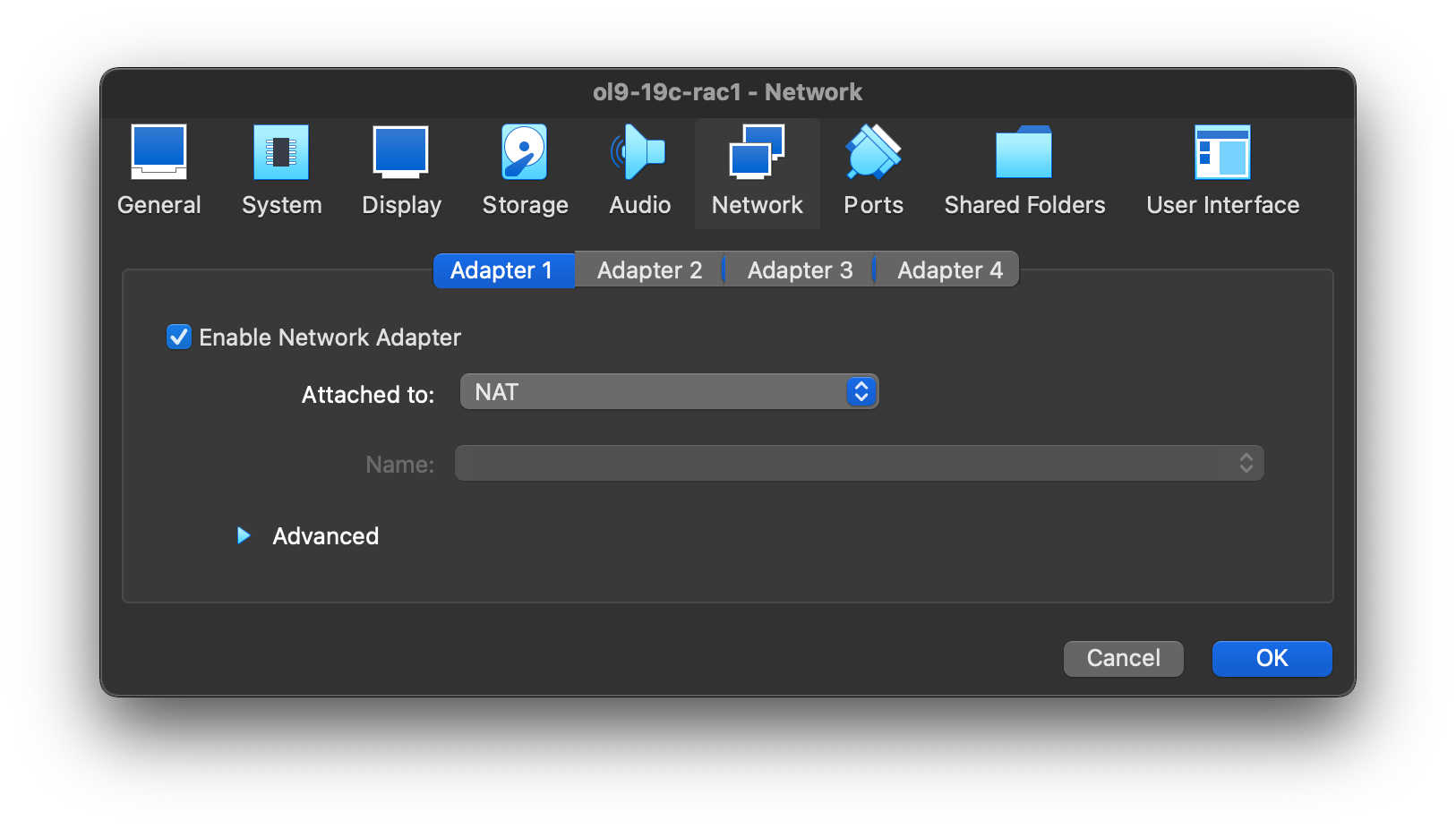 Make sure “Adapter 2” is enabled, set to “Host-only Network”, then click on the “Adapter 3” tab.
Make sure “Adapter 2” is enabled, set to “Host-only Network”, then click on the “Adapter 3” tab. 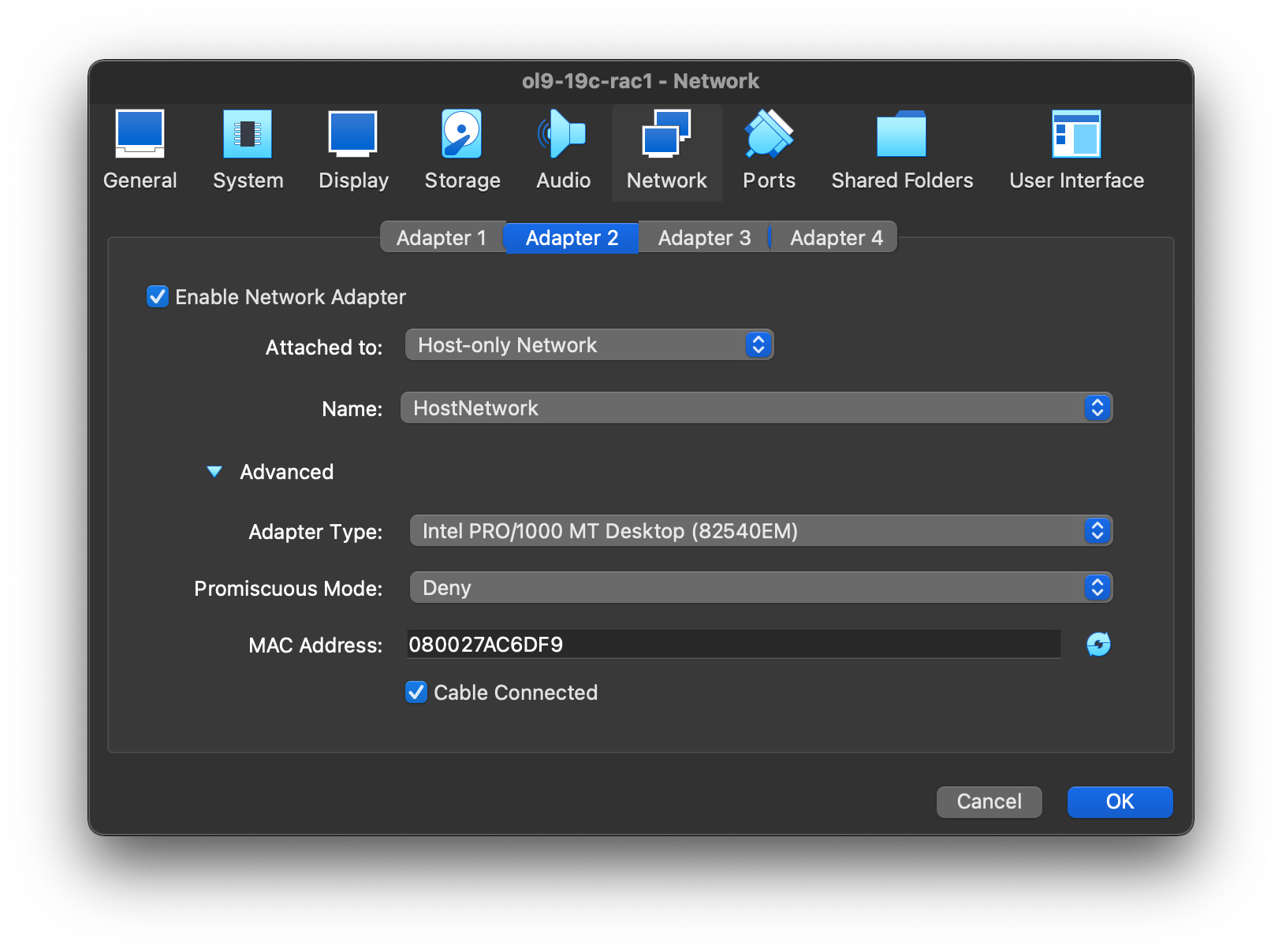 Make sure “Adapter 3” is enabled, set to “Internal Network”, then click on the “System” section.
Make sure “Adapter 3” is enabled, set to “Internal Network”, then click on the “System” section.  On “System” section, move “Hard Disk” to the top of the boot order and uncheck the “Floppy” option, then click the “OK” button.
On “System” section, move “Hard Disk” to the top of the boot order and uncheck the “Floppy” option, then click the “OK” button. 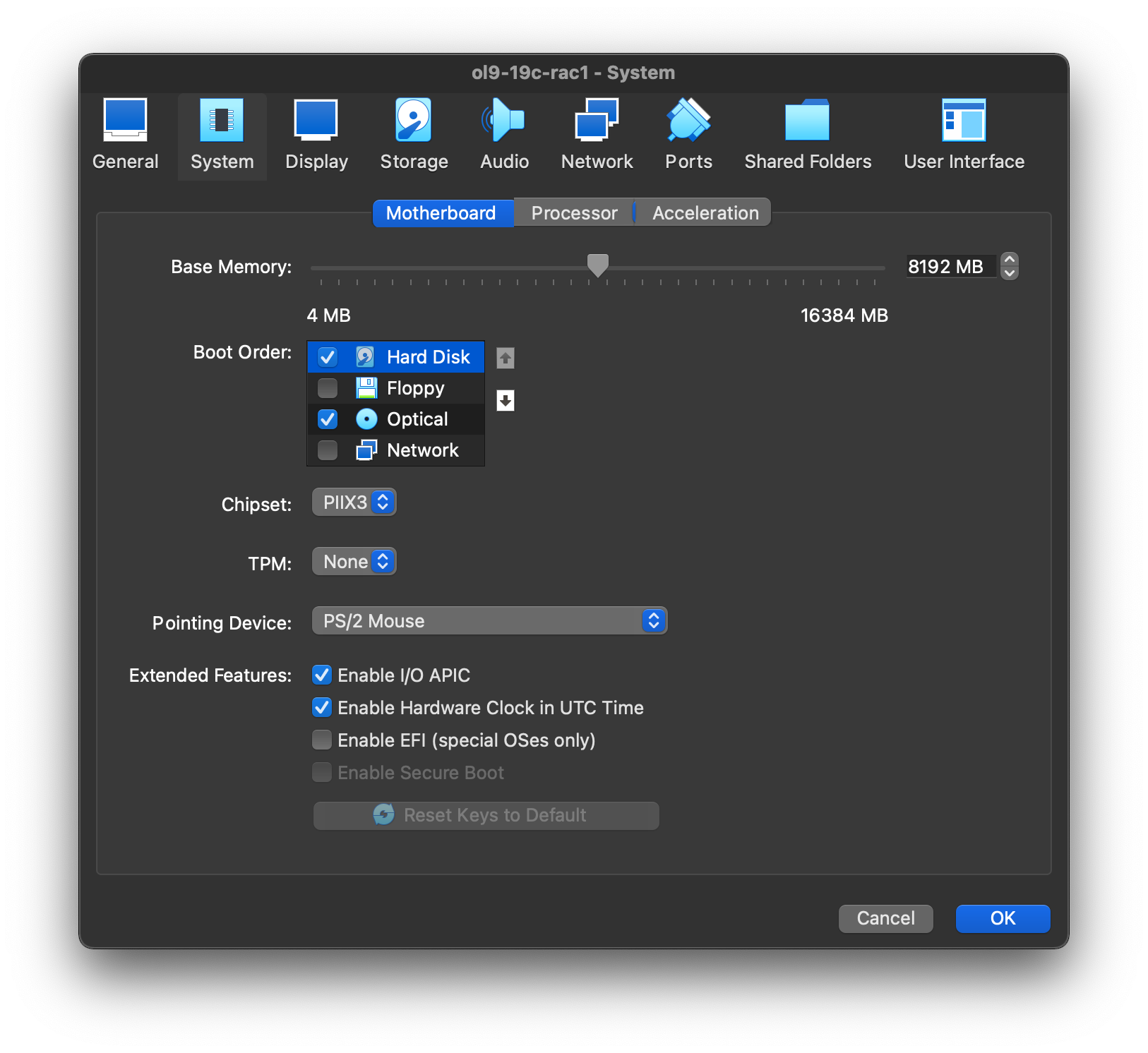 The virtual machine is now configured so we can start the guest operating system installation.
The virtual machine is now configured so we can start the guest operating system installation. 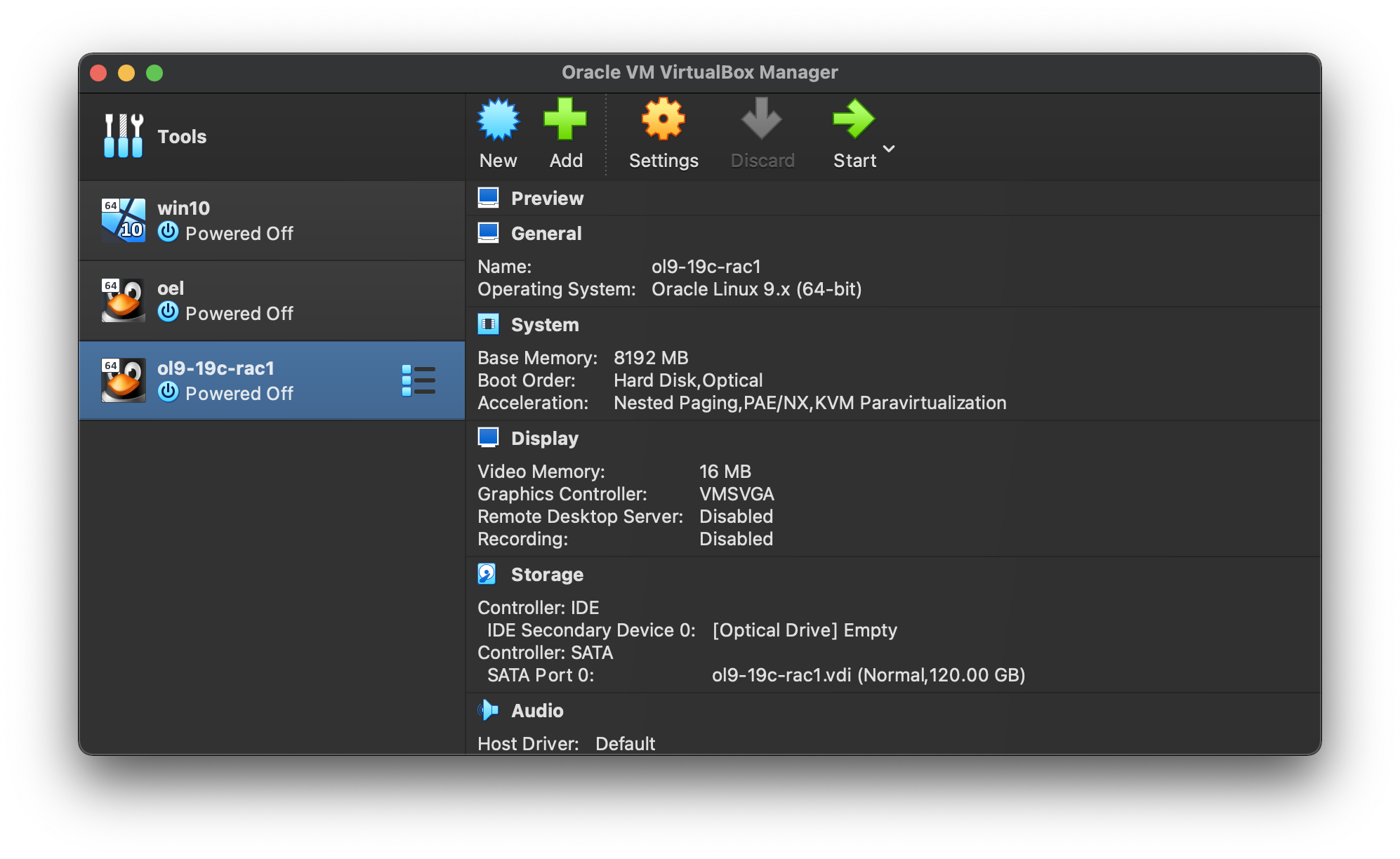
Guest Operating System Installation
With the new VM highlighted, click the “Start” button on the toolbar.  On the “Select start-up disk” screen,
On the “Select start-up disk” screen, 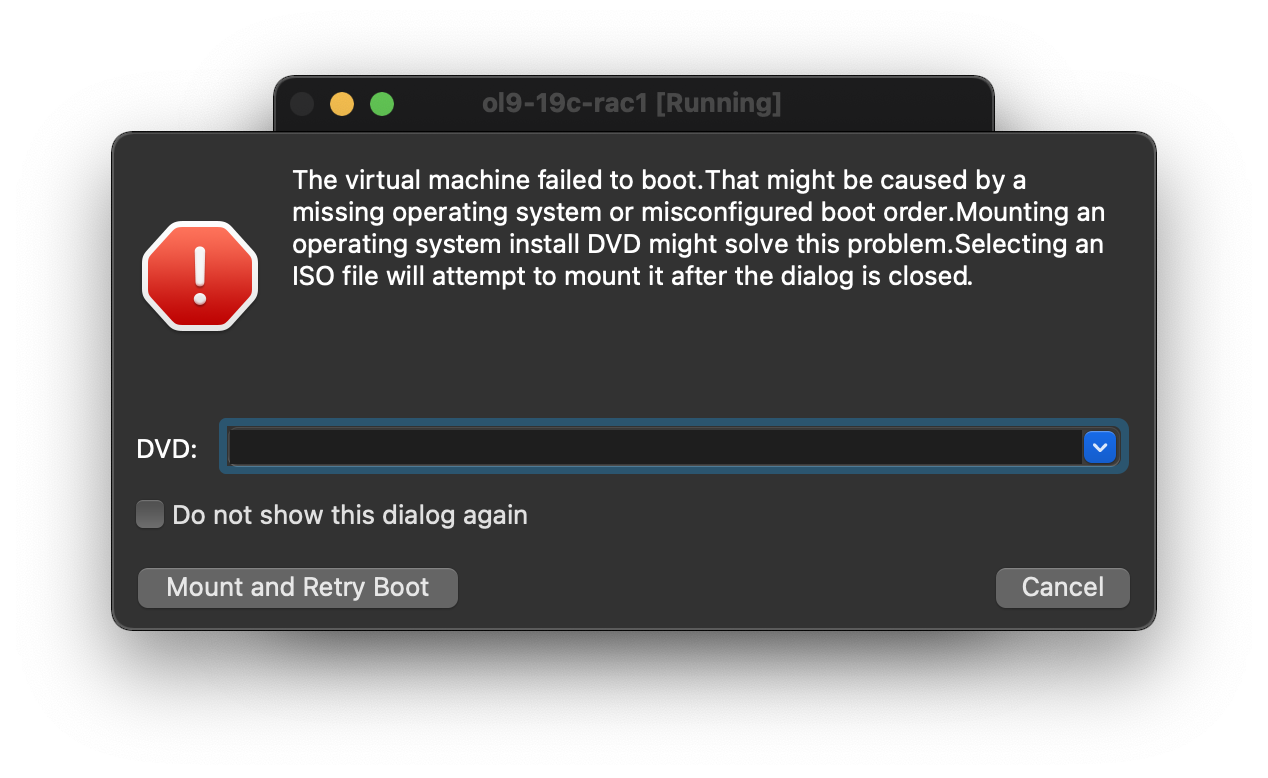 Choose the relevant Oracle Linux ISO image and click the “Mount and Retry Boot” button.
Choose the relevant Oracle Linux ISO image and click the “Mount and Retry Boot” button. 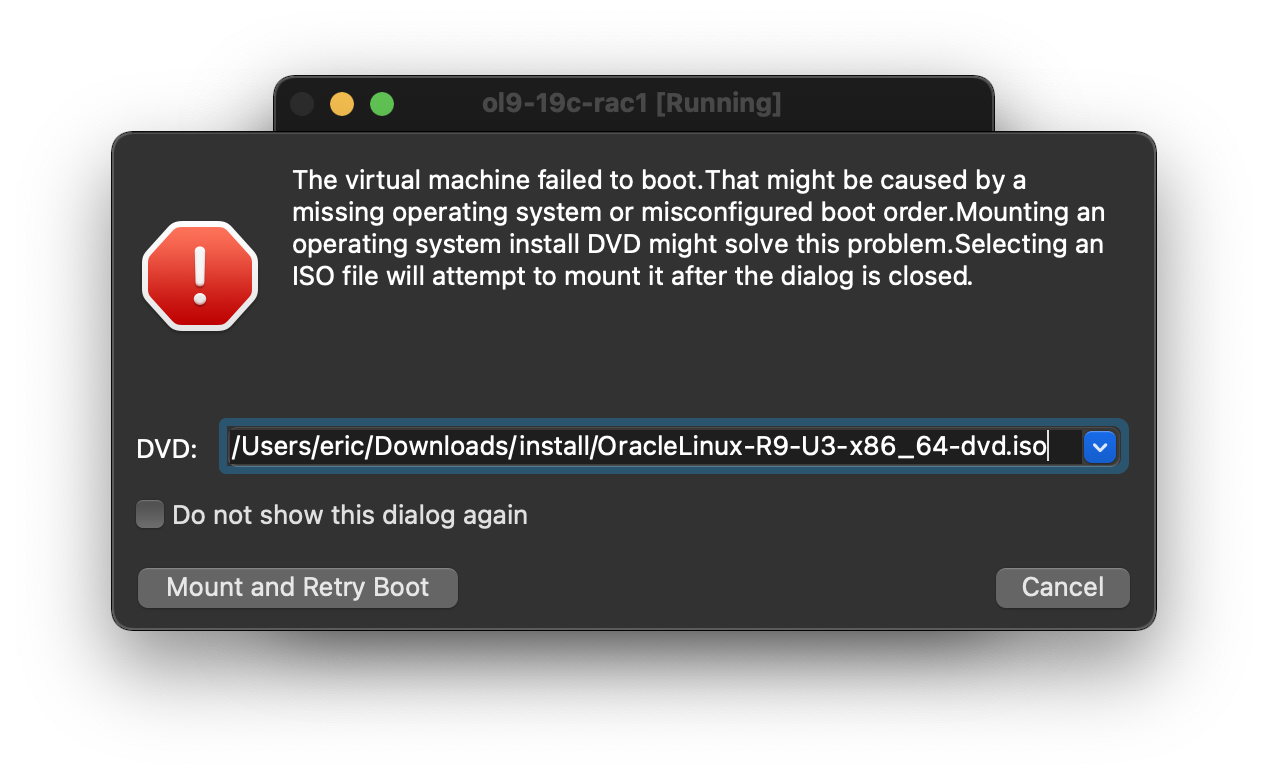 The resulting console window will contain the Oracle Linux boot screen.
The resulting console window will contain the Oracle Linux boot screen.
Click arrow up key to select “Install Oracle Linux 9.3.0” option and click enter key.  Wait a few seconds, the interactive installation window will prepare.
Wait a few seconds, the interactive installation window will prepare.  Continue through the Oracle Linux 9 installation as you would for a basic server.
Continue through the Oracle Linux 9 installation as you would for a basic server.  More specifically, it should be a server installation with a minimum of 4G+ swap, firewall disabled, SELinux set to permissive and the following package groups installed: “Server with GUI”
More specifically, it should be a server installation with a minimum of 4G+ swap, firewall disabled, SELinux set to permissive and the following package groups installed: “Server with GUI” 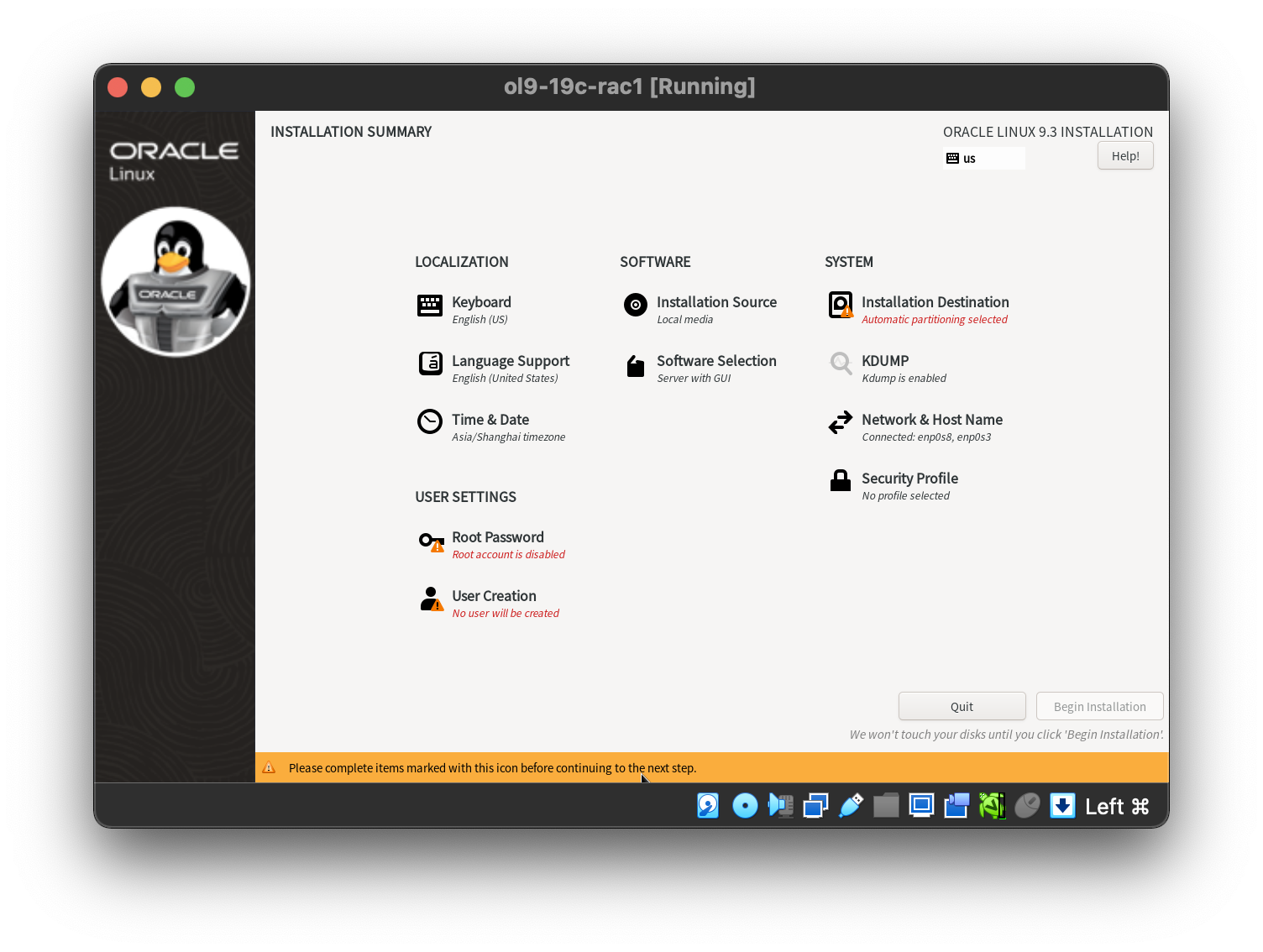 Manual partition the disk with adding swap space.
Manual partition the disk with adding swap space. 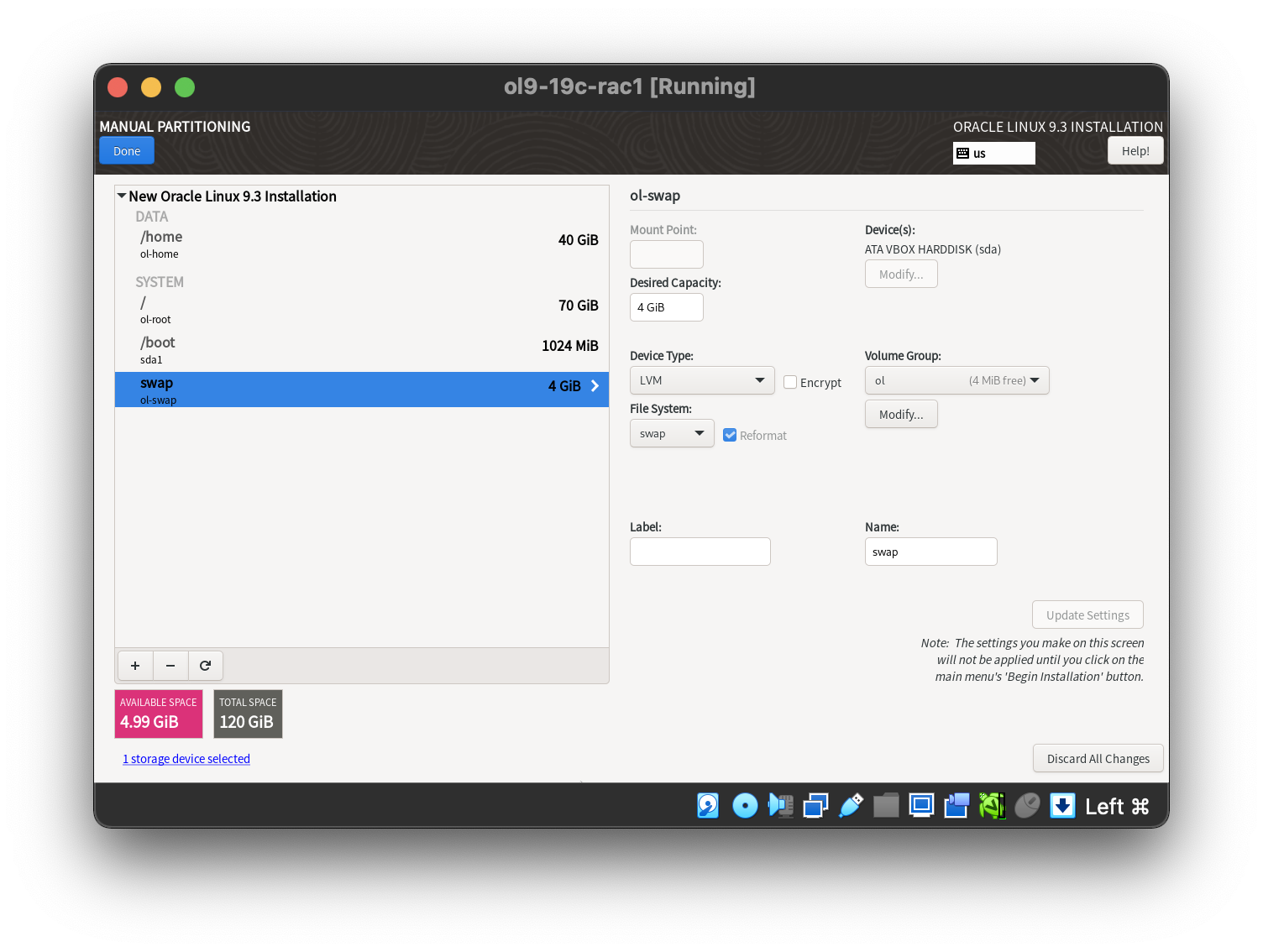 Setting the 1st network adaptor.
Setting the 1st network adaptor. 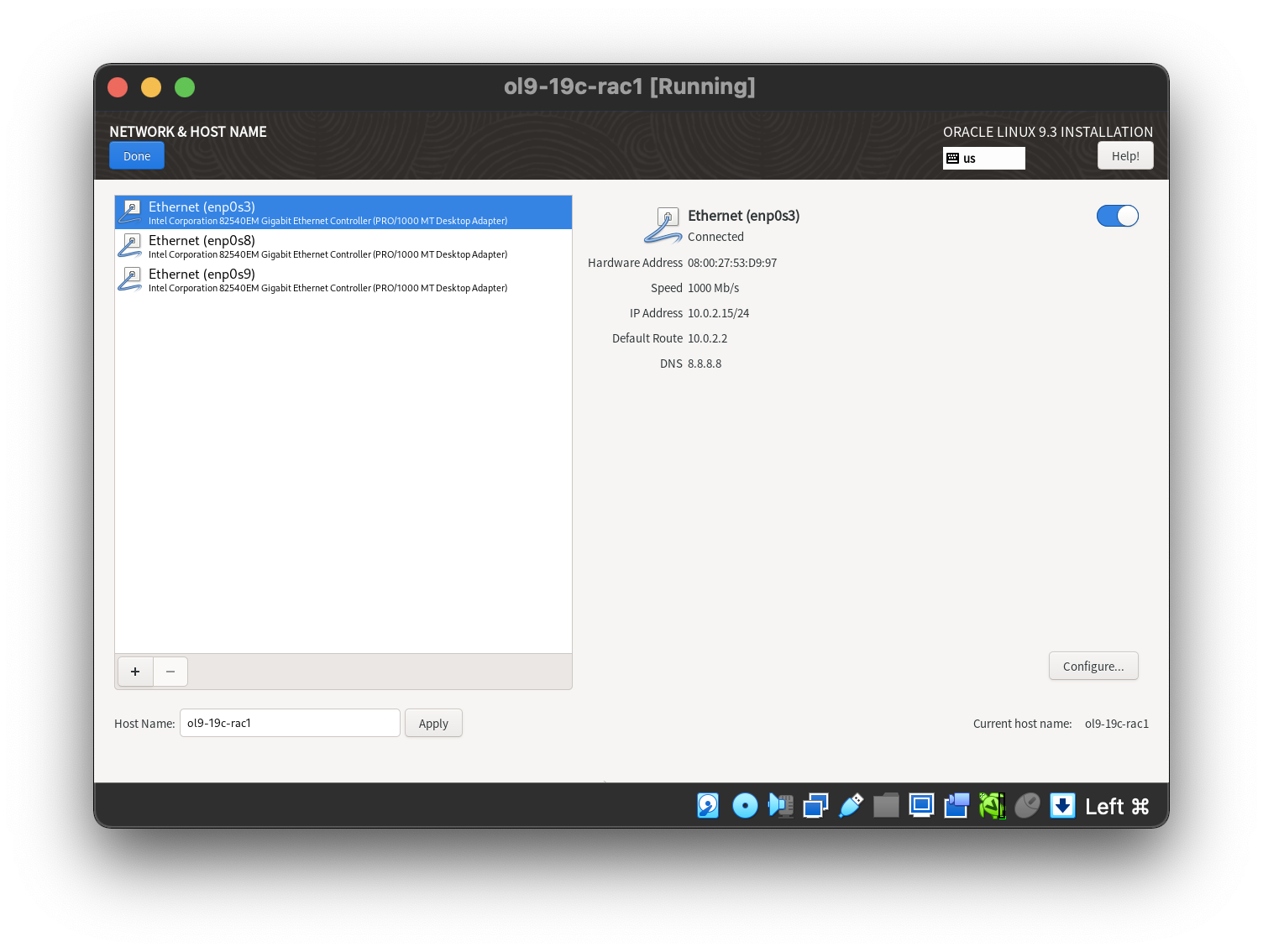 Setting the 2nd network adaptor.
Setting the 2nd network adaptor. 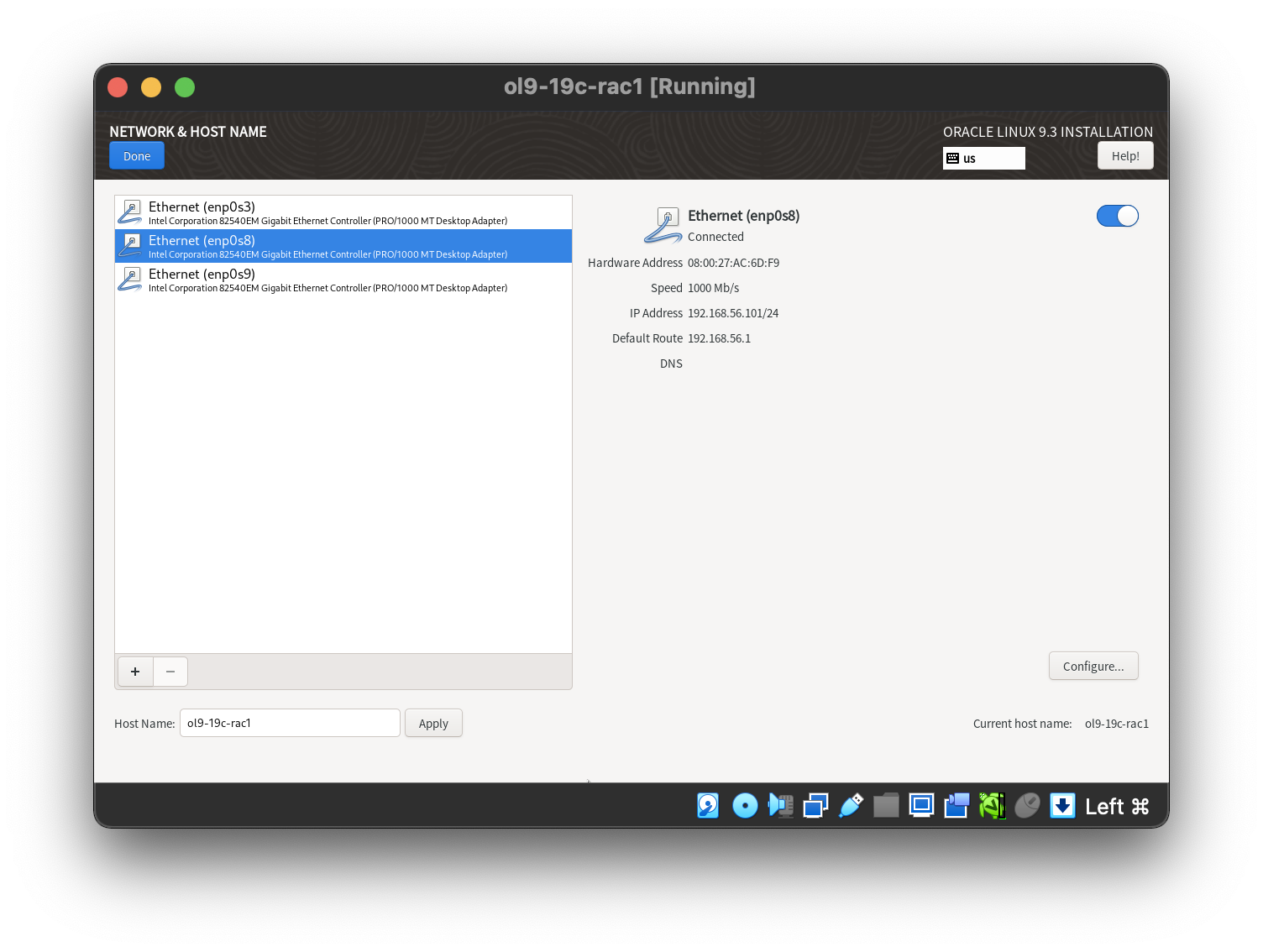 Setting the 3rd network adaptor.
Setting the 3rd network adaptor. 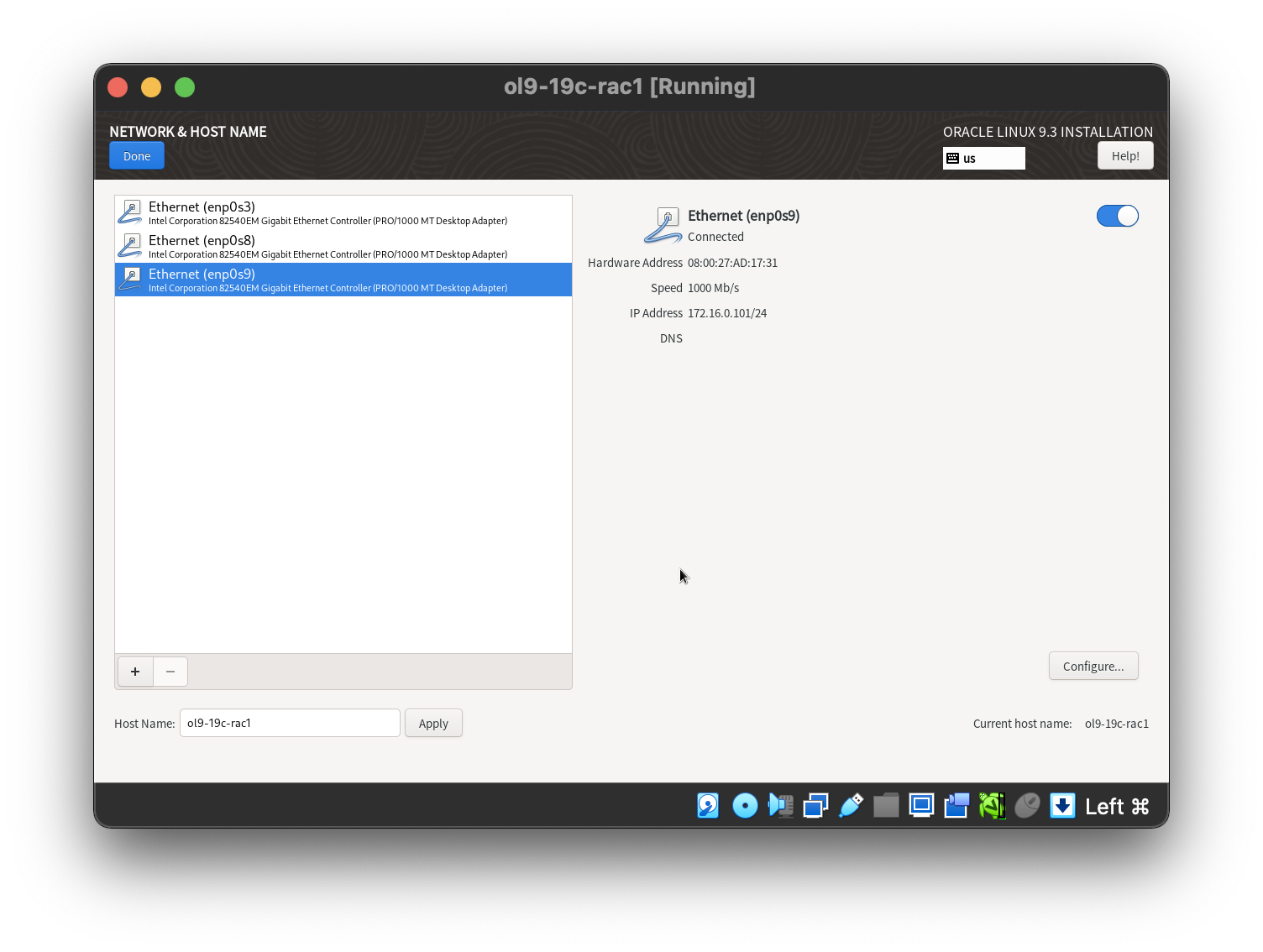 Select the software category.
Select the software category. 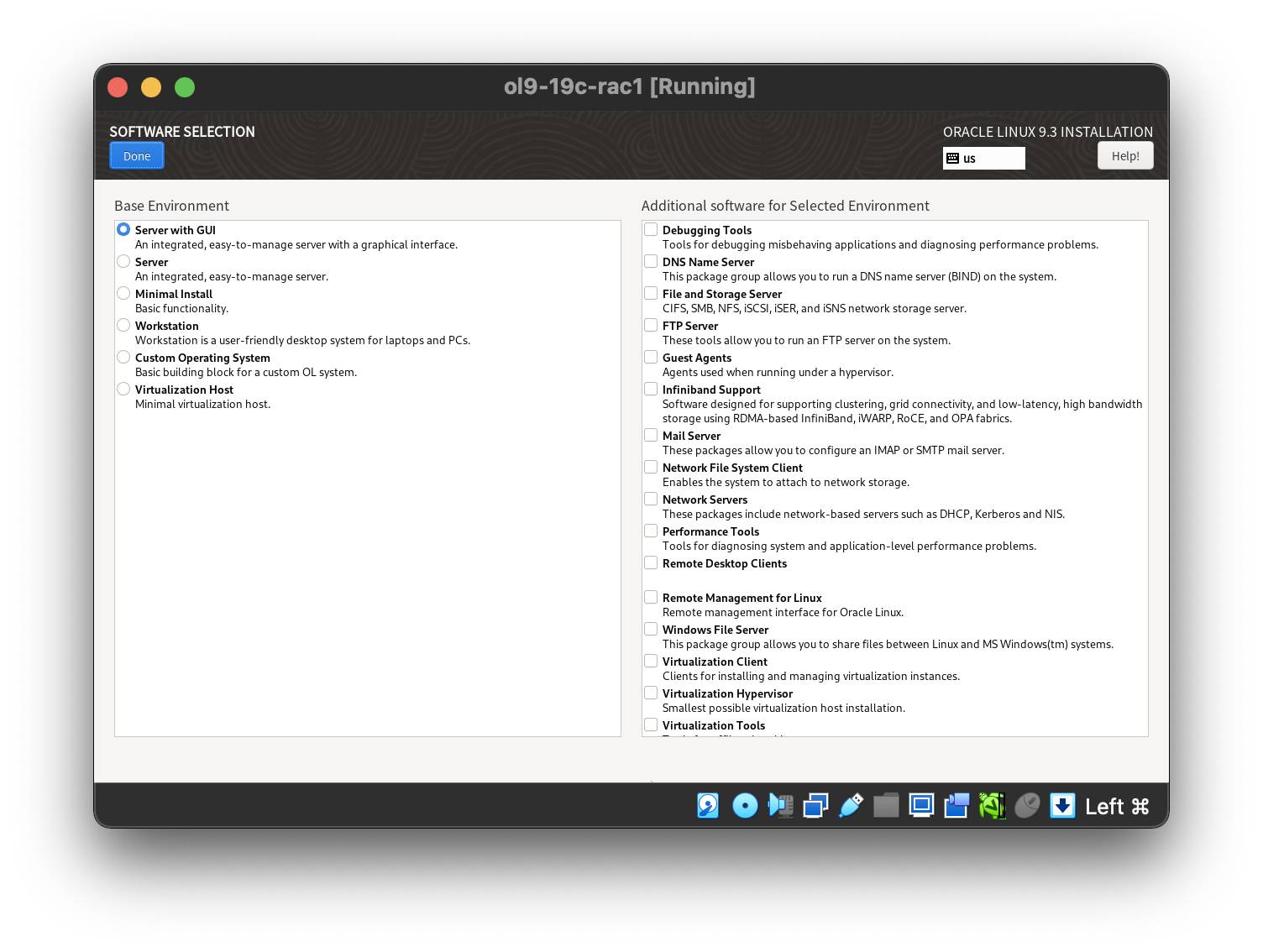 Setting the desired timezone.
Setting the desired timezone. 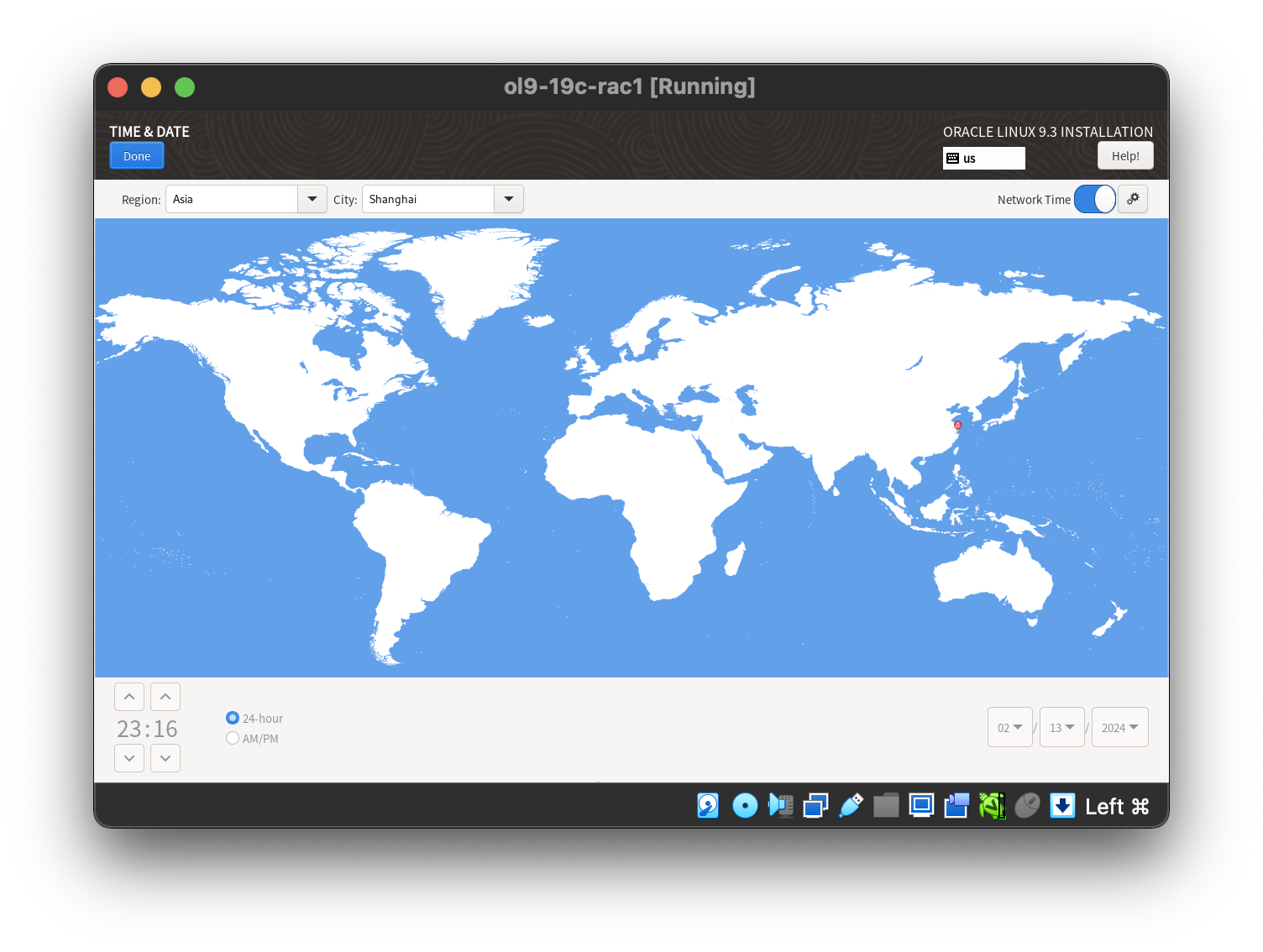 Then start the installation.
Then start the installation. 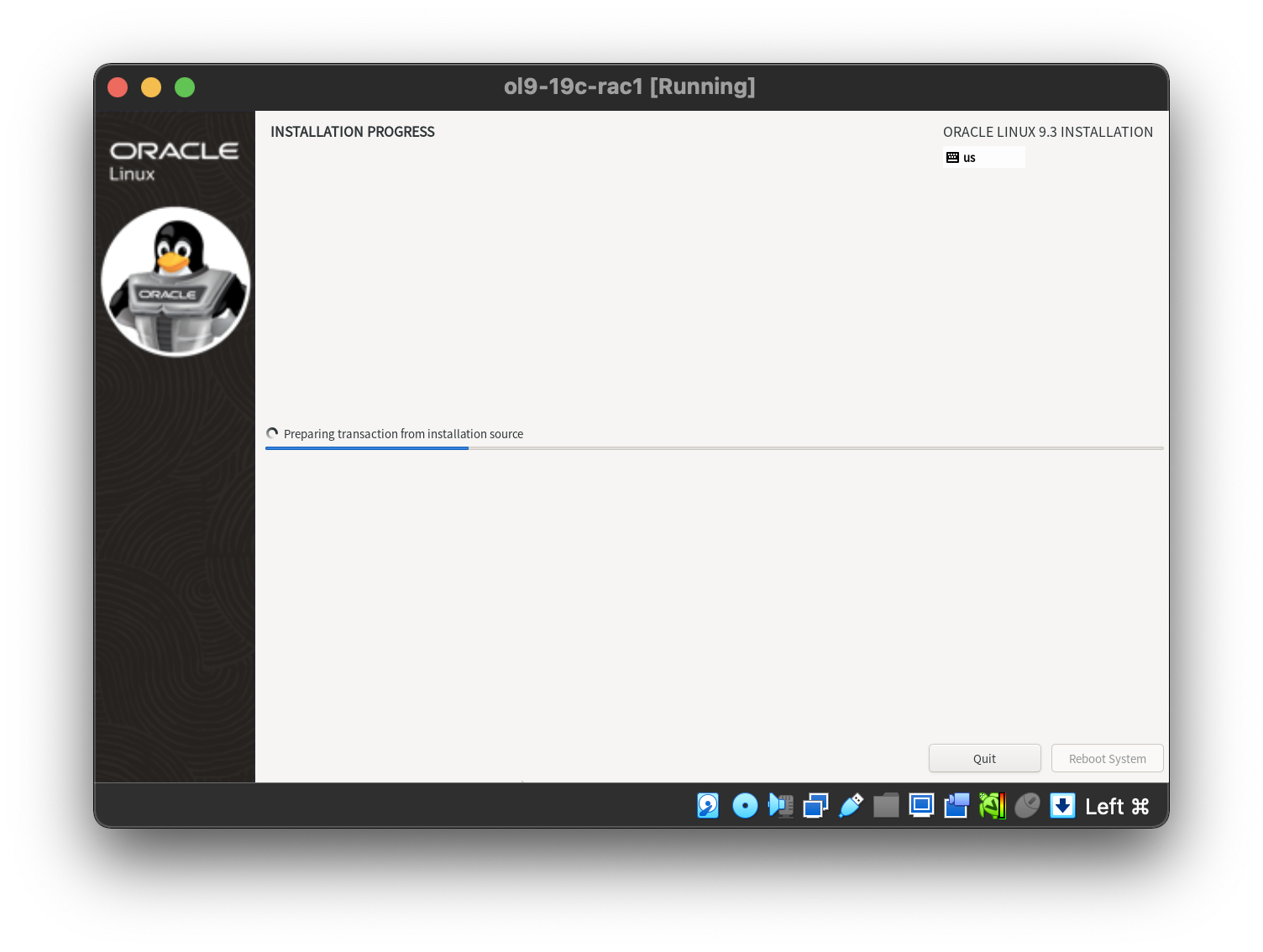 When all packages installed and the installation complete by click “Reboot System”.
When all packages installed and the installation complete by click “Reboot System”. 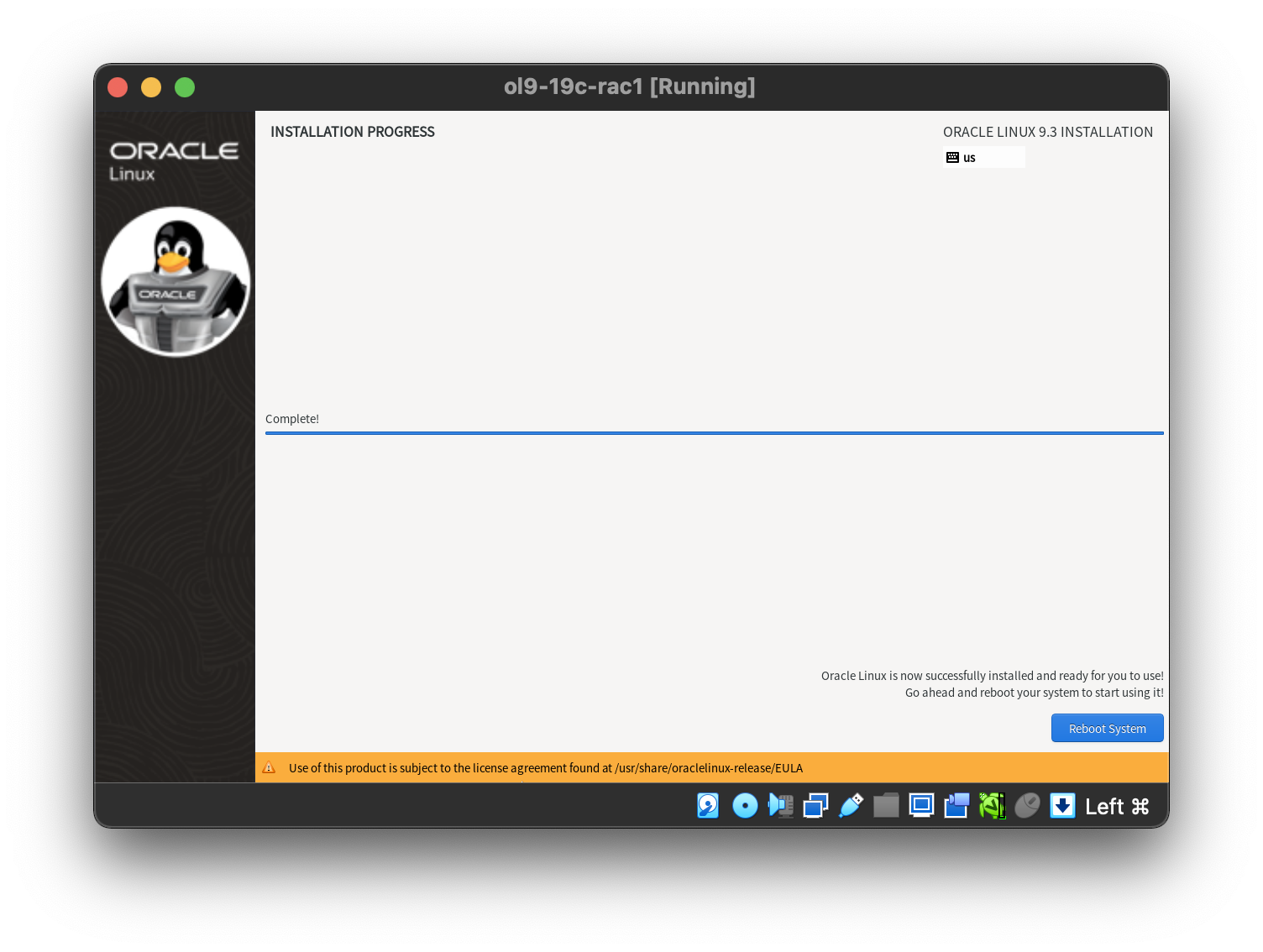
To be consistent with the rest of the article, the following information should be set during the installation.
- hostname: ol9-19c-rac1
- ens224: IP=192.168.56.101, Subnet=255.255.255.0, Gateway=192.168.56.1, DNS=<blank>, Search=<blank> (Connect Automatically)
- ens256: IP=192.168.1.101, Subnet=255.255.255.0, Gateway=<blank>, DNS=<blank>, Search=<blank> (Connect Automatically)
You are free to change the IP addresses to suit your network, but remember to stay consistent with those adjustments throughout the rest of the article. Likewise, in this article I will refer to the network adapters as ens224 and ens256. In previous Linux versions they would have been eth0 and eth2 respectively.
Oracle Installation Prerequisites
Perform either the Automatic Setup or the Manual Setup to complete the basic prerequisites. The Additional Setup is required for all installations.
Automatic Setup
If you plan to use the “oracle-database-preinstall-19c” package to perform all your prerequisite setup, issue the following command.
# yum localinstall -y oracle-database-preinstall-19c-1.0-1.el9.x86_64.rpm
- You may need download the rpm package from Oracle public YUM server before install it manually.
- If you didn’t check the “Allow root SSH login with password” flag while setting the root password during installation of Oracle Linux 9, then you can enable it by edit the /etc/ssh/sshd_config file and set the PermitRootLogin to yes. Remember restarting the sshd service to make it effect.
Earlier versions of Oracle Linux required manual setup of the Yum repository by following the instructions at http://public-yum.oracle.com.
It is probably worth doing a full update as well, but this is not strictly speaking necessary.
# yum update -y
or
# dnf update -y
Create Local YUM source
Delete or backup the .repo file in /etc/yum.repos.d directry including oracle-linux-ol9.repo, uek-ol9.repo, virt-ol9.repo. Create a new local.repo file as following:
[local_server]
name=This is a local repo
baseurl=file:///run/media/root/OL-9-3-0-BaseOS-x86_64/AppStream
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
[baseos_server]
name=This is a local repo
baseurl=file:///run/media/root/OL-9-3-0-BaseOS-x86_64/BaseOS
enabled=1
gpgcheck=0
Execute yum update or dnf update to check the config works.
Manual Setup
If you have not used the “oracle-database-preinstall-19c” package to perform all prerequisites, you will need to manually perform the following setup tasks.
Add the following lines to the “/etc/sysctl.conf” file, or in a file called “/etc/sysctl.d/99-oracle-database-preinstall-19c-sysctl.conf”.
fs.file-max = 6815744
kernel.sem = 250 32000 100 128
kernel.shmmni = 4096
kernel.shmall = 1073741824
kernel.shmmax = 4398046511104
kernel.panic_on_oops = 1
net.core.rmem_default = 262144
net.core.rmem_max = 4194304
net.core.wmem_default = 262144
net.core.wmem_max = 1048576
net.ipv4.conf.all.rp_filter = 2
net.ipv4.conf.default.rp_filter = 2
fs.aio-max-nr = 1048576 >>> 3145728
net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 9000 65500
Run the following command to change the current kernel parameters.
/sbin/sysctl -p
# or
/sbin/sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/99-oracle-database-preinstall-19c-sysctl.conf
Add the following lines to a file called “/etc/security/limits.d/oracle-database-preinstall-19c.conf” file.
oracle soft nofile 1024
oracle hard nofile 65536
oracle soft nproc 16384
oracle hard nproc 16384
oracle soft stack 10240
oracle hard stack 32768
oracle hard memlock 134217728
oracle soft memlock 134217728
oracle soft data unlimited
oracle hard data unlimited
In addition to the basic OS installation, the following packages must be installed whilst logged in as the root user. This includes the 64-bit and 32-bit versions of some packages.
# Install the latest released versions of the following packages:
bc
binutils
compat-openssl11
elfutils-libelf
fontconfig
glibc
glibc-devel
ksh
libaio
libasan
liblsan
libX11
libXau
libXi
libXrender
libXtst
libxcrypt-compat
libgcc
libibverbs
libnsl
librdmacm
libstdc++
libxcb
libvirt-libs
make
policycoreutils
policycoreutils-python-utils
smartmontools
sysstat
# Check status of all packages:
rpm -q bc binutils compat-openssl11 elfutils-libelf fontconfig glibc glibc-devel ksh libaio libasan liblsan \
libX11 libXau libXi libXrender libXtst libxcrypt-compat libgcc libibverbs libnsl librdmacm libstdc++ \
libxcb libvirt-libs make policycoreutils policycoreutils-python-utils smartmontools sysstat
bc-1.07.1-14.el9.x86_64
binutils-2.35.2-42.0.1.el9.x86_64
package compat-openssl11 is not installed
elfutils-libelf-0.189-3.el9.x86_64
fontconfig-2.14.0-2.el9_1.x86_64
glibc-2.34-83.0.1.el9_3.7.x86_64
glibc-devel-2.34-83.0.1.el9_3.7.x86_64
ksh-1.0.0~beta.1-3.0.1.el9.x86_64
libaio-0.3.111-13.el9.x86_64
package libasan is not installed
package liblsan is not installed
libX11-1.7.0-8.el9.x86_64
libXau-1.0.9-8.el9.x86_64
libXi-1.7.10-8.el9.x86_64
libXrender-0.9.10-16.el9.x86_64
libXtst-1.2.3-16.el9.x86_64
libxcrypt-compat-4.4.18-3.el9.x86_64
libgcc-11.4.1-2.1.0.1.el9.x86_64
libibverbs-46.0-1.el9.x86_64
libnsl-2.34-83.0.1.el9_3.7.x86_64
package librdmacm is not installed
libstdc++-11.4.1-2.1.0.1.el9.x86_64
libxcb-1.13.1-9.el9.x86_64
package libvirt-libs is not installed
make-4.3-7.el9.x86_64
policycoreutils-3.5-2.el9.x86_64
policycoreutils-python-utils-3.5-2.el9.noarch
smartmontools-7.2-7.el9.x86_64
sysstat-12.5.4-7.0.1.el9.x86_64
# Install the missing packages after preinstall package installed:
yum install compat-openssl11 libasan liblsan librdmacm libvirt-libs -y
# Check again to ensure all packages installed.
[root@ol9-19c-rac1 limits.d]# rpm -q bc binutils compat-openssl11 elfutils-libelf fontconfig glibc glibc-devel ksh libaio libasan liblsan \
libX11 libXau libXi libXrender libXtst libxcrypt-compat libgcc libibverbs libnsl librdmacm libstdc++ \
libxcb libvirt-libs make policycoreutils policycoreutils-python-utils smartmontools sysstat
bc-1.07.1-14.el9.x86_64
binutils-2.35.2-42.0.1.el9.x86_64
compat-openssl11-1.1.1k-4.0.1.el9_0.x86_64
elfutils-libelf-0.189-3.el9.x86_64
fontconfig-2.14.0-2.el9_1.x86_64
glibc-2.34-83.0.1.el9_3.7.x86_64
glibc-devel-2.34-83.0.1.el9_3.7.x86_64
ksh-1.0.0~beta.1-3.0.1.el9.x86_64
libaio-0.3.111-13.el9.x86_64
libasan-11.4.1-2.1.0.1.el9.x86_64
liblsan-11.4.1-2.1.0.1.el9.x86_64
libX11-1.7.0-8.el9.x86_64
libXau-1.0.9-8.el9.x86_64
libXi-1.7.10-8.el9.x86_64
libXrender-0.9.10-16.el9.x86_64
libXtst-1.2.3-16.el9.x86_64
libxcrypt-compat-4.4.18-3.el9.x86_64
libgcc-11.4.1-2.1.0.1.el9.x86_64
libibverbs-46.0-1.el9.x86_64
libnsl-2.34-83.0.1.el9_3.7.x86_64
librdmacm-46.0-1.el9.x86_64
libstdc++-11.4.1-2.1.0.1.el9.x86_64
libxcb-1.13.1-9.el9.x86_64
libvirt-libs-9.5.0-7.0.1.el9_3.x86_64
make-4.3-7.el9.x86_64
policycoreutils-3.5-2.el9.x86_64
policycoreutils-python-utils-3.5-2.el9.noarch
smartmontools-7.2-7.el9.x86_64
sysstat-12.5.4-7.0.1.el9.x86_64
Create the new groups and users.
groupadd -g 54321 oinstall
groupadd -g 54322 dba
groupadd -g 54323 oper
#groupadd -g 54324 backupdba
#groupadd -g 54325 dgdba
#groupadd -g 54326 kmdba
#groupadd -g 54327 asmdba
#groupadd -g 54328 asmoper
#groupadd -g 54329 asmadmin
useradd -u 54321 -g oinstall -G dba,oper oracle
You could define the additional groups and assign them to the “oracle” users. The would allow you to assign the individual groups during the installation. For this installation I’ve just used the “dba” group.
groupadd -g 54324 backupdba
groupadd -g 54325 dgdba
groupadd -g 54326 kmdba
groupadd -g 54327 asmdba
groupadd -g 54328 asmoper
groupadd -g 54329 asmadmin
groupadd -g 54330 racdba
useradd -u 54321 -g oinstall -G dba,oper,backupdba,dgdba,kmdba,asmdba,asmoper,asmadmin,racdba oracle
create grid system user for role seperated mode.
groupadd -g 54329 asmadmin
useradd -u 54322 -g oinstall -G oinstall,dba,asmadmin grid
Additional Setup
The following steps must be performed, whether you did the manual or automatic setup. Perform the following steps whilst logged into the “ol9-19c-rac1” virtual machine as the root user. Set the password for the “oracle” user.
passwd oracle
Apart form the localhost address, the “/etc/hosts” file can be left blank, but I prefer to put the addresses in for reference.
127.0.0.1 localhost
# Public
192.168.56.101 ol9-19c-rac1
192.168.56.102 ol9-19c-rac2
# Private
192.168.1.101 ol9-19c-rac1-priv
192.168.1.102 ol9-19c-rac2-priv
# Virtual
192.168.56.103 ol9-19c-rac1-vip
192.168.56.104 ol9-19c-rac2-vip
# SCAN
#192.168.56.105 ol9-19c-scan
The SCAN address is commented out of the hosts file because it must be resolved using a DNS, so it can round-robin between 3 addresses on the same subnet as the public IPs. The DNS can be configured on the host machine using BIND or Dnsmasq, which is much simpler. If you are using Dnsmasq, put the RAC-specific entries in the hosts machines “/etc/host” file, with the SCAN entries uncommented, and restart Dnsmasq. Make sure the “/etc/resolv.conf” file includes a nameserver entry that points to the correct nameserver. Also, if the “domain” and “search” entries are both present, comment out one of them. For this installation my “/etc/resolv.conf” looked like this.
#domain localdomain
search localdomain
nameserver 192.168.56.1
The changes to the “resolv.conf” will be overwritten by the network manager, due to the presence of the NAT interface. For this reason, this interface should now be disabled on startup. You can enable it manually if you need to access the internet from the VMs. Edit the “/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0” file, making the following change. This will take effect after the next restart.
ONBOOT=no
There is no need to do the restart now. You can just run the following command.
# ifdown enp0s3
At this point, the networking for the first node should look something like the following. Notice that eth0 has no associated IP address because it is disabled.
[root@oadb1 ~]# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens224: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:50:56:a4:87:b9 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp19s0
inet 10.158.81.103/24 brd 10.158.81.255 scope global noprefixroute ens224
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.158.81.105/24 brd 10.158.81.255 scope global secondary ens224:1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.158.81.107/24 brd 10.158.81.255 scope global secondary ens224:2
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: ens256: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:50:56:a4:00:af brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp27s0
inet 192.168.56.103/24 brd 192.168.56.255 scope global noprefixroute ens256
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 169.254.24.45/19 brd 169.254.31.255 scope global ens256:1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
[root@oadb1 ~]#
With this in place and the DNS configured the SCAN address is being resolved to all three IP addresses.
# nslookup ol9-19c-scan
Server: 192.168.56.1
Address: 192.168.56.1#53
Name: ol9-19c-scan.localdomain
Address: 192.168.56.105
#
Change the setting of SELinux to permissive by editing the “/etc/selinux/config” file, making sure the SELINUX flag is set as follows.
SELINUX=permissive
or
SELINUX=disabled
or
sed -i -e "s|SELINUX=enforcing|SELINUX=permissive|g" /etc/selinux/config
If you have the Linux firewall enabled, you will need to disable or configure it, as shown here or here. The following is an example of disabling the firewall.
# systemctl stop firewalld
# systemctl disable firewalld
Either configure NTP, or make sure it is not configured so the Oracle Cluster Time Synchronization Service (ctssd) can synchronize the times of the RAC nodes.
Make sure NTP (Chrony on OL9/RHEL9) is enabled.
# systemctl enable chronyd
# systemctl restart chronyd
# chronyc -a 'burst 4/4'
# chronyc -a makestep
Create the directories in which the Oracle software will be installed.
mkdir -p /u01/app/19.0.0/grid
mkdir -p /u01/app/grid
mkdir -p /u01/app/oracle
mkdir -p /u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/dbhome_1
chown -R grid:oinstall /u01
chown oracle:oinstall /u01/app/oracle
chmod -R 775 /u01/
We’ve made a lot of changes, so it’s worth doing a reboot of the VM at this point to make sure all the changes have taken effect.
# shutdown -r now
Install Guest Additions
Click on the “Devices > Install Guest Additions” menu option at the top of the VM screen. If you get the option to auto-run take it. If not, then run the following commands.
cd /run/media/VBOXADDITIONS*
sh ./VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
Add the “oracle” user into the “vboxsf” group so it has access to shared drives.
# usermod -G vboxsf,dba oracle
# id oracle
uid=54321(oracle) gid=54321(oinstall) groups=54321(oinstall),54322(dba),54323(vboxsf)
#
Create a shared folder (Devices > Shared Folders) on the virtual machine, pointing to the directory on the host where the Oracle software was unzipped. Check the “Auto-mount” and “Make Permanent” options before clicking the “OK” button.
The VM will need to be restarted for the guest additions to be used properly. The next section requires a shutdown so no additional restart is needed at this time. Once the VM is restarted, the shared folder called “/run//media/sf_19.0.0” will be accessible by the “oracle” user.
Create Shared Disks
Shut down the “ol9-19c-rac1” virtual machine using the following command.
# shutdown -h now
On the host server, create 4 sharable virtual disks and associate them as virtual media using the following commands. You can pick a different location, but make sure they are outside the existing VM directory.
$ mkdir -p /u04/VirtualBox/ol9-19c-rac
$ cd /u04/VirtualBox/ol9-19c-rac
$
$ # Create the disks and associate them with VirtualBox as virtual media.
$ VBoxManage createhd --filename asm1.vdi --size 10240 --format VDI --variant Fixed
$ VBoxManage createhd --filename asm2.vdi --size 10240 --format VDI --variant Fixed
$ VBoxManage createhd --filename asm3.vdi --size 10240 --format VDI --variant Fixed
$ VBoxManage createhd --filename asm4.vdi --size 10240 --format VDI --variant Fixed
$
$ # Connect them to the VM.
$ VBoxManage storageattach ol9-19c-rac1 --storagectl "SATA" --port 1 --device 0 --type hdd \
--medium asm1.vdi --mtype shareable
$ VBoxManage storageattach ol9-19c-rac1 --storagectl "SATA" --port 2 --device 0 --type hdd \
--medium asm2.vdi --mtype shareable
$ VBoxManage storageattach ol9-19c-rac1 --storagectl "SATA" --port 3 --device 0 --type hdd \
--medium asm3.vdi --mtype shareable
$ VBoxManage storageattach ol9-19c-rac1 --storagectl "SATA" --port 4 --device 0 --type hdd \
--medium asm4.vdi --mtype shareable
$
$ # Make shareable.
$ VBoxManage modifyhd asm1.vdi --type shareable
$ VBoxManage modifyhd asm2.vdi --type shareable
$ VBoxManage modifyhd asm3.vdi --type shareable
$ VBoxManage modifyhd asm4.vdi --type shareable
If you are using a Windows host, you will have to modify the paths, but the process is the same.
C:
mkdir C:\VirtualBox\ol9-19c-rac
cd C:\VirtualBox\ol9-19c-rac
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" createhd --filename asm1.vdi --size 10240 --format VDI --variant Fixed
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" createhd --filename asm2.vdi --size 10240 --format VDI --variant Fixed
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" createhd --filename asm3.vdi --size 10240 --format VDI --variant Fixed
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" createhd --filename asm4.vdi --size 10240 --format VDI --variant Fixed
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" storageattach ol9-19c-rac1 --storagectl "SATA" --port 1 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm1.vdi --mtype shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" storageattach ol9-19c-rac1 --storagectl "SATA" --port 2 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm2.vdi --mtype shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" storageattach ol9-19c-rac1 --storagectl "SATA" --port 3 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm3.vdi --mtype shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" storageattach ol9-19c-rac1 --storagectl "SATA" --port 4 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm4.vdi --mtype shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" modifyhd asm1.vdi --type shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" modifyhd asm2.vdi --type shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" modifyhd asm3.vdi --type shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" modifyhd asm4.vdi --type shareable
Start the “ol9-19c-rac1” virtual machine by clicking the “Start” button on the toolbar. When the server has started, log in as the root user so you can configure the shared disks. The current disks can be seen by issuing the following commands.
# cd /dev
# ls sd*
sda sda1 sda2 sdb sdc sdd sde
#
Use the “fdisk” command to partition the disks sdb to sde. The following output shows the expected fdisk output for the sdb disk.
# fdisk /dev/sdb
Welcome to fdisk (util-linux 2.23.2).
Changes will remain in memory only, until you decide to write them.
Be careful before using the write command.
Device does not contain a recognized partition table
Building a new DOS disklabel with disk identifier 0x14a4629c.
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1):
First sector (2048-41943039, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-41943039, default 41943039):
Using default value 41943039
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 20 GiB is set
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
#
In each case, the sequence of answers is “n”, “p”, “1”, “Return”, “Return” and “w”.
echo -e "n\np\n1\n\n\nw" | fdisk /dev/sdb
Once all the disks are partitioned, the results can be seen by repeating the previous “ls” command.
# cd /dev
# ls sd*
sda sda1 sda2 sdb sdb1 sdc sdc1 sdd sdd1 sde sde1
#
Configure your UDEV rules, as shown here. Add the following to the “/etc/scsi_id.config” file to configure SCSI devices as trusted. Create the file if it doesn’t already exist.
options=-g
The SCSI ID of my disks are displayed below.
# /usr/lib/udev/scsi_id -g -u -d /dev/sdb1
1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VB189c7a69-689f61b0
# /usr/lib/udev/scsi_id -g -u -d /dev/sdc1
1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VBc4ae174e-fc756d12
# /usr/lib/udev/scsi_id -g -u -d /dev/sdd1
1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VBa4e03079-ae751cbd
# /usr/lib/udev/scsi_id -g -u -d /dev/sde1
1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VBf00747dc-10252f06
#
Using these values, edit the “/etc/udev/rules.d/99-oracle-asmdevices.rules” file adding the following 4 entries. All parameters for a single entry must be on the same line.
KERNEL=="sd?1", SUBSYSTEM=="block", PROGRAM=="/usr/lib/udev/scsi_id -g -u -d /dev/$parent", RESULT=="1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VB189c7a69-689f61b0", SYMLINK+="oracleasm/asm-disk1", OWNER="oracle", GROUP="dba", MODE="0660"
KERNEL=="sd?1", SUBSYSTEM=="block", PROGRAM=="/usr/lib/udev/scsi_id -g -u -d /dev/$parent", RESULT=="1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VBc4ae174e-fc756d12", SYMLINK+="oracleasm/asm-disk2", OWNER="oracle", GROUP="dba", MODE="0660"
KERNEL=="sd?1", SUBSYSTEM=="block", PROGRAM=="/usr/lib/udev/scsi_id -g -u -d /dev/$parent", RESULT=="1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VBa4e03079-ae751cbd", SYMLINK+="oracleasm/asm-disk3", OWNER="oracle", GROUP="dba", MODE="0660"
KERNEL=="sd?1", SUBSYSTEM=="block", PROGRAM=="/usr/lib/udev/scsi_id -g -u -d /dev/$parent", RESULT=="1ATA_VBOX_HARDDISK_VBf00747dc-10252f06", SYMLINK+="oracleasm/asm-disk4", OWNER="oracle", GROUP="dba", MODE="0660"
Load updated block device partition tables.
# /sbin/partprobe /dev/sdb1
# /sbin/partprobe /dev/sdc1
# /sbin/partprobe /dev/sdd1
# /sbin/partprobe /dev/sde1
Test the rules are working as expected.
# /sbin/udevadm test /block/sdb/sdb1
Reload the UDEV rules and start UDEV.
# /sbin/udevadm control --reload-rules
The disks should now be visible and have the correct ownership using the following command. If they are not visible, your UDEV configuration is incorrect and must be fixed before you proceed.
# ls -al /dev/oracleasm/*
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Mar 6 17:41 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk1 -> ../sdb1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Mar 6 17:41 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk2 -> ../sdc1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Mar 6 17:41 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk3 -> ../sdd1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Mar 6 17:41 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk4 -> ../sde1
#
The symbolic links are owned by root, but the devices they point to now have the correct ownership.
# ls -al /dev/sd*1
brw-rw----. 1 root disk 8, 1 Apr 25 14:11 /dev/sda1
brw-rw----. 1 oracle dba 8, 17 Apr 25 14:11 /dev/sdb1
brw-rw----. 1 oracle dba 8, 33 Apr 25 14:11 /dev/sdc1
brw-rw----. 1 oracle dba 8, 49 Apr 25 14:11 /dev/sdd1
brw-rw----. 1 oracle dba 8, 65 Apr 25 14:11 /dev/sde1
#
The shared disks are now configured for the grid infrastructure.
Clone the Virtual Machine
Later versions of VirtualBox allow you to clone VMs, but these also attempt to clone the shared disks, which is not what we want. Instead we must manually clone the VM. Shut down the “ol9-19c-rac1” virtual machine using the following command.
# shutdown -h now
Manually clone the “ol9-19c-rac1.vdi” disk using the following commands on the host server.
$ mkdir -p /u03/VirtualBox/ol9-19c-rac2
$ VBoxManage clonehd /u01/VirtualBox/ol9-19c-rac1/ol9-19c-rac1.vdi /u03/VirtualBox/ol9-19c-rac2/ol9-19c-rac2.vdi
Rem Windows
mkdir "C:\VirtualBox\ol9-19c-rac2"
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" clonehd "C:\VirtualBox\ol9-19c-rac1\ol9-19c-rac1.vdi" "C:\VirtualBox\ol9-19c-rac2\ol9-19c-rac2.vdi"
Create the “ol9-19c-rac2” virtual machine in VirtualBox in the same way as you did for “ol9-19c-rac1”, with the exception of using an existing “ol9-19c-rac2.vdi” virtual hard drive.
Remember to add the three network adaptor as you did on the “ol9-19c-rac1” VM. When the VM is created, attach the shared disks to this VM.
$ # Linux : Switch to the shared storage location and attach them.
$ cd /u04/VirtualBox/ol9-19c-rac
$
$ VBoxManage storageattach ol9-19c-rac2 --storagectl "SATA" --port 1 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm1.vdi --mtype shareable
$ VBoxManage storageattach ol9-19c-rac2 --storagectl "SATA" --port 2 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm2.vdi --mtype shareable
$ VBoxManage storageattach ol9-19c-rac2 --storagectl "SATA" --port 3 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm3.vdi --mtype shareable
$ VBoxManage storageattach ol9-19c-rac2 --storagectl "SATA" --port 4 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm4.vdi --mtype shareable
Rem Windows : Switch to the shared storage location and attach them.
C:
cd C:\VirtualBox\ol9-19c-rac
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" storageattach ol9-19c-rac2 --storagectl "SATA" --port 1 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm1.vdi --mtype shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" storageattach ol9-19c-rac2 --storagectl "SATA" --port 2 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm2.vdi --mtype shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" storageattach ol9-19c-rac2 --storagectl "SATA" --port 3 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm3.vdi --mtype shareable
"c:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox\VBoxManage" storageattach ol9-19c-rac2 --storagectl "SATA" --port 4 --device 0 --type hdd --medium asm4.vdi --mtype shareable
Start the “ol9-19c-rac2” virtual machine by clicking the “Start” button on the toolbar. Ignore any network errors during the startup.
Log in to the “ol9-19c-rac2” virtual machine as the “root” user so we can reconfigure the network settings to match the following.
- hostname: ol9-19c-rac2
- ens224: IP=192.168.56.102, Subnet=255.255.255.0, Gateway=192.168.56.1, DNS=<blank>, Search=<blank> (Connect Automatically)
- ens256: IP=192.168.1.102, Subnet=255.255.255.0, Gateway=<blank>, DNS=<blank>, Search=<blank> (Connect Automatically)
Amend the hostname in the “/etc/hostname” file.
ol9-19c-rac2
or
# hostnamectl set-hostname ol9-19c-rac2
Unlike previous Linux versions, we shouldn’t have to edit the MAC address associated with the network adapters, but we will have to alter their IP addresses.
Edit the “/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s8” (eth1), amending only the IPADDR settings as follows and deleting the UUID entry.
IPADDR=192.168.56.102
Edit the “/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s9” (eth2), amending only the IPADDR settings as follows and deleting the UUID entry.
IPADDR=192.168.1.102
Restart the virtual machines.
# shutdown -r now
At this point, the networking for the second node should look something like the following. Notice that eth0 has no associated IP address because it is disabled.
# ip a
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: ens224: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:50:56:a4:b3:ca brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp19s0
inet 10.158.81.104/24 brd 10.158.81.255 scope global noprefixroute ens224
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 10.158.81.106/24 brd 10.158.81.255 scope global secondary ens224:1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
3: ens256: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 00:50:56:a4:6e:f1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
altname enp27s0
inet 192.168.56.104/24 brd 192.168.56.255 scope global noprefixroute ens256
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet 169.254.9.44/19 brd 169.254.31.255 scope global ens256:1
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
#
Edit the “/home/oracle/.bash_profile” file on the “ol9-19c-rac2” node to correct the ORACLE_SID and ORACLE_HOSTNAME values.
export ORACLE_SID=cdbrac2
export ORACLE_HOSTNAME=ol9-19c-rac2
Also, amend the ORACLE_SID setting in the “/home/oracle/db_env” and “/home/oracle/grid_env” files.
Restart the “ol9-19c-rac2” virtual machine and start the “ol9-19c-rac1” virtual machine. When both nodes have started, check they can both ping all the public and private IP addresses using the following commands.
ping -c 3 ol9-19c-rac1
ping -c 3 ol9-19c-rac1-priv
ping -c 3 ol9-19c-rac2
ping -c 3 ol9-19c-rac2-priv
Check the SCAN address is still being resolved properly on both nodes.
# nslookup ol9-19c-scan
Server: 192.168.56.1
Address: 192.168.56.1#53
Name: ol9-19c-scan.localdomain
Address: 192.168.56.105
#
At this point the virtual IP addresses defined in the “/etc/hosts” file will not work, so don’t bother testing them. Check the UDEV rules are working on both machines.
# ls -al /dev/oracleasm/*
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Sep 18 08:19 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk1 -> ../sdb1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Sep 18 08:19 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk2 -> ../sdc1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Sep 18 08:19 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk3 -> ../sdd1
lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 7 Sep 18 08:19 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk4 -> ../sde1
#
Prior to 11gR2 we would probably use the “runcluvfy.sh” utility in the clusterware root directory to check the prerequisites have been met. If you are intending to configure SSH connectivity using the installer this check should be omitted as it will always fail. If you want to setup SSH connectivity manually, then once it is done you can run the “runcluvfy.sh” with the following command.
/mountpoint/clusterware/runcluvfy.sh stage -pre crsinst -n ol9-19c-rac1,ol9-19c-rac2 -verbose
The SSH equivalence during the OUI installer will fail for unsupported SSH key format. OpenSSH v7.8 and higher generates RSA private keys by default in the OpenSSH format, instead of the previous default PEM format. The OpenSSH key format offers substantially better protection against offline password guessing and supports key comments in private keys. Manually setup SSH passwordless is necessary for a successfully installation, with ssh-keygen -m pem option. use ssh-copy-id to setup passwordless for both grid and oracle user.
If you get any failures be sure to correct them before proceeding. The virtual machine setup is now complete. Before moving forward you should probably shut down your VMs and take snapshots of them. If any failures happen beyond this point it is probably better to switch back to those snapshots, clean up the shared drives and start the grid installation again. An alternative to cleaning up the shared disks is to back them up now using zip and just replace them in the event of a failure.
$ # Linux
$ cd /u04/VirtualBox/ol9-19c-rac
$ zip PreGrid.zip *.vdi
Rem Windows
C:
cd C:\VirtualBox\ol9-19c-rac
zip PreGrid.zip *.vdi
Install the Grid Infrastructure
Make sure both virtual machines are started. The GI is now an image installation, so perform the following on the first node as the “oracle” user.
export SOFTWARE_LOCATION=/media/sf_19.0.0/
cd /u01/app/19.0.0/grid
unzip -qq $SOFTWARE_LOCATION/linuxx64_1900_grid_home.zip
or unzip the grid software to target directory on the first node. Don’t do this on the second node.
unzip -d /u01/app/19.0.0/grid V982068-01.zip
Install the following package from the grid home as the “root” user on all nodes.
su -
# Local node.
cd /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/cv/rpm
rpm -Uvh cvuqdisk*
# Remote node.
scp ./cvuqdisk* root@ol9-19c-rac2:/tmp
ssh root@ol9-19c-rac2 rpm -Uvh /tmp/cvuqdisk*
exit
If you were planning on using the AFD Driver (the new ASMLib) you would configure the shared disks using the asmcmd command as shown below. We are using UDEV, so this is not necessary.
2024-2-14, at the moment of writing this article, ASMLib and AFD are not fully support Oracle Linux 9 kernel UEK 7.x, please do not use the feature.
If you insist using ASMLib and AFD, additional database patch is needed.
# !!!! I did not do this! !!!!
su -
# Set environment.
export ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/19.0.0/grid
export ORACLE_BASE=/tmp
# Mark disks.
$ORACLE_HOME/bin/asmcmd afd_label DISK1 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk1 --init
$ORACLE_HOME/bin/asmcmd afd_label DISK2 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk2 --init
$ORACLE_HOME/bin/asmcmd afd_label DISK3 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk3 --init
$ORACLE_HOME/bin/asmcmd afd_label DISK4 /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk4 --init
# Test Disks.
$ORACLE_HOME/bin/asmcmd afd_lslbl /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk1
$ORACLE_HOME/bin/asmcmd afd_lslbl /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk2
$ORACLE_HOME/bin/asmcmd afd_lslbl /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk3
$ORACLE_HOME/bin/asmcmd afd_lslbl /dev/oracleasm/asm-disk4
# unset environment.
unset ORACLE_BASE
exit
Configure the Grid Infrastructure by running the following as the “oracle” user.
I could have run the configuration in silent mode using this edited response file (grid_config.rsp) with the following command.
cd /u01/app/19.0.0/grid
./gridSetup.sh -silent -responseFile /tmp/grid_config.rsp
Instead, here’s the interactive configuration.
cd /u01/app/19.0.0/grid
export CV_ASSUME_DISTID=OL8
./gridsetup -applyRU <GI RU 35940989> -applyOneOffs <OJVM RU 35926646>
Select the “Configure Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a New Cluster” option, then click the “Next” button. 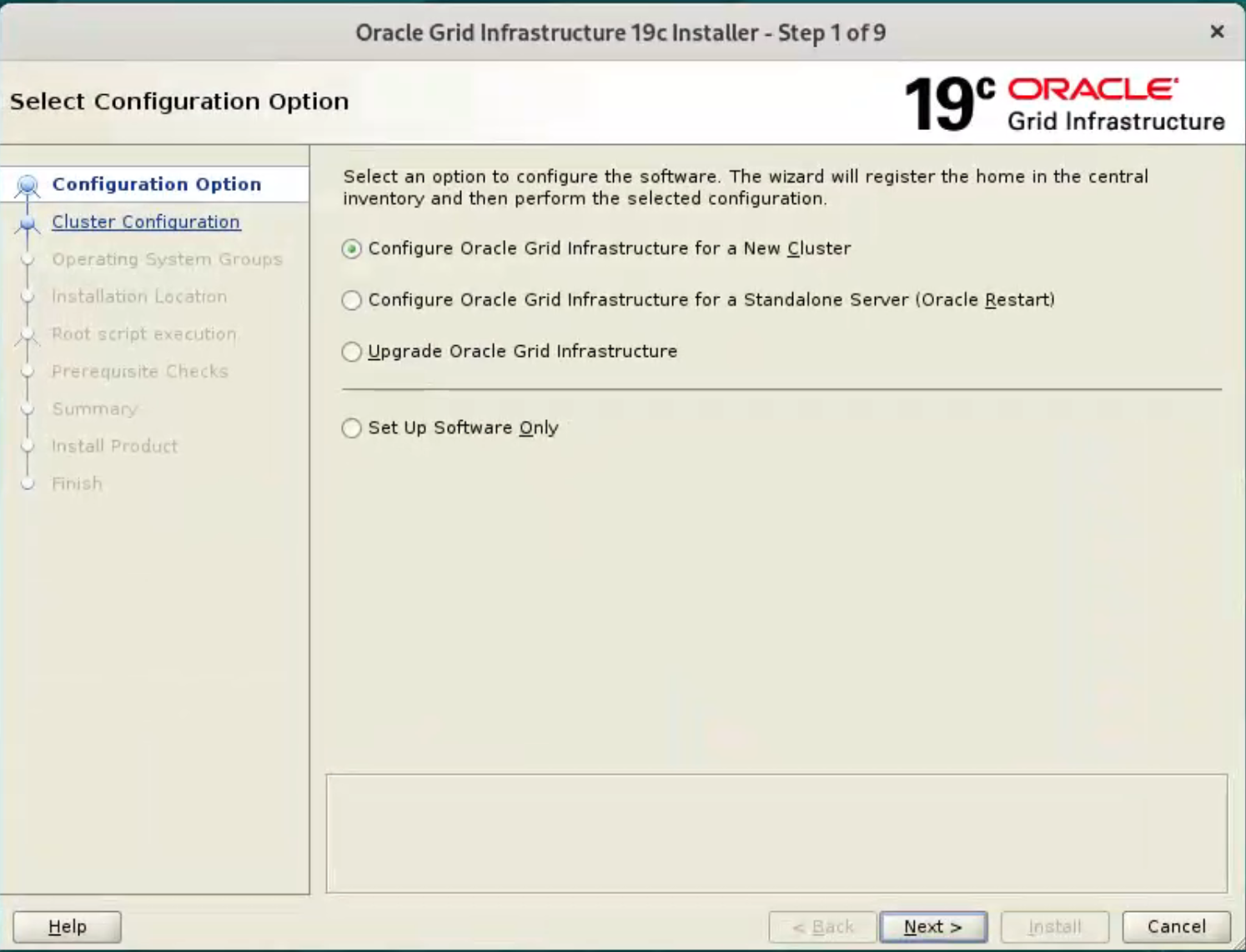
Accept the “Configure an Oracle Standalone Cluster” option by clicking the “Next” button. 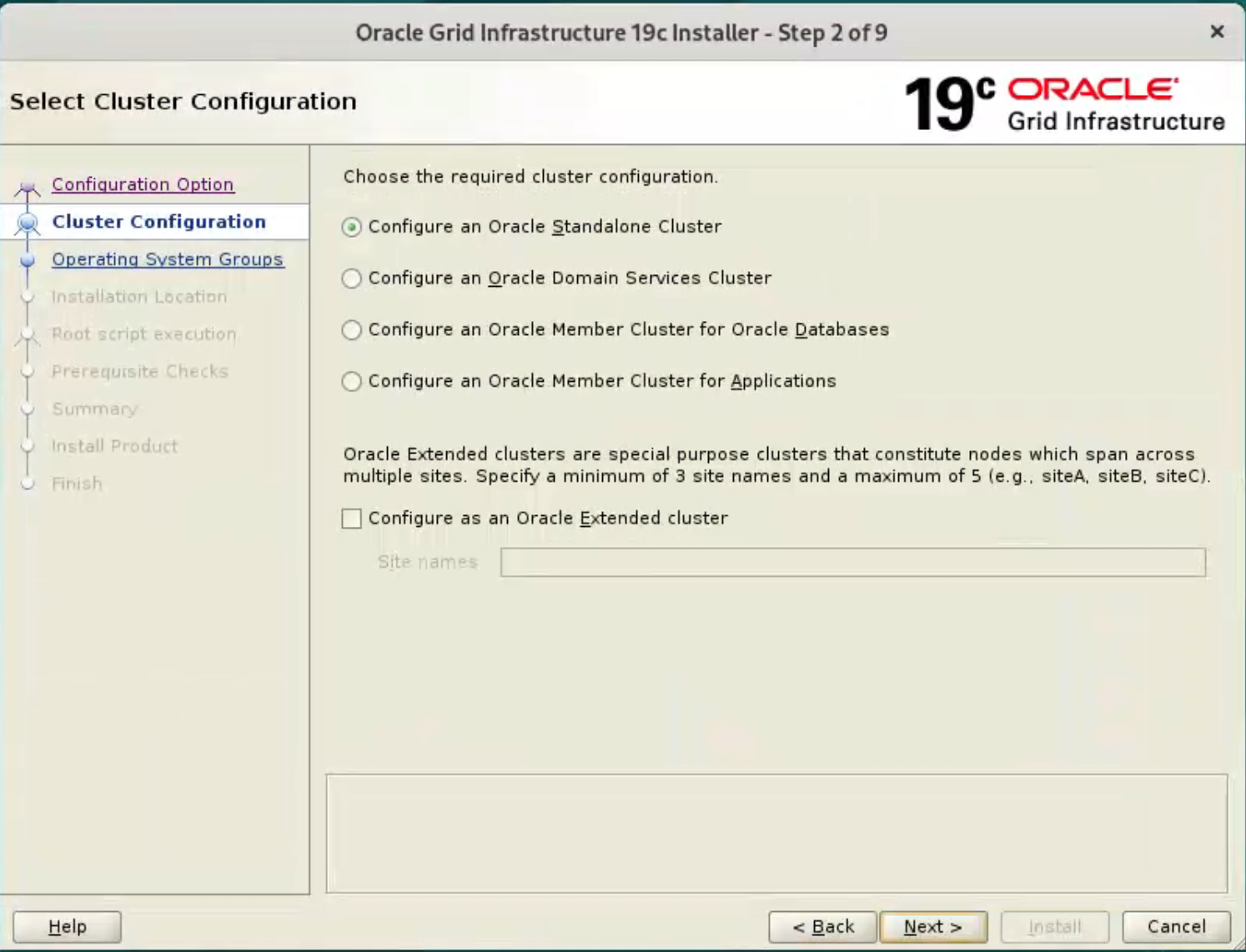
Enter the cluster name “ol9-19c-cluster”, SCAN name “ol9-19c-scan” and SCAN port “1521”, then click the “Next” button. 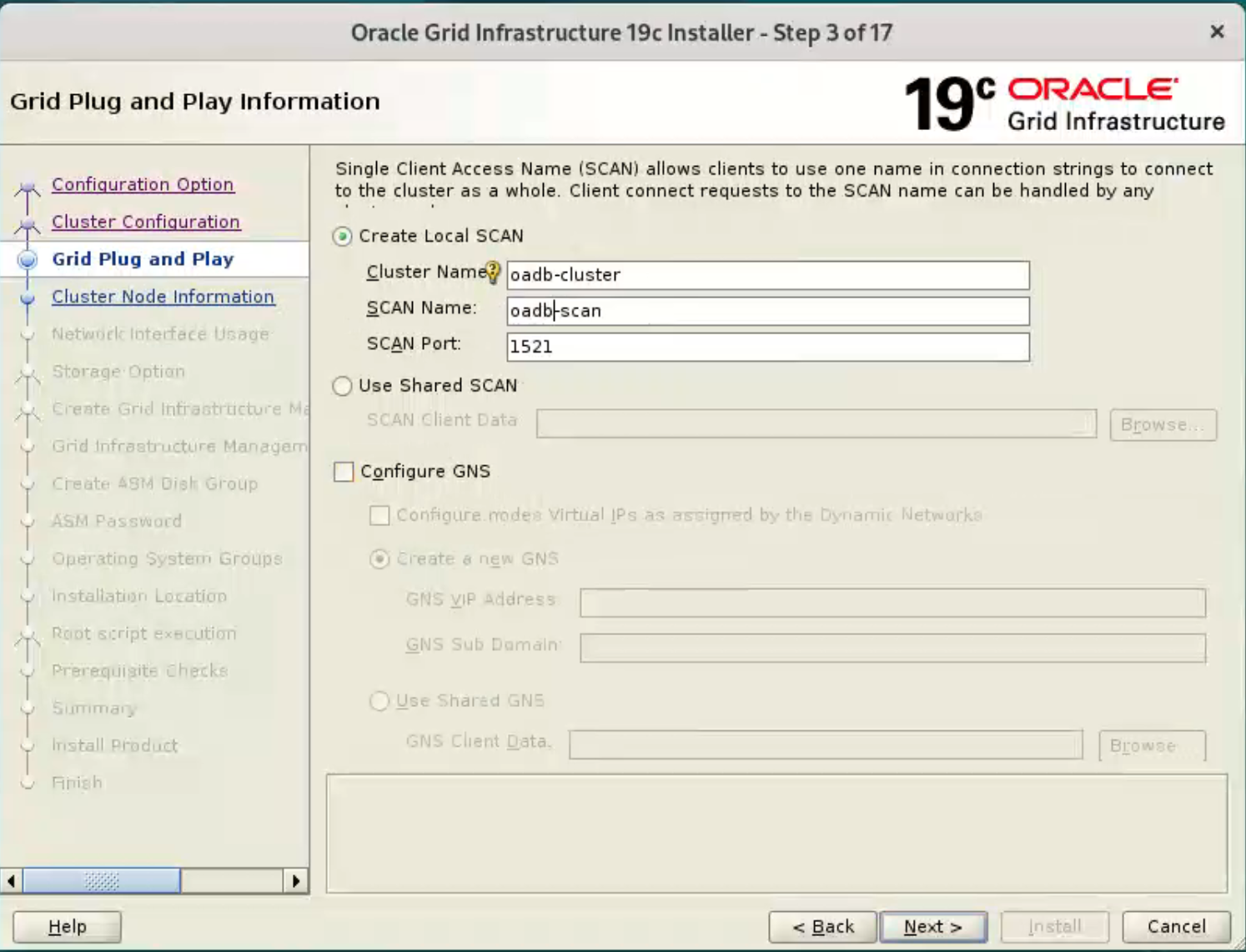
On the “Cluster Node Information” screen, 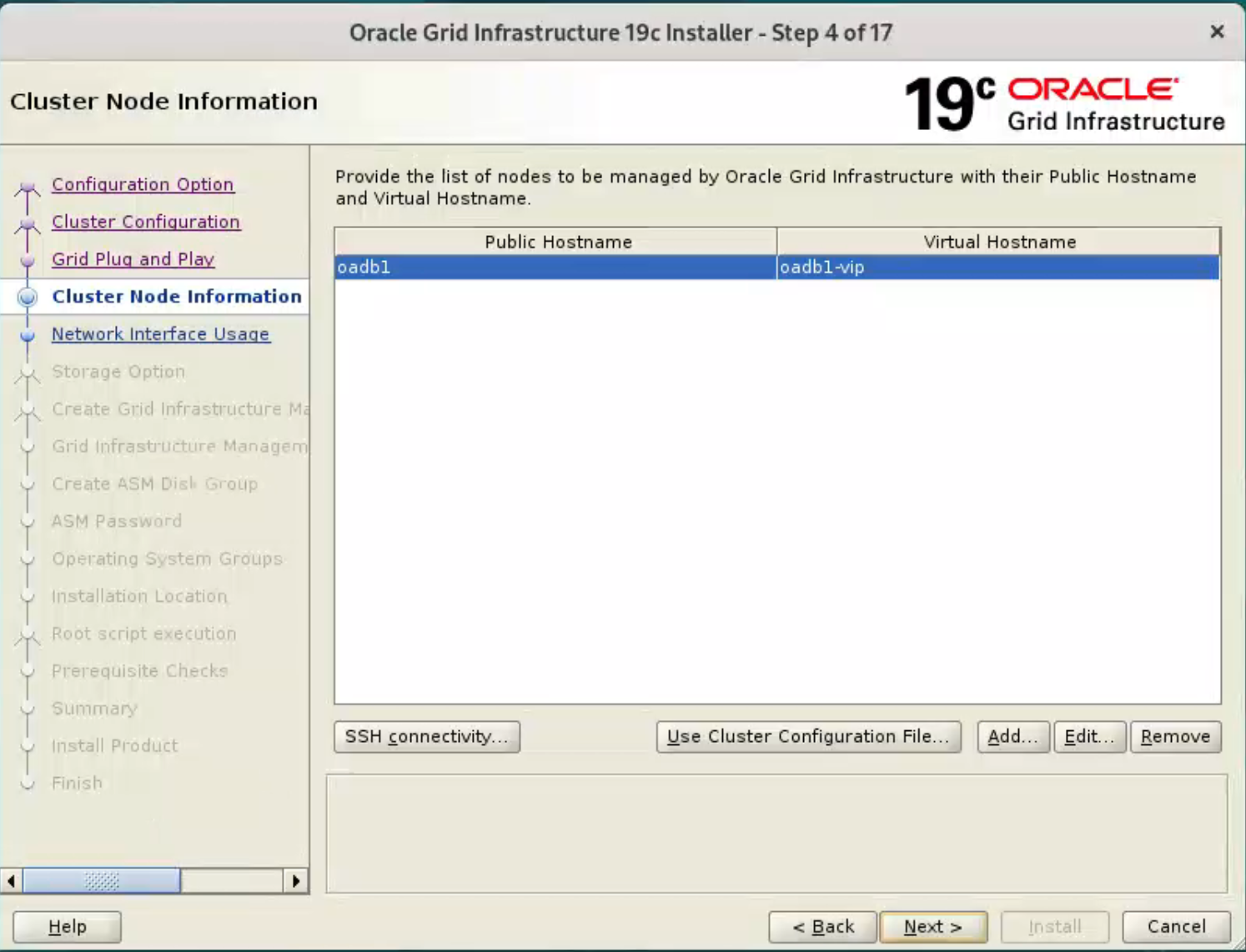
click the “Add” button. 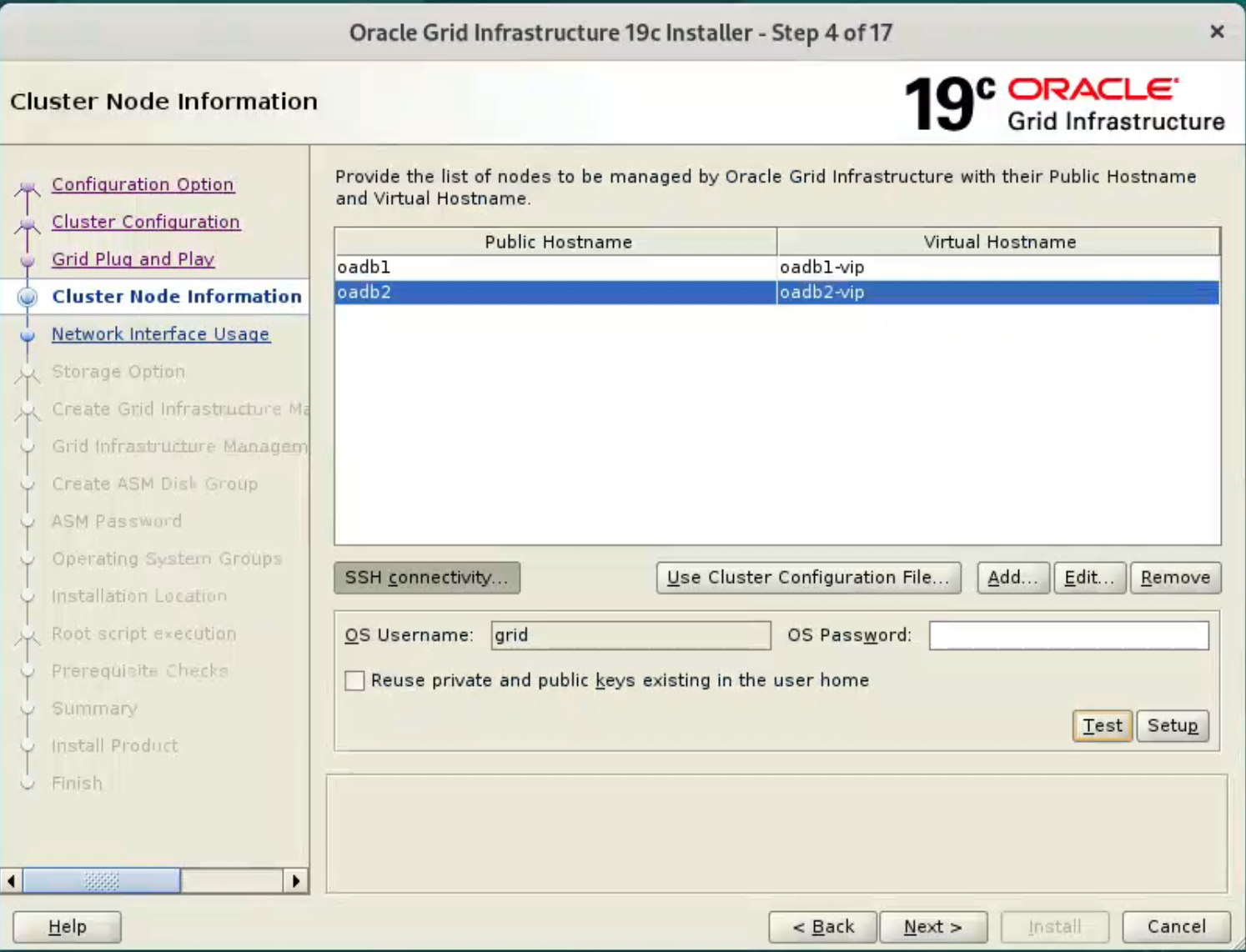
Click “Test” button to test it once it is complete. 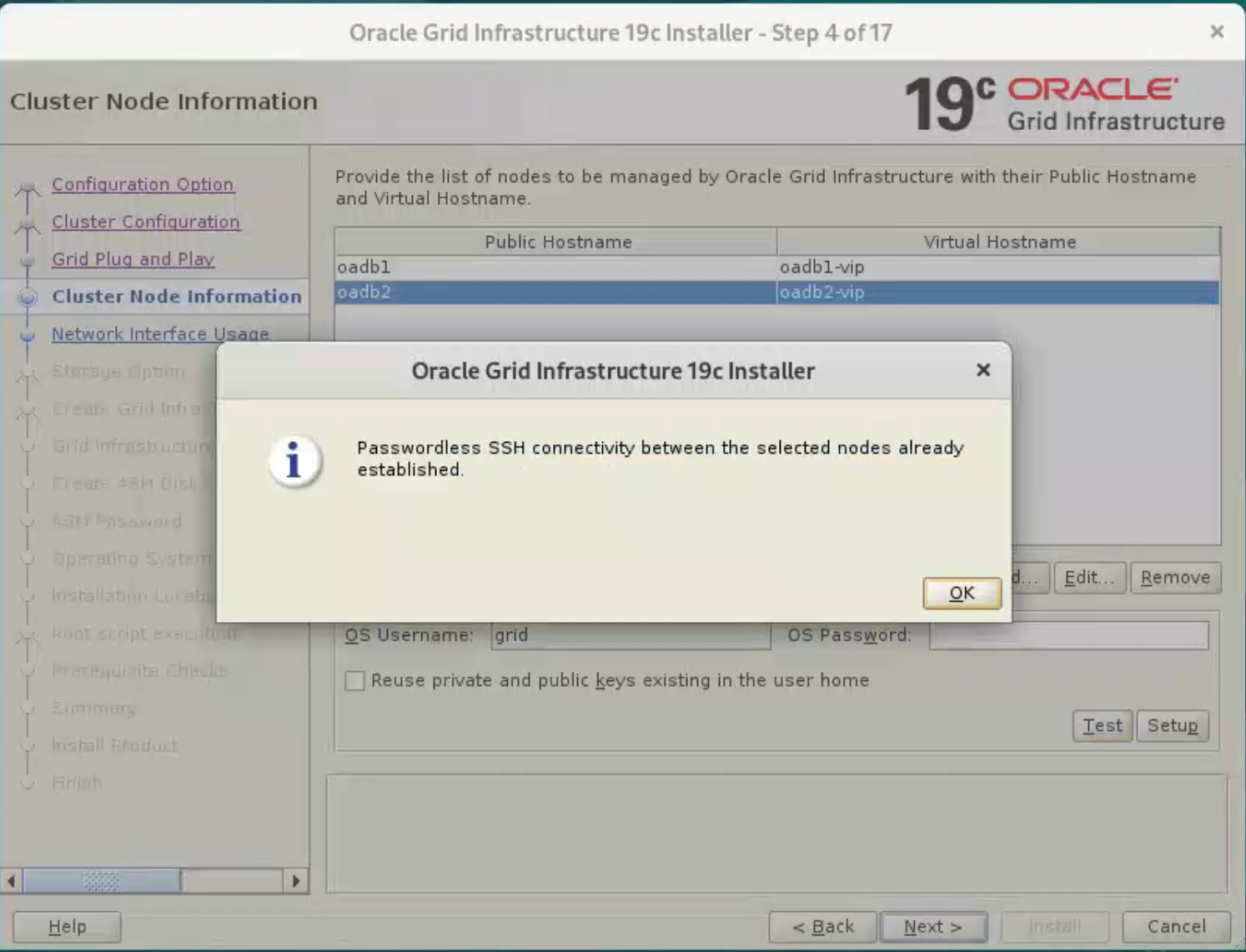
Once the test is complete, click the “Next” button.
the ssh equivalence setup will fail on this screen, please use manual method mentioned above, and just test it.
Check the public and private networks are specified correctly. Make sure enp0s8 are used for “Public”, enp0s9 are used for “ASM & Private”, If the NAT interface is displayed, remember to mark it as “Do Not Use”. Click the “Next” button. 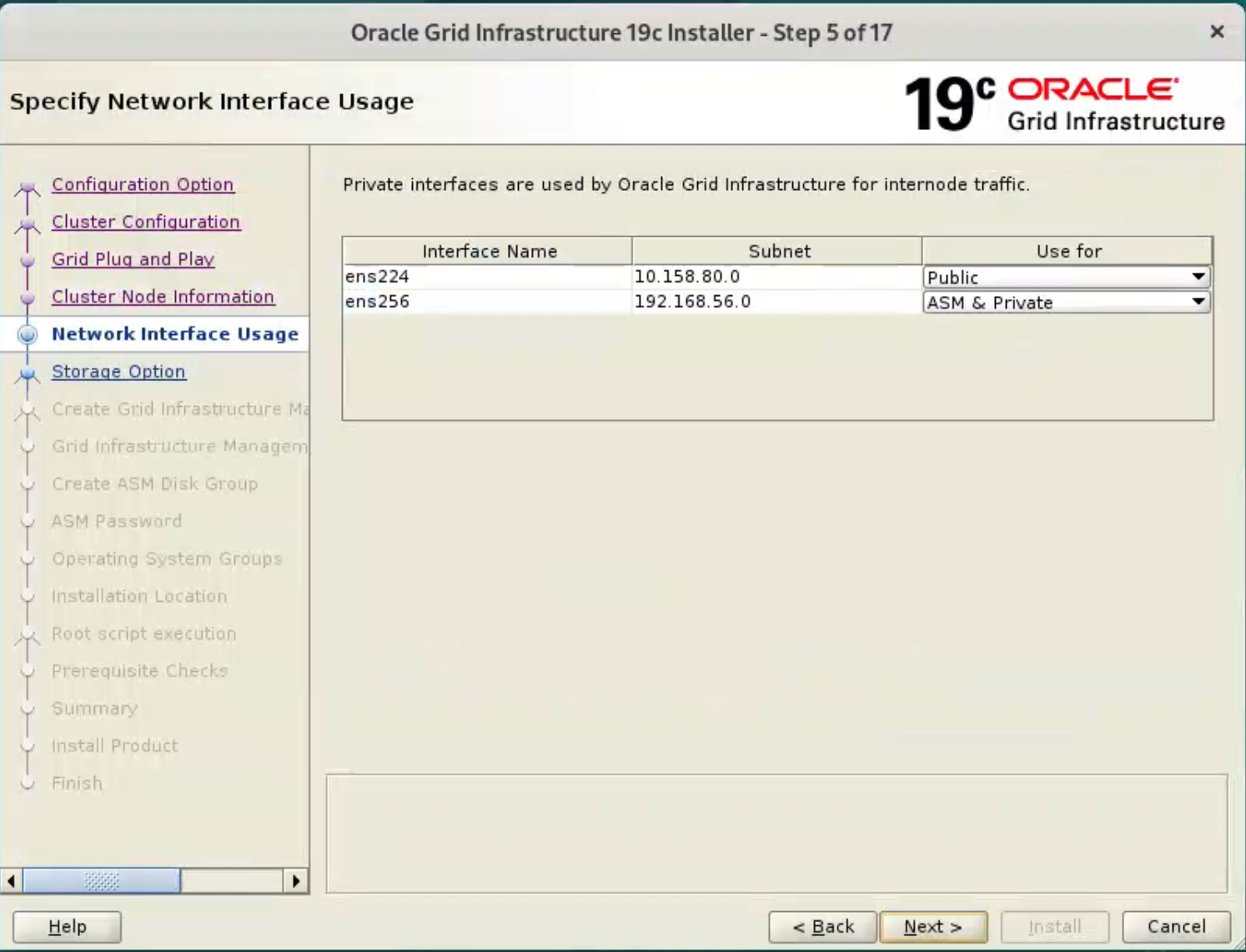
Accept the “Use Oracle Flex ASM for storage” option by clicking the “Next” button. 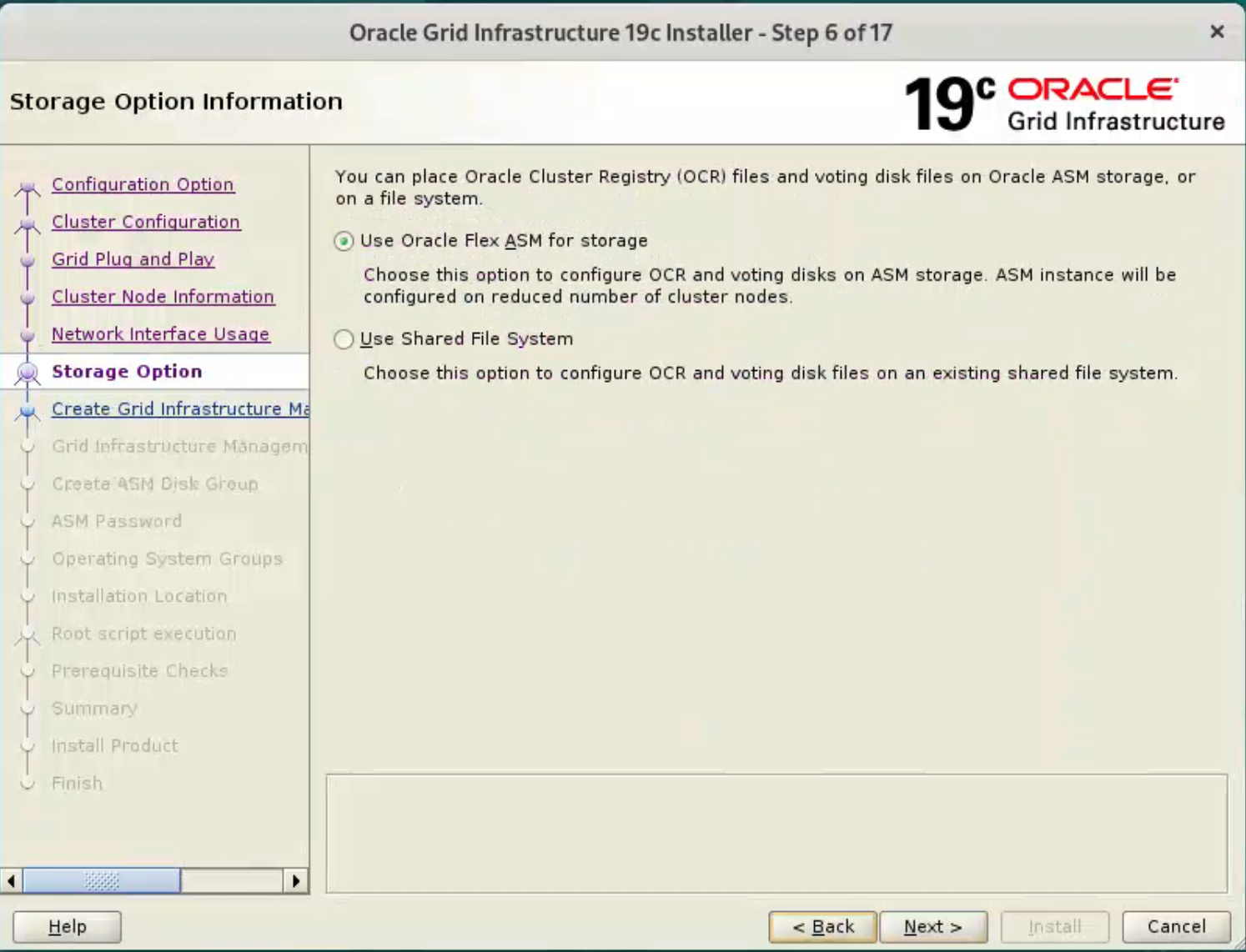
Select the “No” option, as we don’t want to create a separate disk group for the GIMR in this case. Click the “Next” button. 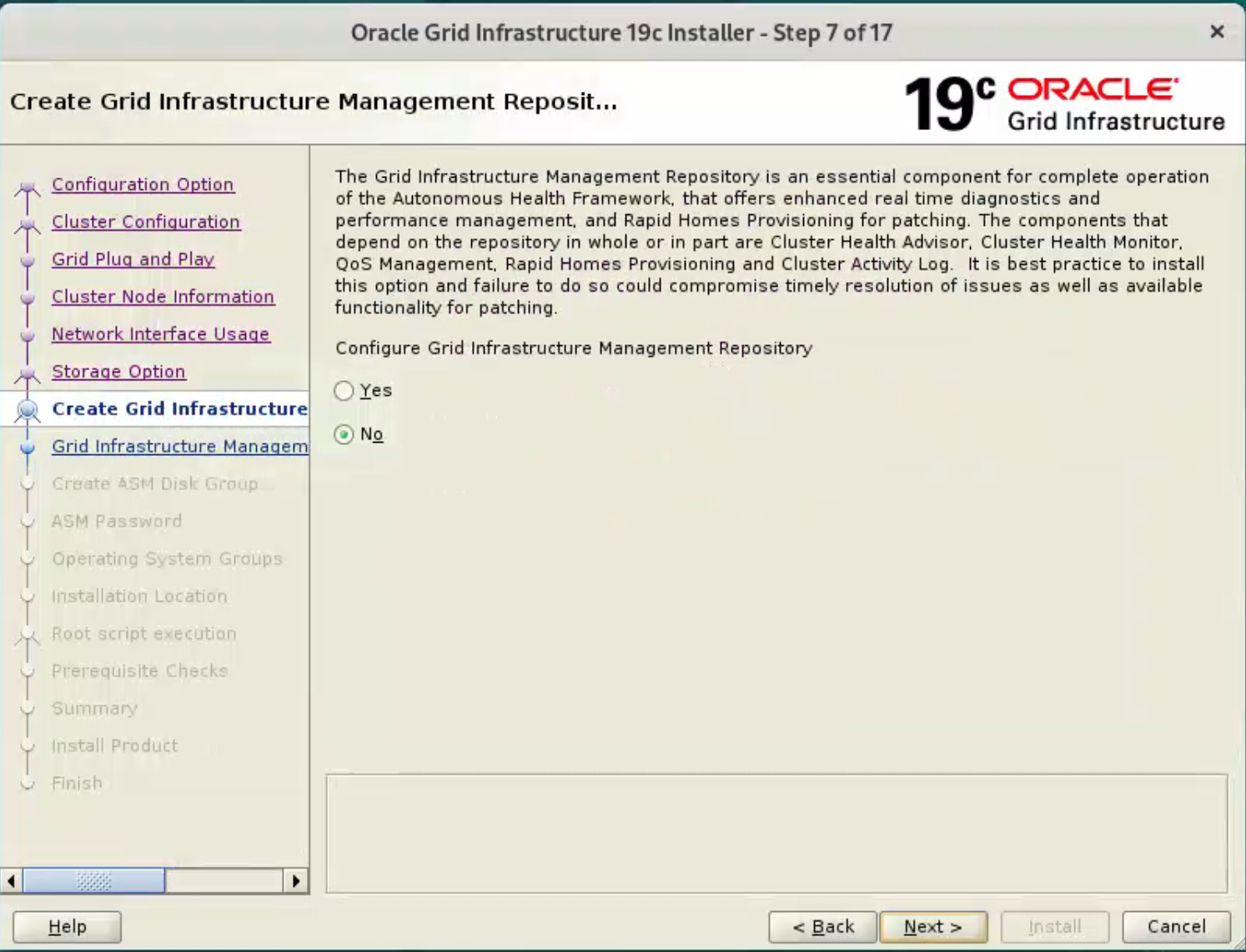
Set the redundancy to “External”, click the “Change Discovery Path” button and set the path to “/dev/oracleasm/asm-disk*”. Return to the main screen and select all 4 disks. Uncheck the “Configure Oracle ASM Filter Driver” option, then click the “Next” button. 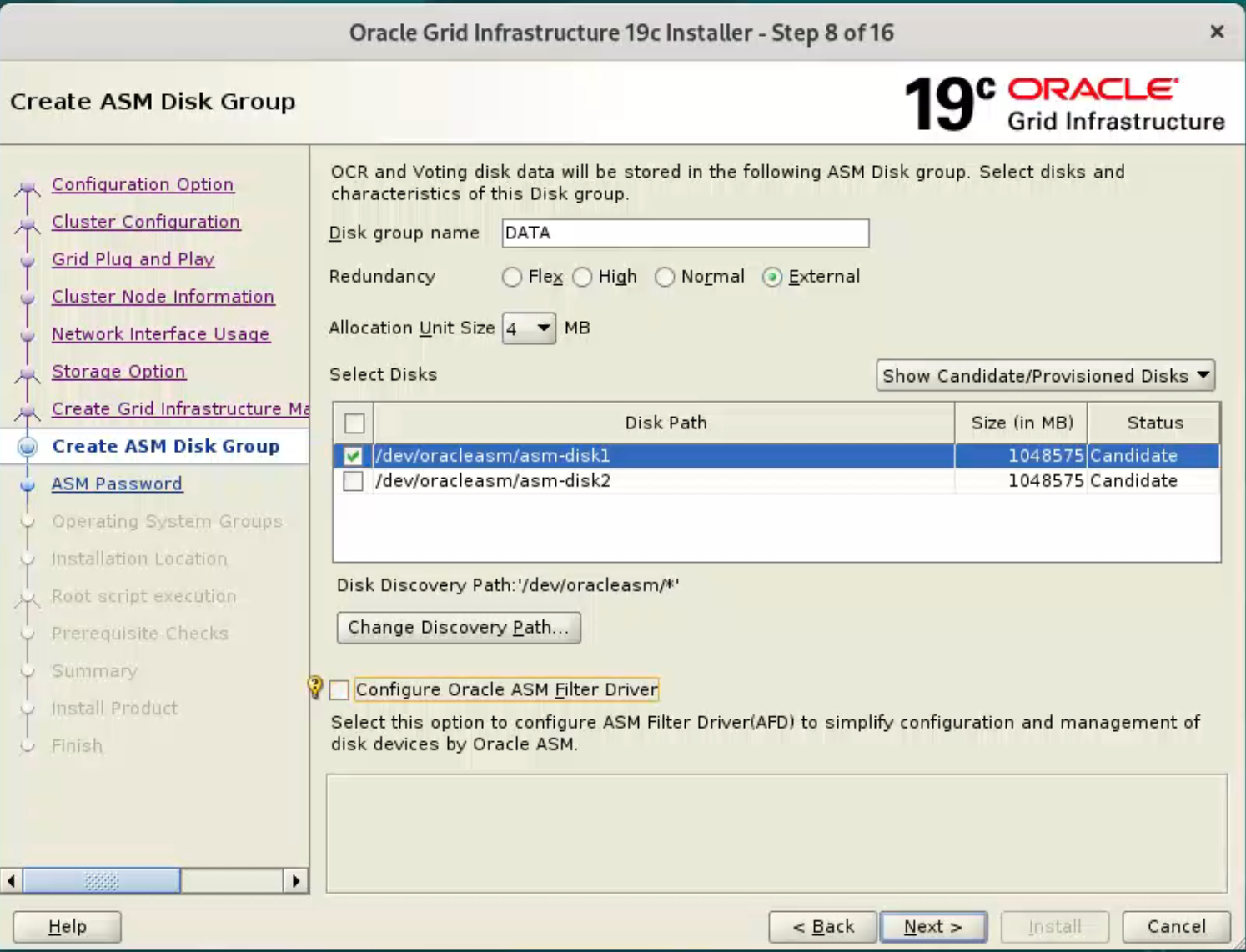 Enter the credentials and click the “Next” button.
Enter the credentials and click the “Next” button. 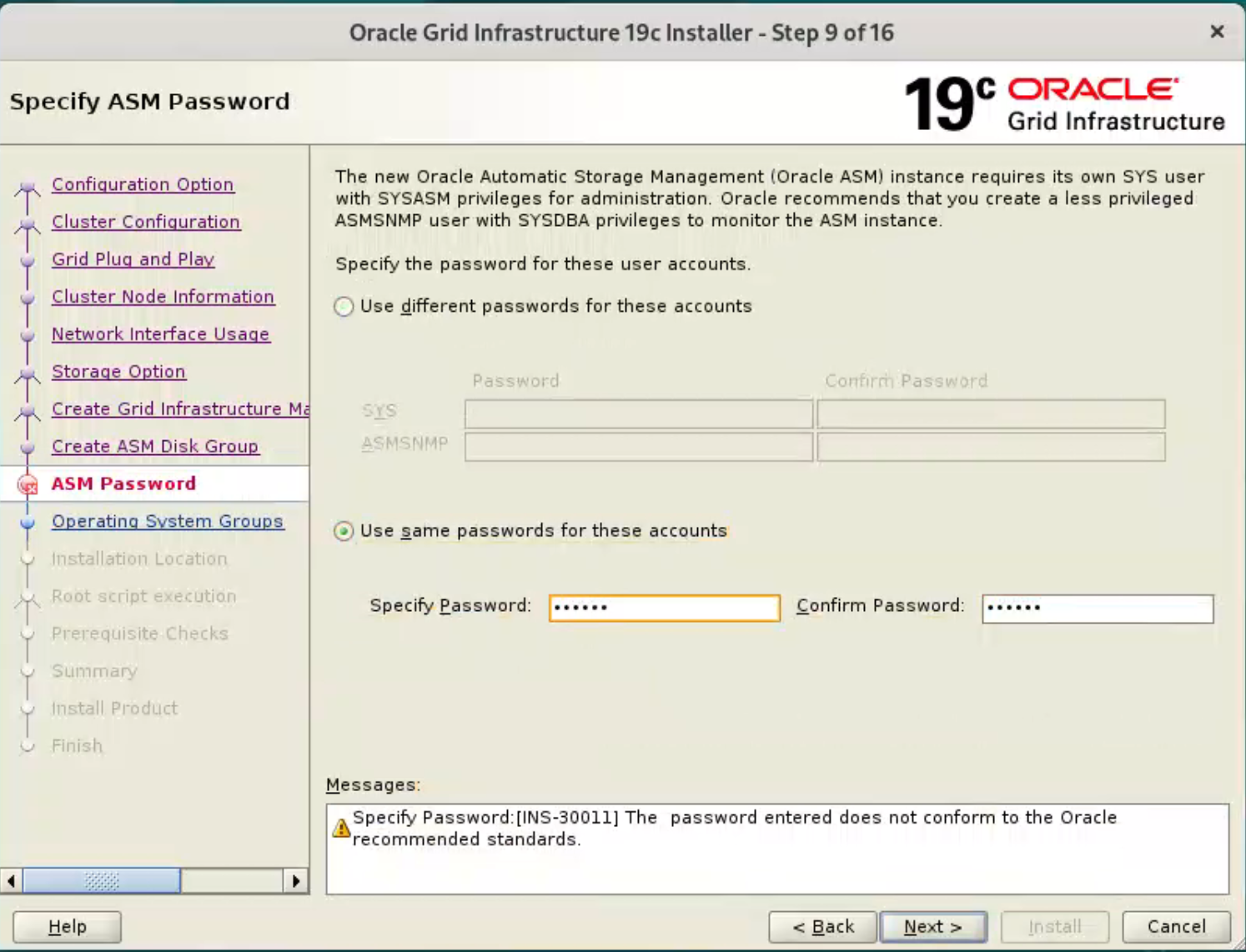
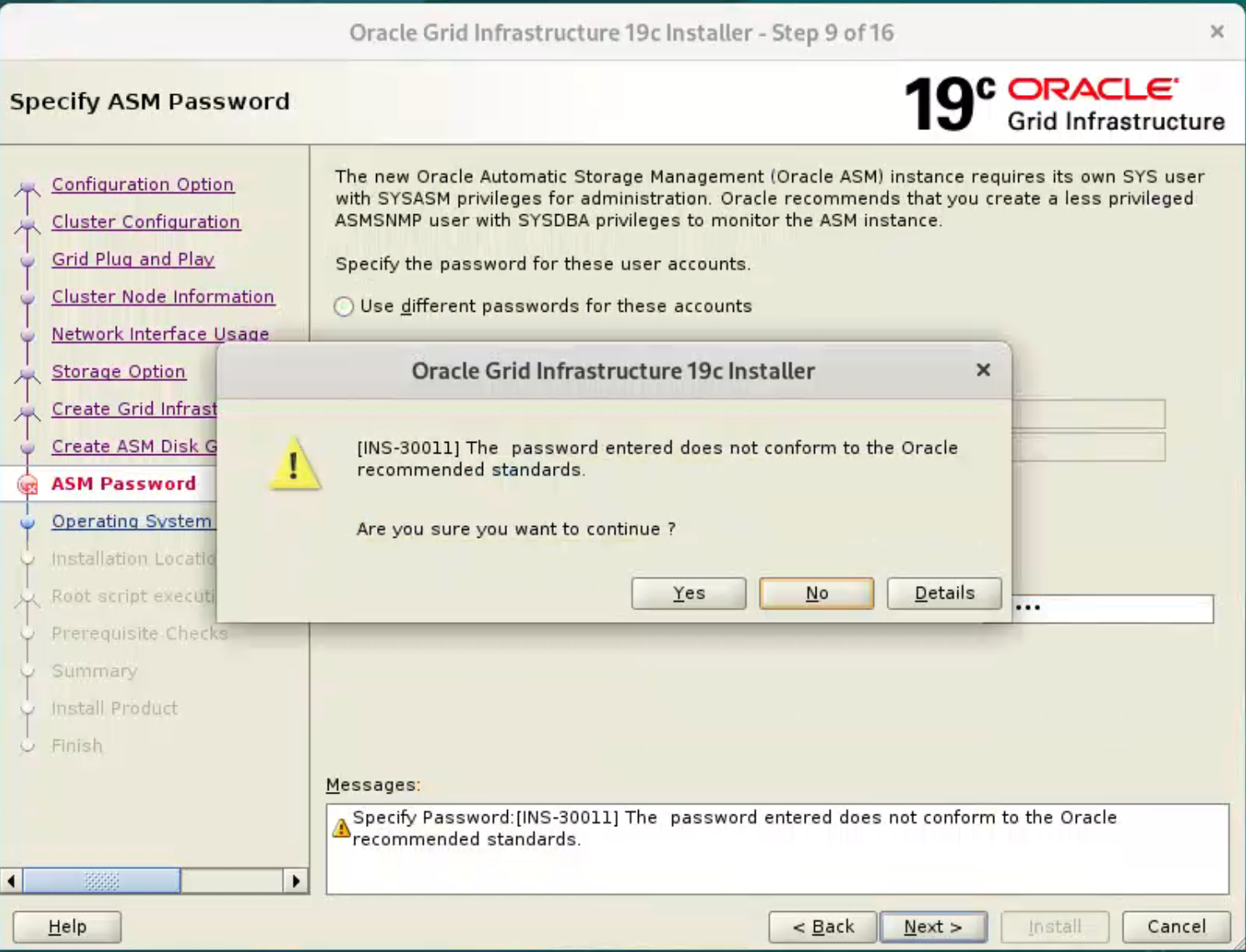
Accept the default IPMI option by clicking the “Next” button.  Don’t register with EM. Click the “Next” button.
Don’t register with EM. Click the “Next” button.  We are using a single user and group manage both ASM add the database, so set the groups to “dba” and click the “Next” button.
We are using a single user and group manage both ASM add the database, so set the groups to “dba” and click the “Next” button. 
Accept the warnings on the subsequent dialog by clicking the “Yes” button. 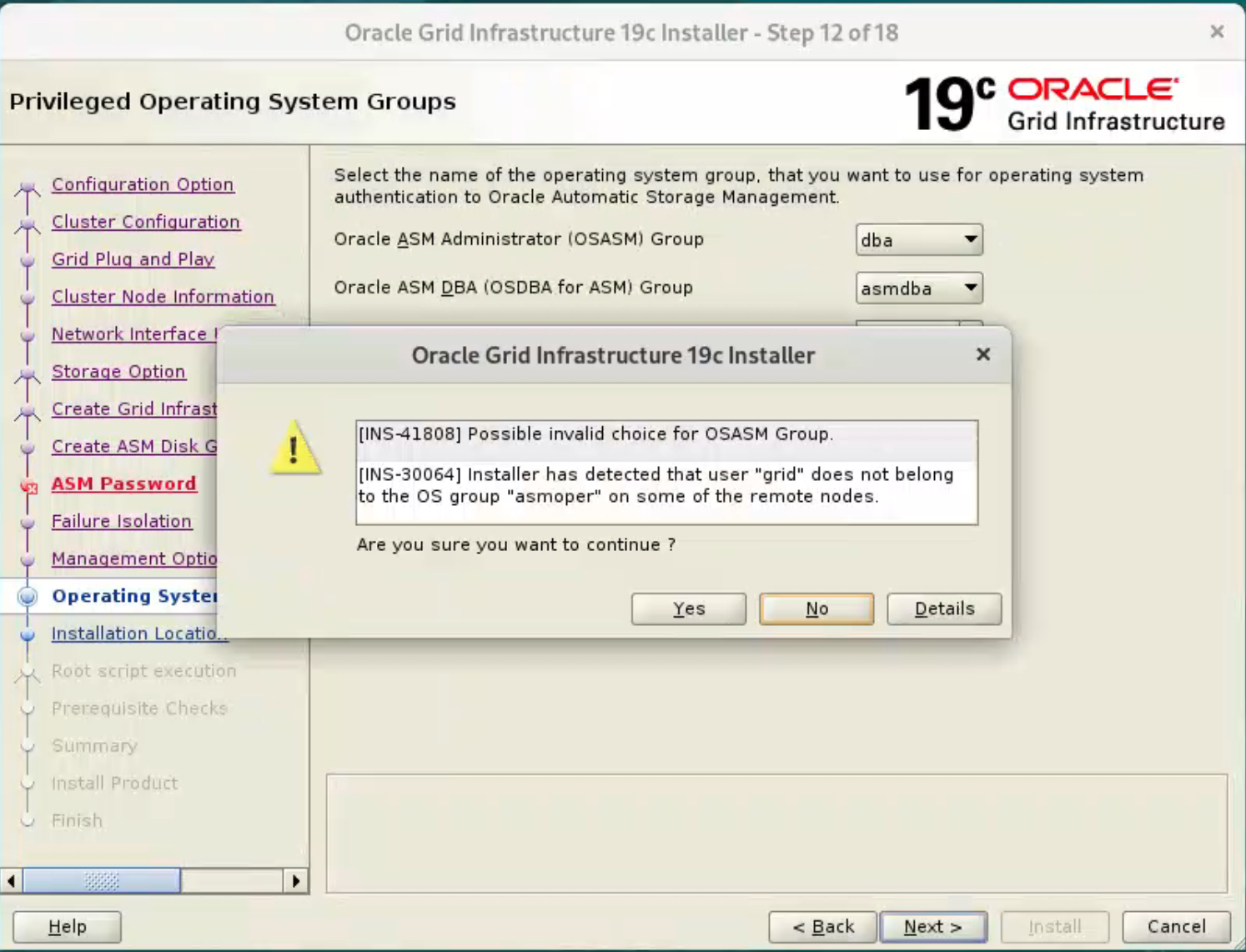
Enter the Oracle Base location “/u01/app/oracle” and click the “Next” button. 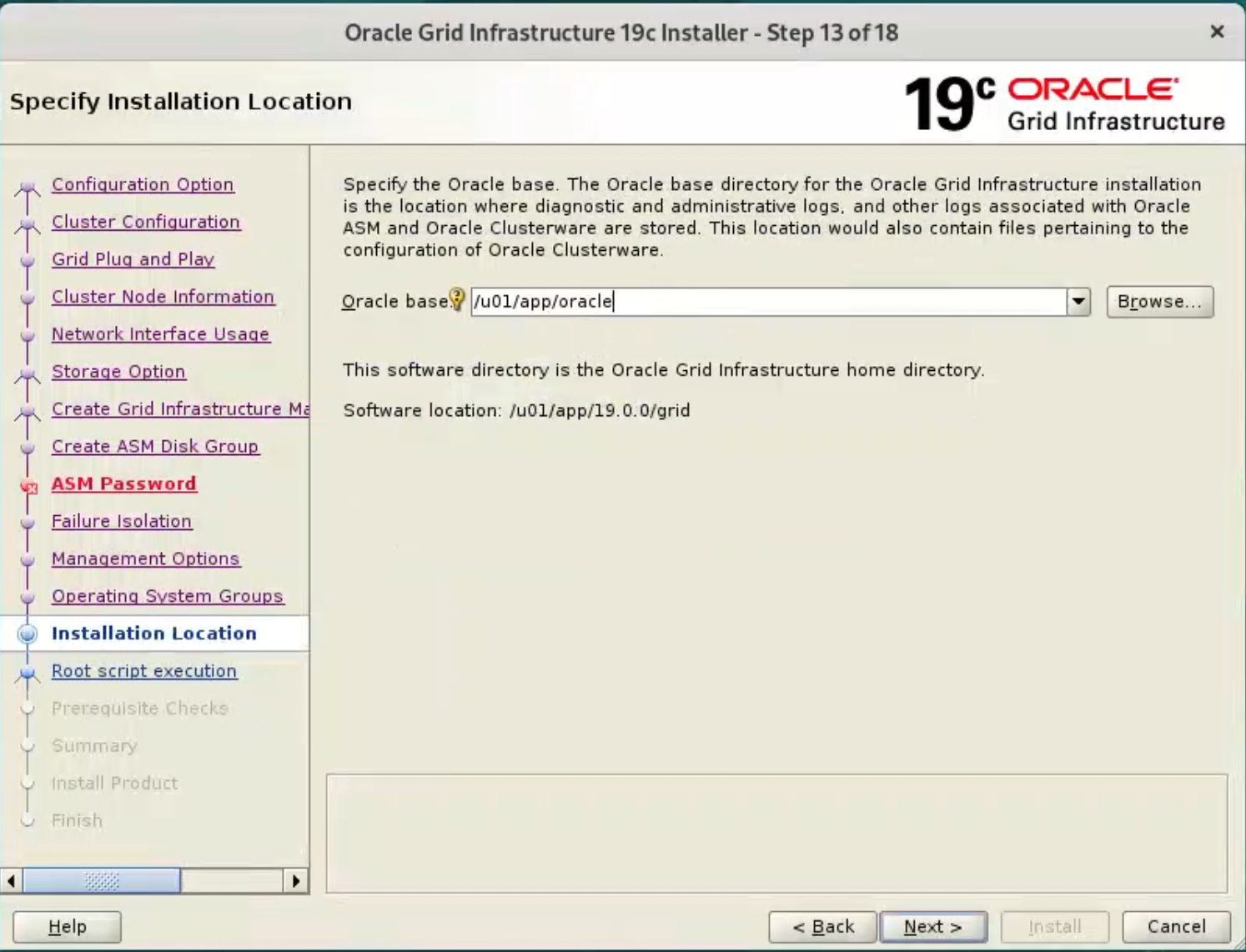 We have already pre-created directories for the later database installation, so ignore the subsequent warning about the Oracle Base not being empty by clicking the “Yes” button.
We have already pre-created directories for the later database installation, so ignore the subsequent warning about the Oracle Base not being empty by clicking the “Yes” button. 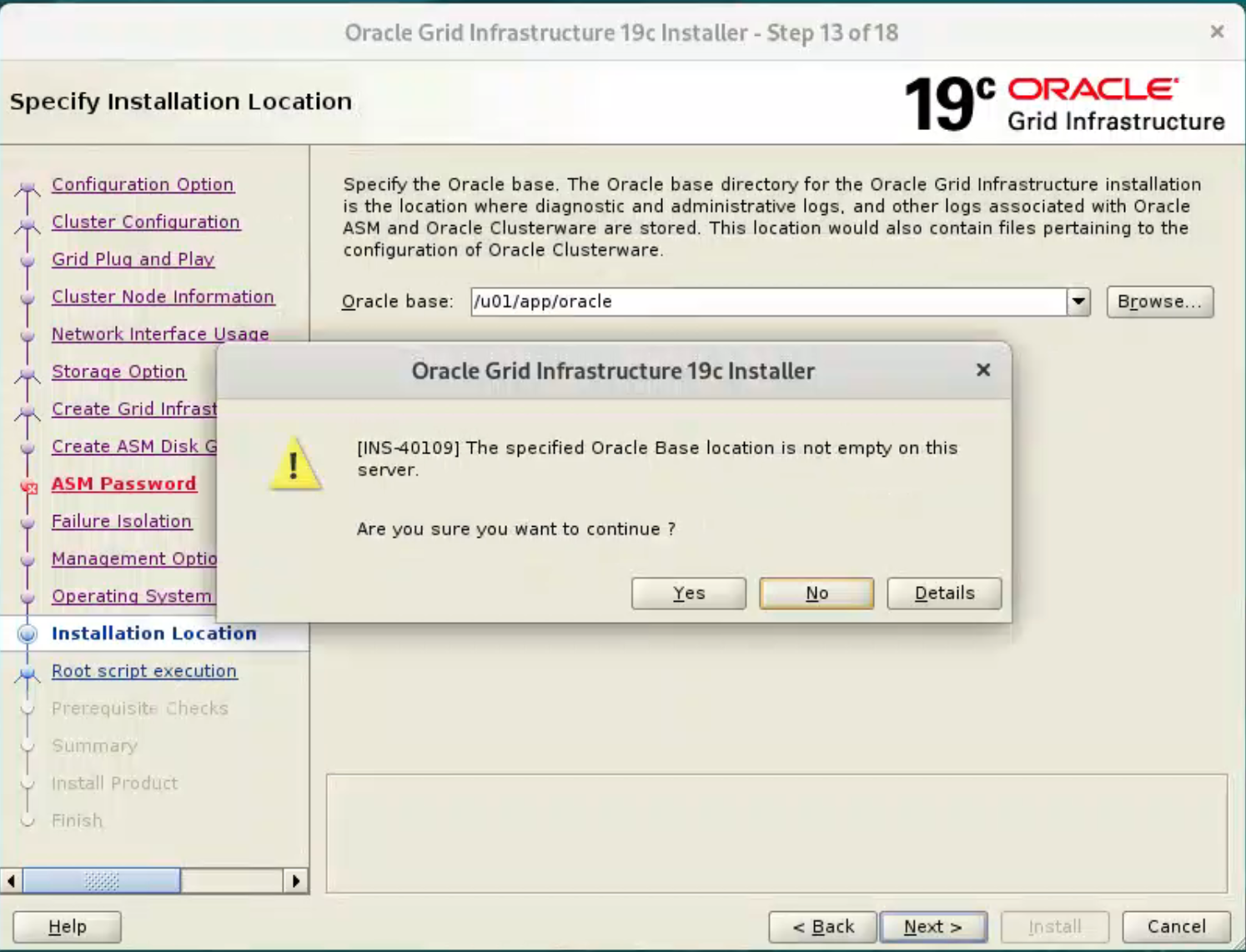
Accept the default inventory directory by clicking the “Next” button. 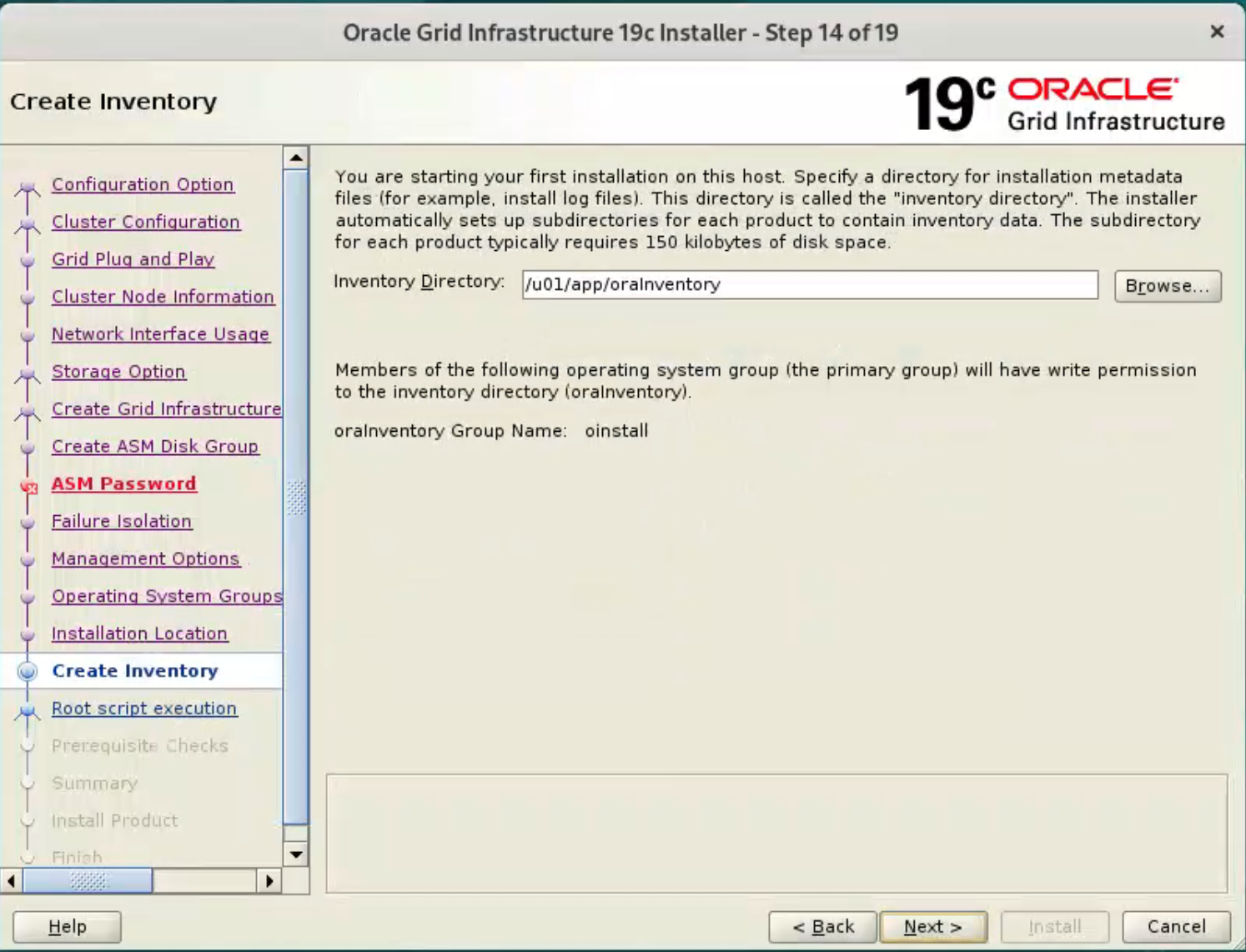 Accept the default root script execution.
Accept the default root script execution. 
Wait while the prerequisite checks complete. If you have any issues use the “Fix & Check Again” button. 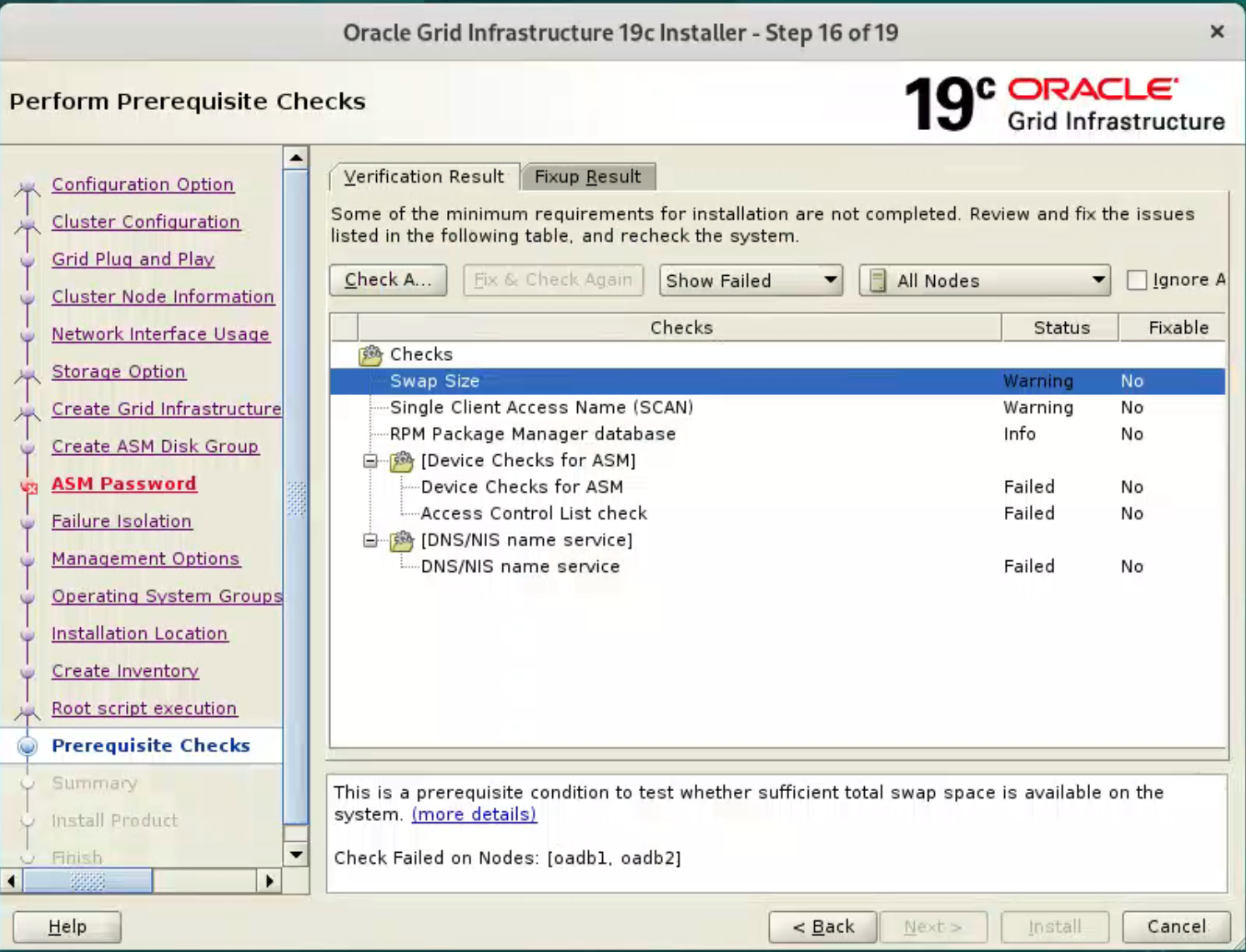
Once possible fixes are complete, check the “Ignore All” checkbox and click the “Next” button. It is likely the “Physical Memory” and “Network Time Protocol (NTP)” tests will fail for this type of installation. This is OK.
By check “Ignore All” to proceed the installation. 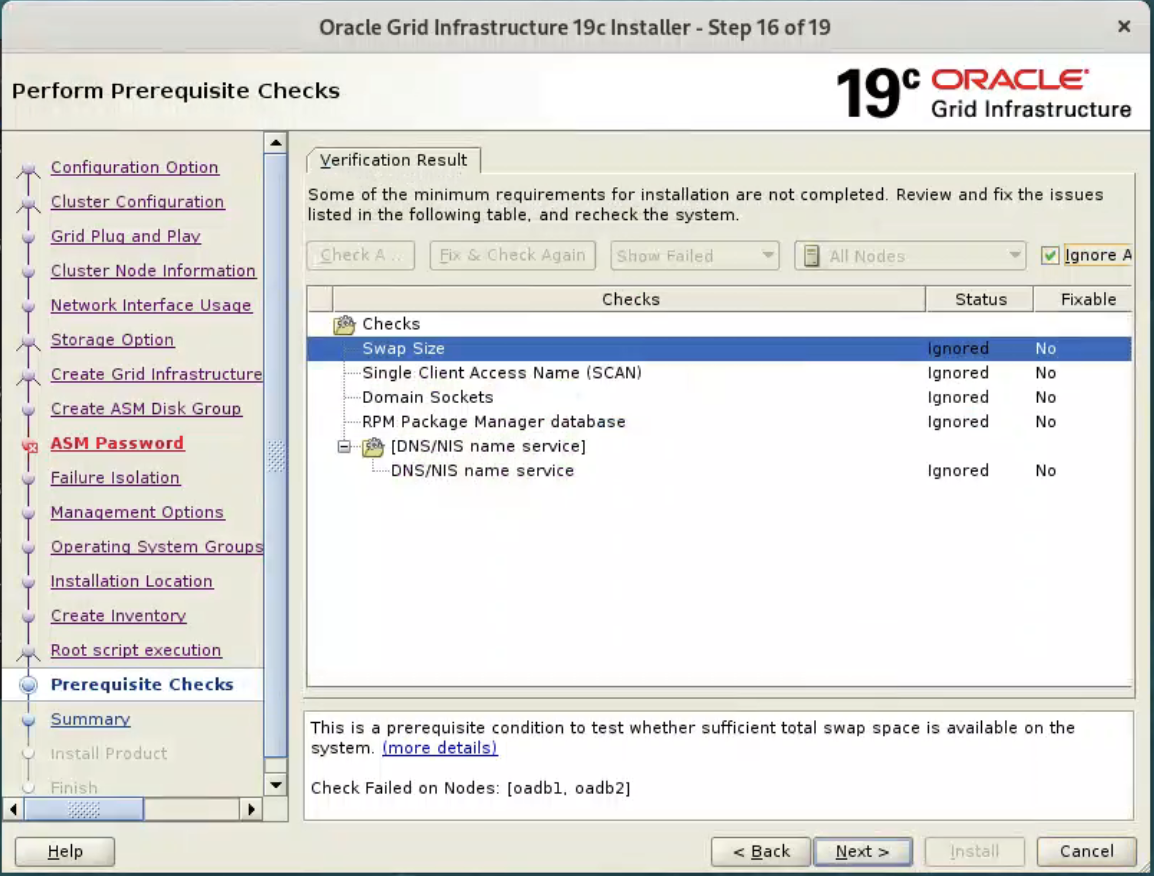
Wait while the installation takes place. 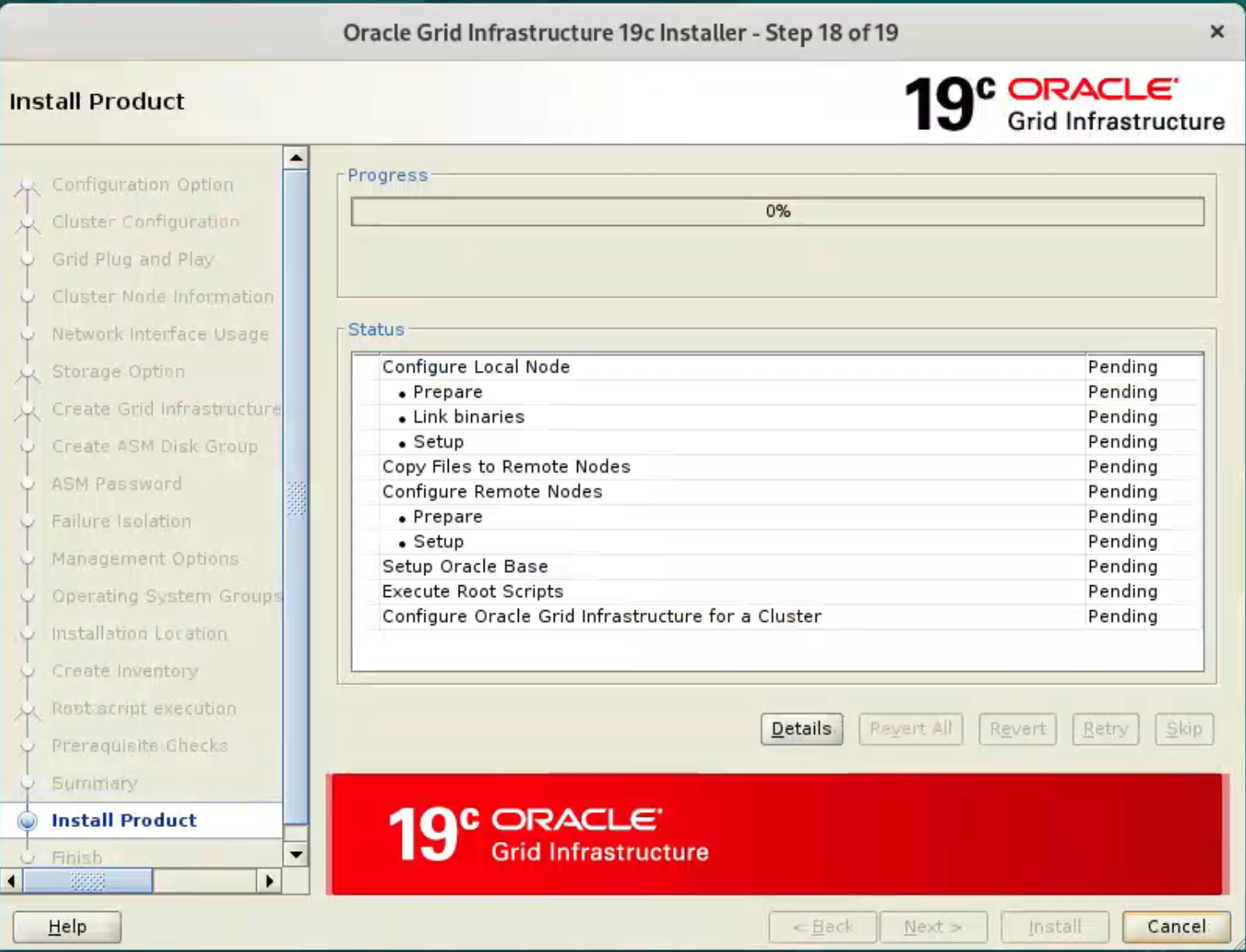 When prompted, run the configuration scripts on each node.
When prompted, run the configuration scripts on each node. 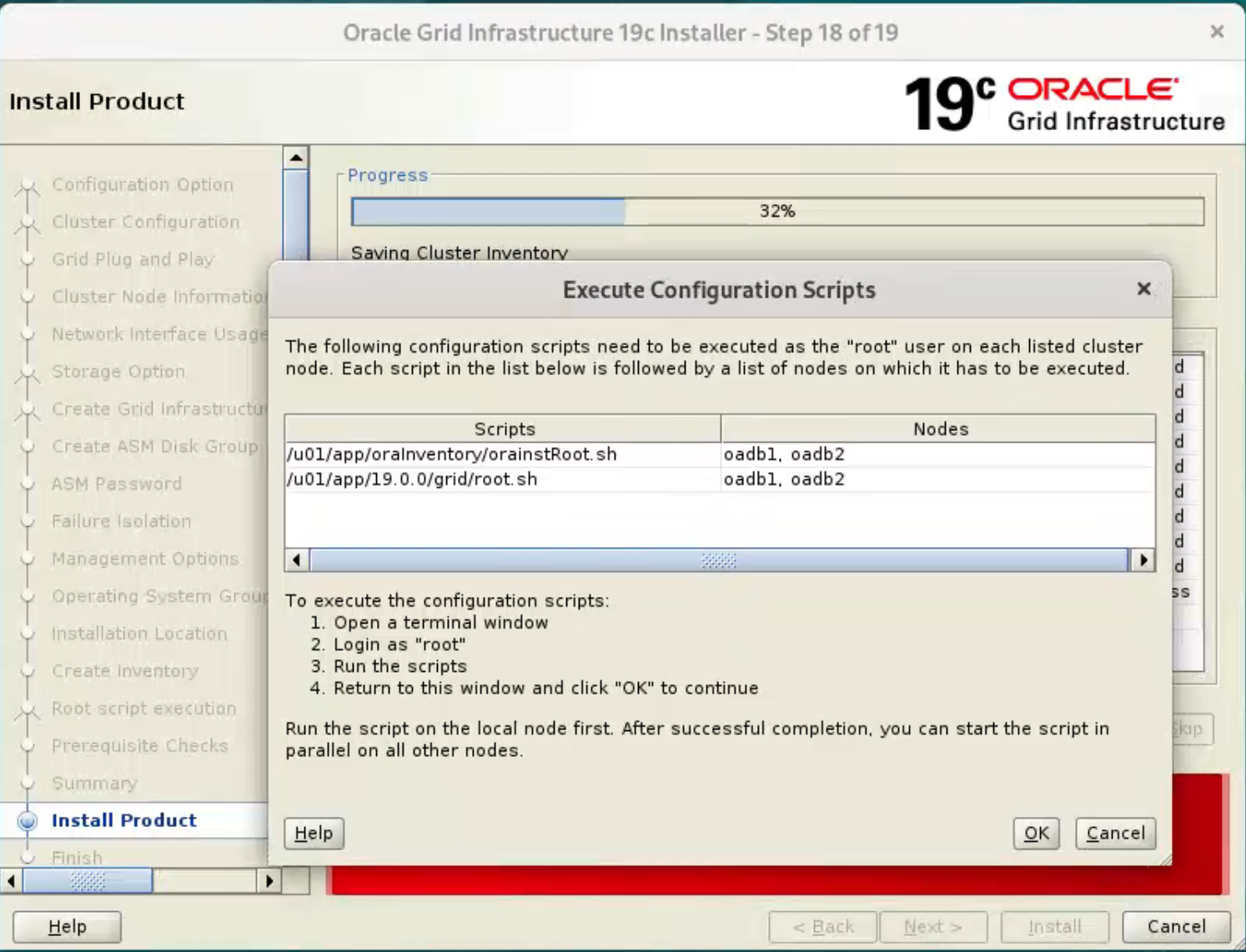 The output from the “orainstRoot.sh” file should look something like that listed below.
The output from the “orainstRoot.sh” file should look something like that listed below.
[root@ol9-19c-rac1 ~]# /u01/app/oraInventory/orainstRoot.sh
Changing permissions of /u01/app/oraInventory.
Adding read,write permissions for group.
Removing read,write,execute permissions for world.
Changing groupname of /u01/app/oraInventory to oinstall.
The execution of the script is complete.
[root@ol9-19c-rac1 ~]#
The output of the “root.sh” will vary a little depending on the node it is run on. Example output can be seen here.
[root@oadb1 ~]# /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/root.sh
Performing root user operation.
The following environment variables are set as:
ORACLE_OWNER= grid
ORACLE_HOME= /u01/app/19.0.0/grid
Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]:
Copying dbhome to /usr/local/bin ...
Copying oraenv to /usr/local/bin ...
Copying coraenv to /usr/local/bin ...
Creating /etc/oratab file...
Entries will be added to the /etc/oratab file as needed by
Database Configuration Assistant when a database is created
Finished running generic part of root script.
Now product-specific root actions will be performed.
Relinking oracle with rac_on option
Using configuration parameter file: /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/crs/install/crsconfig_params
The log of current session can be found at:
/u01/app/oracle/crsdata/oadb1/crsconfig/rootcrs_oadb1_2024-03-06_04-41-30PM.log
2024/03/06 16:41:50 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 1 of 19: 'ValidateEnv'.
2024/03/06 16:41:51 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 2 of 19: 'CheckFirstNode'.
2024/03/06 16:41:52 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 3 of 19: 'GenSiteGUIDs'.
2024/03/06 16:41:53 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 4 of 19: 'SetupOSD'.
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart rsyslog.service
2024/03/06 16:41:54 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 5 of 19: 'CheckCRSConfig'.
2024/03/06 16:41:54 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 6 of 19: 'SetupLocalGPNP'.
2024/03/06 16:42:06 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 7 of 19: 'CreateRootCert'.
2024/03/06 16:42:10 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 8 of 19: 'ConfigOLR'.
2024/03/06 16:42:26 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 9 of 19: 'ConfigCHMOS'.
2024/03/06 16:42:26 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 10 of 19: 'CreateOHASD'.
2024/03/06 16:42:32 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 11 of 19: 'ConfigOHASD'.
2024/03/06 16:42:36 CLSRSC-330: Adding Clusterware entries to file 'oracle-ohasd.service'
2024/03/06 16:43:01 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 12 of 19: 'SetupTFA'.
2024/03/06 16:43:01 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 13 of 19: 'InstallAFD'.
2024/03/06 16:43:01 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 14 of 19: 'InstallACFS'.
2024/03/06 16:43:49 CLSRSC-400: A system reboot is required to continue installing.
[root@oadb1 ~]# 2024/03/06 16:46:29 CLSRSC-4002: Successfully installed Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA) Collector.
If you are not using ACFS, you can safely disable ACFS by renaming $GRID_HOME/bin/acfsroot, acfsload and acfsdriverstate.
then we try reexecute root.sh
[root@oadb1 grid]# ./root.sh
Performing root user operation.
The following environment variables are set as:
ORACLE_OWNER= grid
ORACLE_HOME= /u01/app/19.0.0/grid
Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]:
The contents of "dbhome" have not changed. No need to overwrite.
The contents of "oraenv" have not changed. No need to overwrite.
The contents of "coraenv" have not changed. No need to overwrite.
Entries will be added to the /etc/oratab file as needed by
Database Configuration Assistant when a database is created
Finished running generic part of root script.
Now product-specific root actions will be performed.
Relinking oracle with rac_on option
Using configuration parameter file: /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/crs/install/crsconfig_params
The log of current session can be found at:
/u01/app/oracle/crsdata/oadb1/crsconfig/rootcrs_oadb1_2024-03-06_05-04-38PM.log
2024/03/06 17:04:43 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 1 of 19: 'ValidateEnv'.
2024/03/06 17:04:43 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 2 of 19: 'CheckFirstNode'.
2024/03/06 17:04:45 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 3 of 19: 'GenSiteGUIDs'.
2024/03/06 17:04:46 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 4 of 19: 'SetupOSD'.
2024/03/06 17:04:46 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 5 of 19: 'CheckCRSConfig'.
2024/03/06 17:04:46 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 6 of 19: 'SetupLocalGPNP'.
2024/03/06 17:04:47 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 7 of 19: 'CreateRootCert'.
2024/03/06 17:04:51 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 8 of 19: 'ConfigOLR'.
2024/03/06 17:04:51 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 9 of 19: 'ConfigCHMOS'.
2024/03/06 17:05:22 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 10 of 19: 'CreateOHASD'.
2024/03/06 17:05:23 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 11 of 19: 'ConfigOHASD'.
2024/03/06 17:05:29 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 12 of 19: 'SetupTFA'.
2024/03/06 17:05:29 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 13 of 19: 'InstallAFD'.
2024/03/06 17:05:29 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 14 of 19: 'InstallACFS'.
2024/03/06 17:05:34 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 15 of 19: 'InstallKA'.
2024/03/06 17:05:40 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 16 of 19: 'InitConfig'.
2024/03/06 17:06:29 CLSRSC-4002: Successfully installed Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA) Collector.
ASM has been created and started successfully.
[DBT-30001] Disk groups created successfully. Check /u01/app/oracle/cfgtoollogs/asmca/asmca-240306PM050610.log for details.
2024/03/06 17:07:13 CLSRSC-482: Running command: '/u01/app/19.0.0/grid/bin/ocrconfig -upgrade grid oinstall'
CRS-4256: Updating the profile
Successful addition of voting disk 60c091675e1e4f70bfe52f98de9b83f4.
Successfully replaced voting disk group with +DATA.
CRS-4256: Updating the profile
CRS-4266: Voting file(s) successfully replaced
## STATE File Universal Id File Name Disk group
-- ----- ----------------- --------- ---------
1. ONLINE 60c091675e1e4f70bfe52f98de9b83f4 (/dev/oracleasm/asm-disk1) [DATA]
Located 1 voting disk(s).
2024/03/06 17:08:17 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 17 of 19: 'StartCluster'.
2024/03/06 17:09:19 CLSRSC-343: Successfully started Oracle Clusterware stack
2024/03/06 17:09:19 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 18 of 19: 'ConfigNode'.
2024/03/06 17:10:32 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 19 of 19: 'PostConfig'.
2024/03/06 17:10:54 CLSRSC-325: Configure Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a Cluster ... succeeded
[root@oadb1 grid]#
[root@oadb2 ~]# /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/root.sh
Performing root user operation.
The following environment variables are set as:
ORACLE_OWNER= grid
ORACLE_HOME= /u01/app/19.0.0/grid
Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]:
Copying dbhome to /usr/local/bin ...
Copying oraenv to /usr/local/bin ...
Copying coraenv to /usr/local/bin ...
Creating /etc/oratab file...
Entries will be added to the /etc/oratab file as needed by
Database Configuration Assistant when a database is created
Finished running generic part of root script.
Now product-specific root actions will be performed.
Relinking oracle with rac_on option
Using configuration parameter file: /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/crs/install/crsconfig_params
The log of current session can be found at:
/u01/app/oracle/crsdata/oadb2/crsconfig/rootcrs_oadb2_2024-03-06_05-12-47PM.log
2024/03/06 17:13:10 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 1 of 19: 'ValidateEnv'.
2024/03/06 17:13:11 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 2 of 19: 'CheckFirstNode'.
2024/03/06 17:13:12 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 3 of 19: 'GenSiteGUIDs'.
2024/03/06 17:13:12 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 4 of 19: 'SetupOSD'.
Redirecting to /bin/systemctl restart rsyslog.service
2024/03/06 17:13:12 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 5 of 19: 'CheckCRSConfig'.
2024/03/06 17:13:12 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 6 of 19: 'SetupLocalGPNP'.
2024/03/06 17:13:13 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 7 of 19: 'CreateRootCert'.
2024/03/06 17:13:14 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 8 of 19: 'ConfigOLR'.
2024/03/06 17:13:24 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 9 of 19: 'ConfigCHMOS'.
2024/03/06 17:13:24 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 10 of 19: 'CreateOHASD'.
2024/03/06 17:13:25 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 11 of 19: 'ConfigOHASD'.
2024/03/06 17:13:29 CLSRSC-330: Adding Clusterware entries to file 'oracle-ohasd.service'
2024/03/06 17:13:49 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 12 of 19: 'SetupTFA'.
2024/03/06 17:13:49 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 13 of 19: 'InstallAFD'.
2024/03/06 17:13:49 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 14 of 19: 'InstallACFS'.
2024/03/06 17:14:27 CLSRSC-400: A system reboot is required to continue installing.
[root@oadb2 ~]# cd /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/bin
[root@oadb2 bin]# mv acfsroot acfsroot.bak
[root@oadb2 bin]# mv acfsload acfsload.bak
[root@oadb2 bin]# mv acfsdriverstate acfsdriverstate.bak
[root@oadb2 bin]# cd ..
[root@oadb2 grid]# /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/root.sh
Performing root user operation.
The following environment variables are set as:
ORACLE_OWNER= grid
ORACLE_HOME= /u01/app/19.0.0/grid
Enter the full pathname of the local bin directory: [/usr/local/bin]:
The contents of "dbhome" have not changed. No need to overwrite.
The contents of "oraenv" have not changed. No need to overwrite.
The contents of "coraenv" have not changed. No need to overwrite.
Entries will be added to the /etc/oratab file as needed by
Database Configuration Assistant when a database is created
Finished running generic part of root script.
Now product-specific root actions will be performed.
Relinking oracle with rac_on option
Using configuration parameter file: /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/crs/install/crsconfig_params
The log of current session can be found at:
/u01/app/oracle/crsdata/oadb2/crsconfig/rootcrs_oadb2_2024-03-06_05-15-24PM.log
2024/03/06 17:15:28 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 1 of 19: 'ValidateEnv'.
2024/03/06 17:15:28 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 2 of 19: 'CheckFirstNode'.
2024/03/06 17:15:29 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 3 of 19: 'GenSiteGUIDs'.
2024/03/06 17:15:29 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 4 of 19: 'SetupOSD'.
2024/03/06 17:15:29 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 5 of 19: 'CheckCRSConfig'.
2024/03/06 17:15:30 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 6 of 19: 'SetupLocalGPNP'.
2024/03/06 17:15:31 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 7 of 19: 'CreateRootCert'.
2024/03/06 17:15:31 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 8 of 19: 'ConfigOLR'.
2024/03/06 17:15:32 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 9 of 19: 'ConfigCHMOS'.
2024/03/06 17:16:02 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 10 of 19: 'CreateOHASD'.
2024/03/06 17:16:03 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 11 of 19: 'ConfigOHASD'.
2024/03/06 17:16:09 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 12 of 19: 'SetupTFA'.
2024/03/06 17:16:09 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 13 of 19: 'InstallAFD'.
2024/03/06 17:16:09 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 14 of 19: 'InstallACFS'.
2024/03/06 17:16:09 CLSRSC-4004: Failed to install Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA) Collector. Grid Infrastructure operations will continue.
2024/03/06 17:16:11 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 15 of 19: 'InstallKA'.
2024/03/06 17:16:12 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 16 of 19: 'InitConfig'.
2024/03/06 17:16:22 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 17 of 19: 'StartCluster'.
2024/03/06 17:17:05 CLSRSC-343: Successfully started Oracle Clusterware stack
2024/03/06 17:17:05 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 18 of 19: 'ConfigNode'.
2024/03/06 17:17:13 CLSRSC-594: Executing installation step 19 of 19: 'PostConfig'.
2024/03/06 17:17:21 CLSRSC-4002: Successfully installed Oracle Trace File Analyzer (TFA) Collector.
2024/03/06 17:17:21 CLSRSC-325: Configure Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a Cluster ... succeeded
[root@oadb2 grid]#
Once the scripts have completed, return to the “Execute Configuration Scripts” screen on “ol9-19c-rac1” and click the “OK” button.
Wait for the configuration assistants to complete. 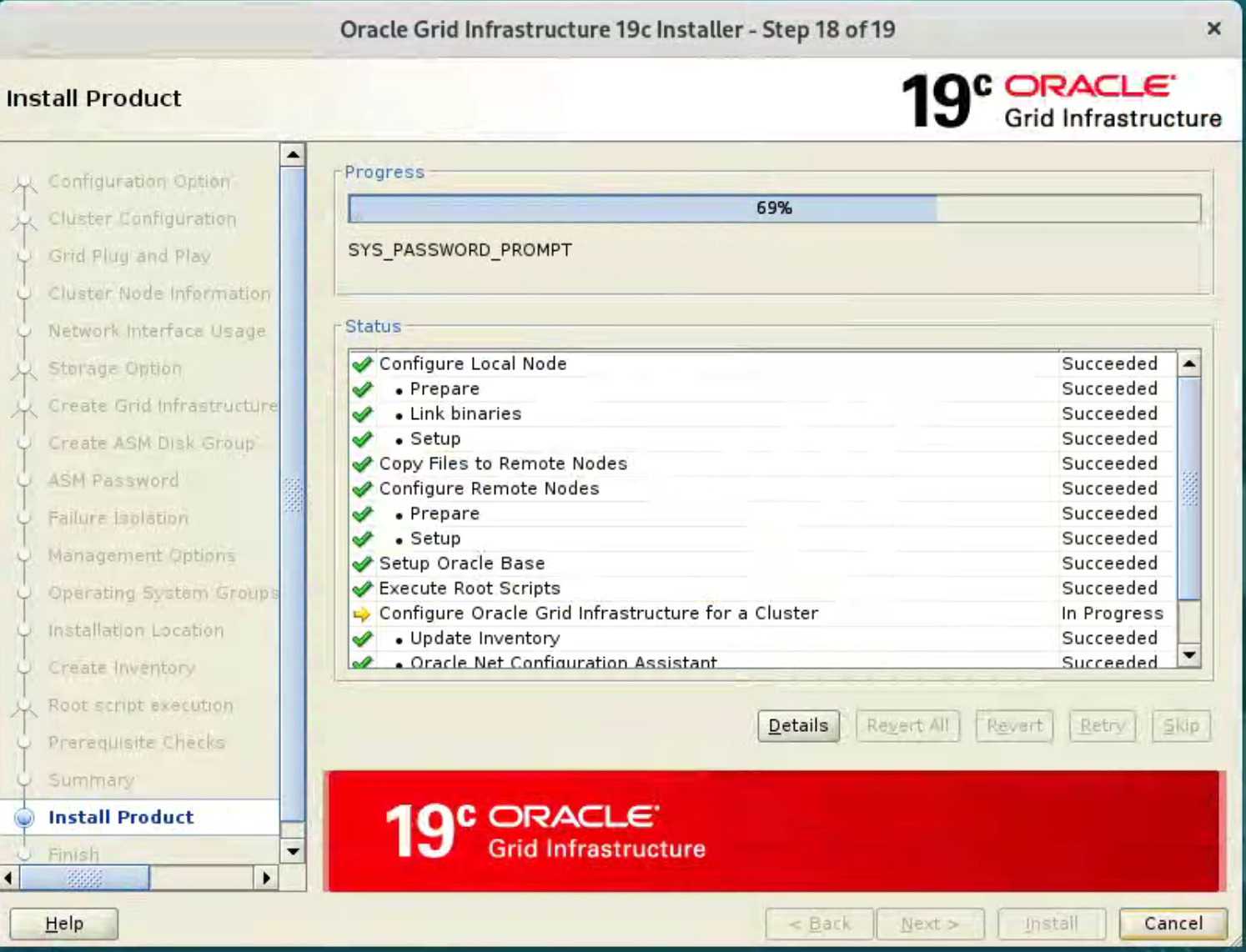 If any of the configuration steps fail you should check the specified log to see if the error is a show-stopper or not.
If any of the configuration steps fail you should check the specified log to see if the error is a show-stopper or not.
Provided you don’t have any show-stoppers, it is safe to ignore the errors by clicking “Next” button. 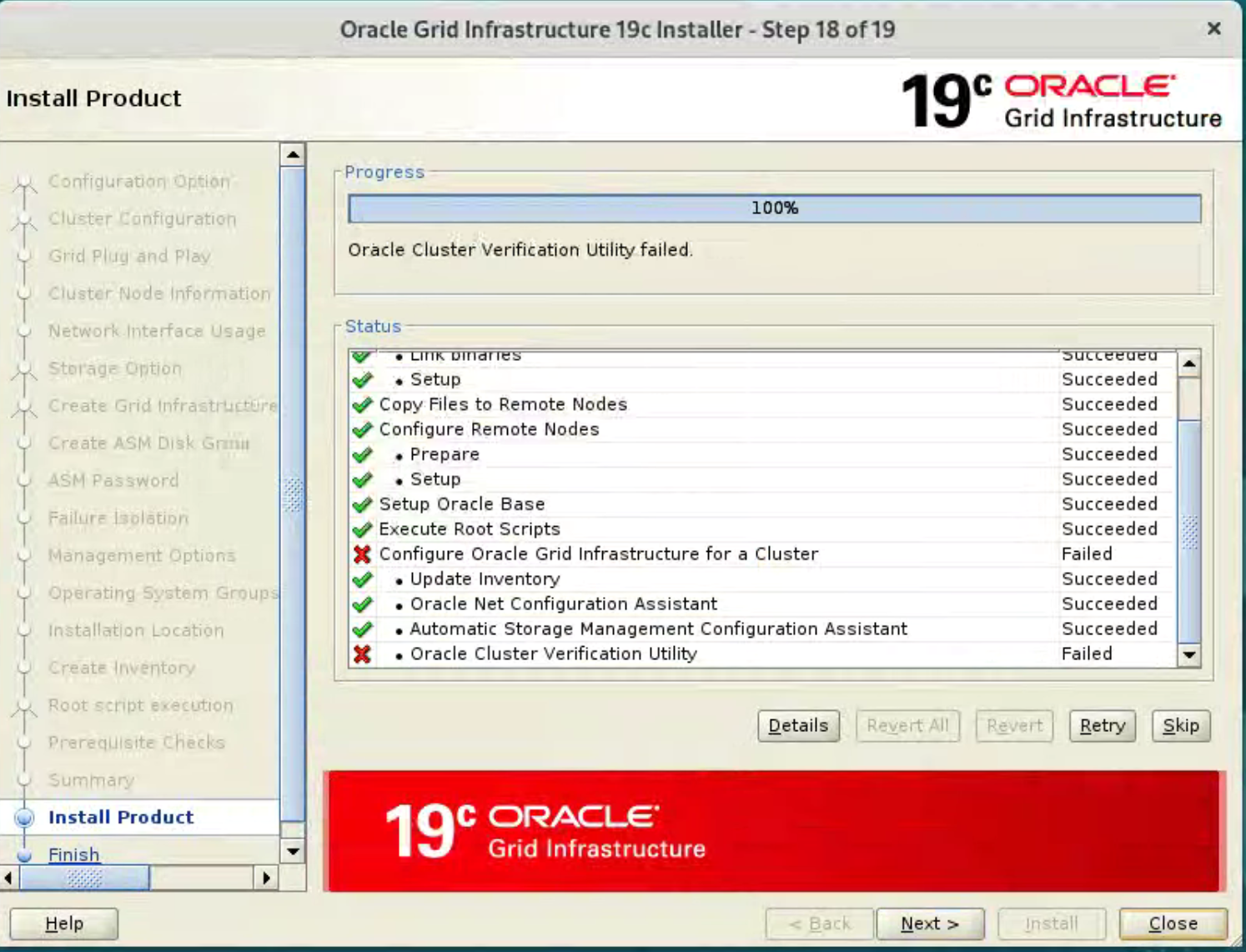 Click the “Yes” button to continue.
Click the “Yes” button to continue. 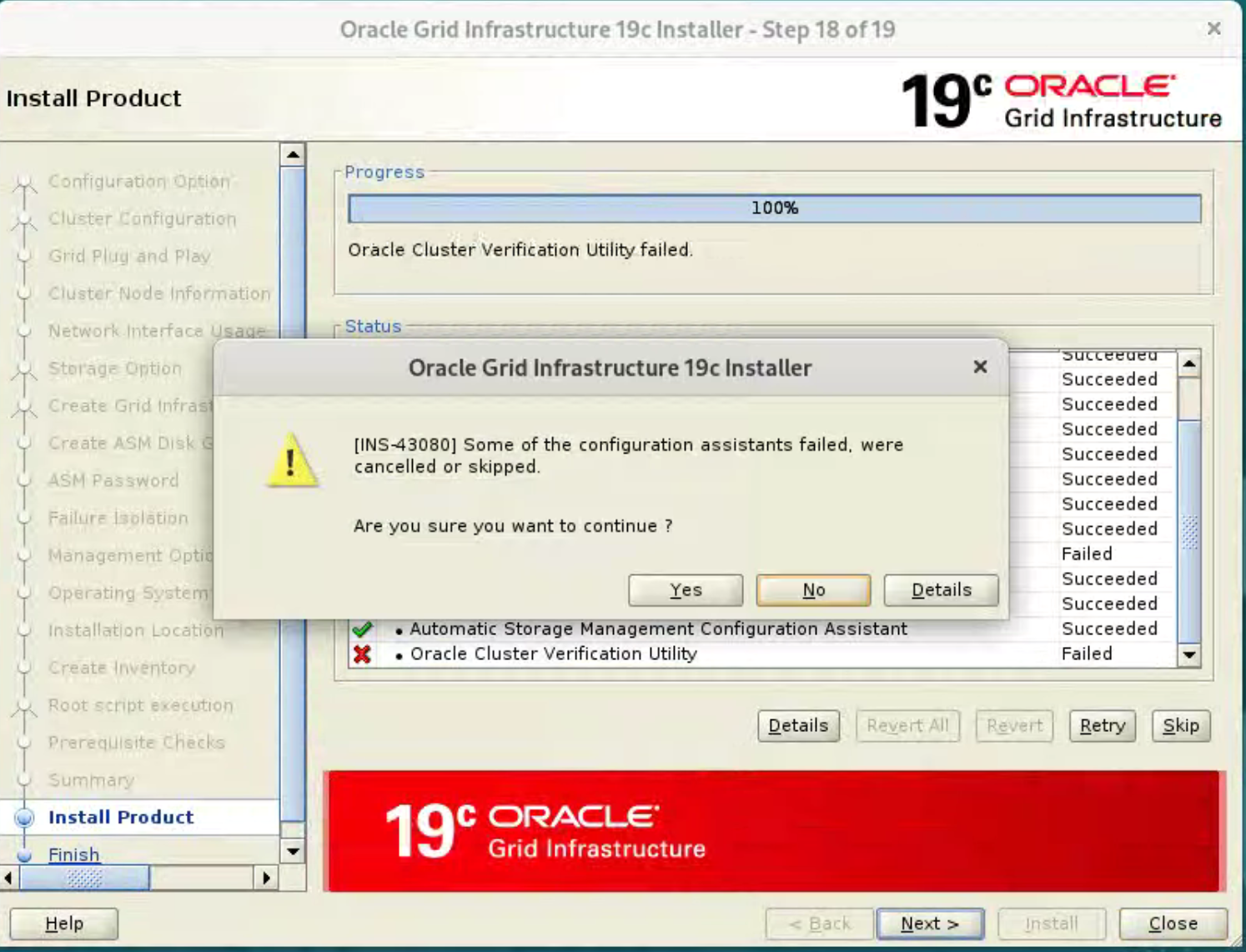
Click the “Close” button to exit the installer. 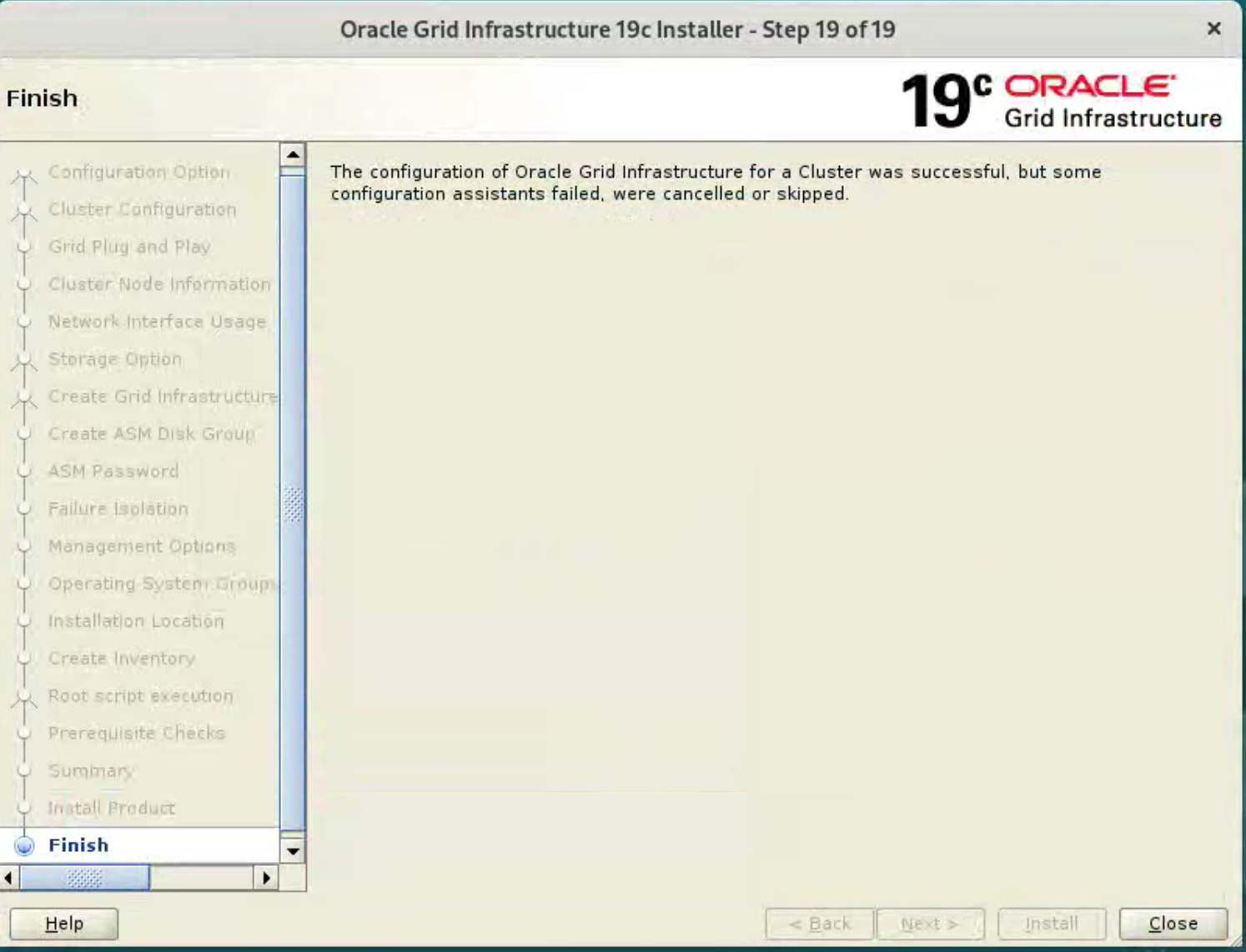 The grid infrastructure installation is now complete. We can check the status of the installation using the following commands.
The grid infrastructure installation is now complete. We can check the status of the installation using the following commands.
[root@oadb1 grid]# /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/bin/crsctl stat res -t
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Name Target State Server State details
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Local Resources
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ora.LISTENER.lsnr
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.chad
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.net1.network
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.ons
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cluster Resources
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ora.ASMNET1LSNR_ASM.lsnr(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.DATA.dg(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.LISTENER_SCAN1.lsnr
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ora.asm(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 Started,STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 Started,STABLE
ora.asmnet1.asmnetwork(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.cvu
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ora.oadb1.vip
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ora.oadb2.vip
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.qosmserver
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ora.scan1.vip
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@oadb1 grid]#
[root@oadb2 grid]# /u01/app/19.0.0/grid/bin/crsctl stat res -t
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Name Target State Server State details
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Local Resources
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ora.LISTENER.lsnr
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.chad
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.net1.network
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.ons
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cluster Resources
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ora.ASMNET1LSNR_ASM.lsnr(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.DATA.dg(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.LISTENER_SCAN1.lsnr
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ora.asm(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 Started,STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 Started,STABLE
ora.asmnet1.asmnetwork(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.cvu
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ora.oadb1.vip
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ora.oadb2.vip
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.qosmserver
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ora.scan1.vip
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[root@oadb2 grid]#
To check the patch installed.
grid@oadb1[+ASM1]:/home/grid$ opatch lspatches
35983839;ACFS Interim patch for 35983839
35926646;OJVM RELEASE UPDATE: 19.22.0.0.240116 (35926646)
36115038;TOMCAT RELEASE UPDATE 19.0.0.0.0 (36115038)
35967489;OCW RELEASE UPDATE 19.22.0.0.0 (35967489)
35943157;Database Release Update : 19.22.0.0.240116 (35943157)
33575402;DBWLM RELEASE UPDATE 19.0.0.0.0 (33575402)
OPatch succeeded.
grid@oadb1[+ASM1]:/home/grid$
grid@oadb2[+ASM2]:/home/grid$ opatch lspatches
35983839;ACFS Interim patch for 35983839
35926646;OJVM RELEASE UPDATE: 19.22.0.0.240116 (35926646)
36115038;TOMCAT RELEASE UPDATE 19.0.0.0.0 (36115038)
35967489;OCW RELEASE UPDATE 19.22.0.0.0 (35967489)
35943157;Database Release Update : 19.22.0.0.240116 (35943157)
33575402;DBWLM RELEASE UPDATE 19.0.0.0.0 (33575402)
OPatch succeeded.
grid@oadb2[+ASM2]:/home/grid$
At this point it is probably a good idea to shutdown both VMs and take snapshots. Remember to make a fresh zip of the ASM disks on the host machine, which you will need to restore if you revert to the post-grid snapshots.
$ cd /u04/VirtualBox/ol9-19c-rac
$ zip PostGrid.zip *.vdi
Install the Database Software
Make sure the “ol9-19c-rac1” and “ol9-19c-rac2” virtual machines are started, then login to “ol9-19c-rac1” as the oracle user and unzip the database software to target directory on the first node. Don’t do this on the second node.
unzip -qqd /u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/db_1 V982063-01.zip
Replace the old OPatch with new version.
$ mv /u01/app/oracle/product/19c/dbhome_1/OPatch /u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/db_1/OPatch_bkp
$ unzip -qqd /u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/db_1 /soft/p6880880_190000_Linux-x86-64.zip
Then start the Oracle installer to perform Installation using 19.22 DB RU+19.22 OCW Merge Patch. Check that all services are up using “crsctl stat res -t”, as described before.
$ db_env
$ cd $ORACLE_HOME
$ ./runInstaller -applyRU <19.22 DBRU Patch 35943157 unzip Location> -applyOneOffs <19.22 OCW RU 35967489 unzip location>,<19.22 OJVM RU unzip location>,<ACFS patch 35983839>
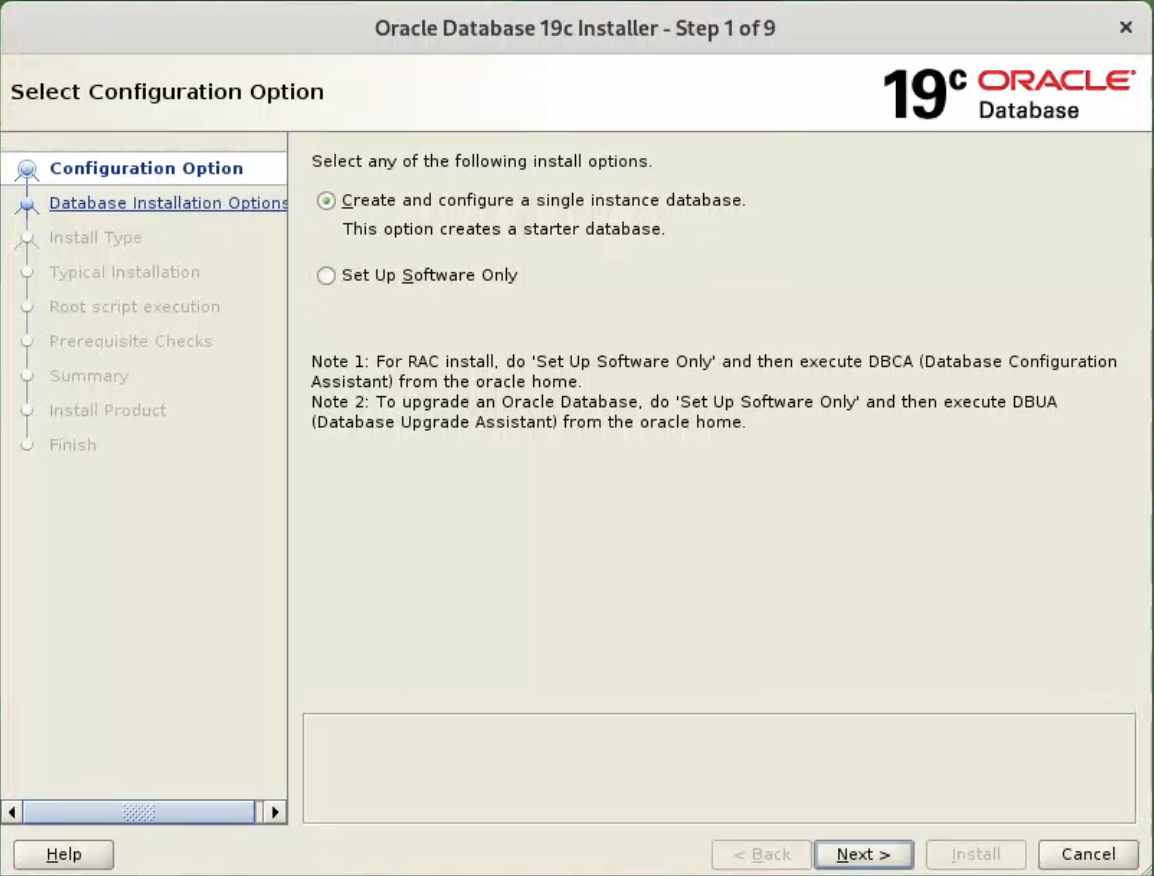
Select the “Set Up Software Only” option, then click the “Next” button. 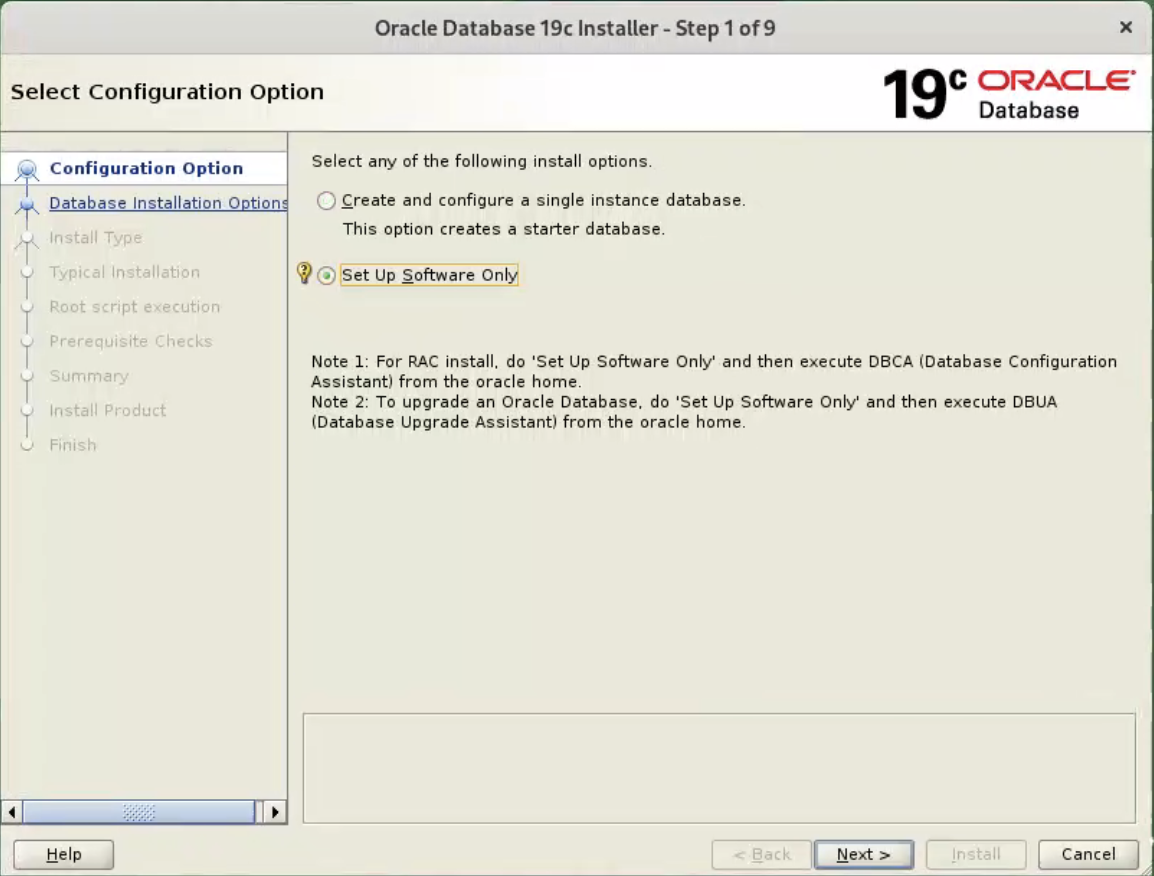 Accept the “Oracle Real Application Clusters database installation” option by clicking the “Next” button.
Accept the “Oracle Real Application Clusters database installation” option by clicking the “Next” button. 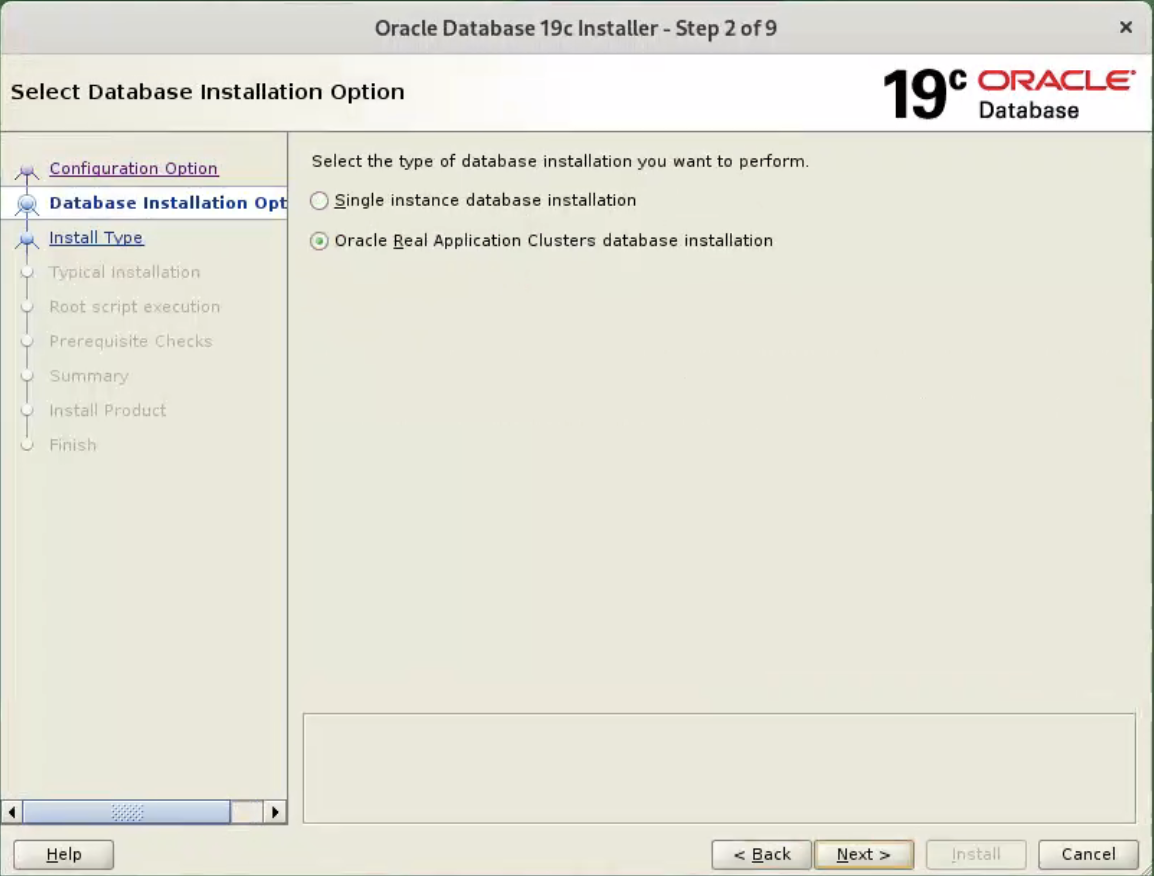 Make sure both nodes are selected, then click the “Next” button.
Make sure both nodes are selected, then click the “Next” button. 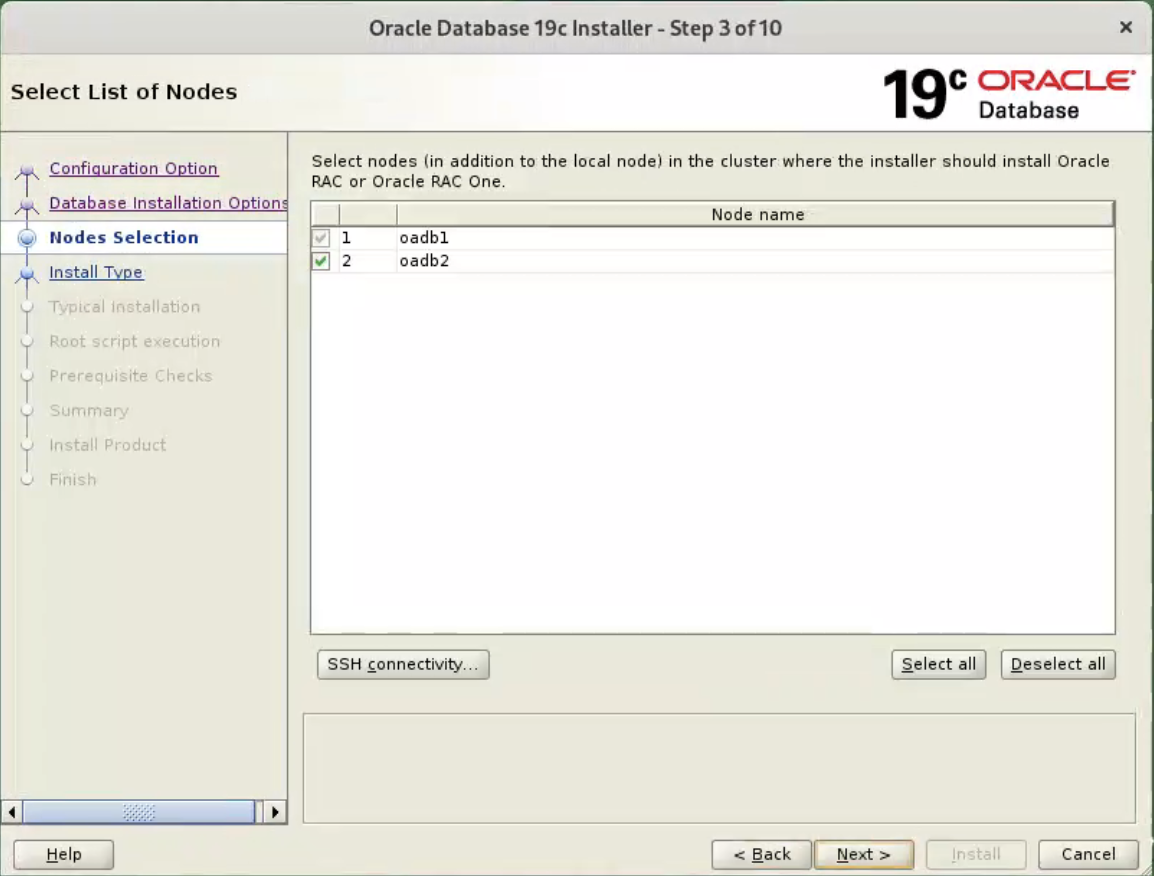 Click the “Test” to make sure nodes connection without password.
Click the “Test” to make sure nodes connection without password. 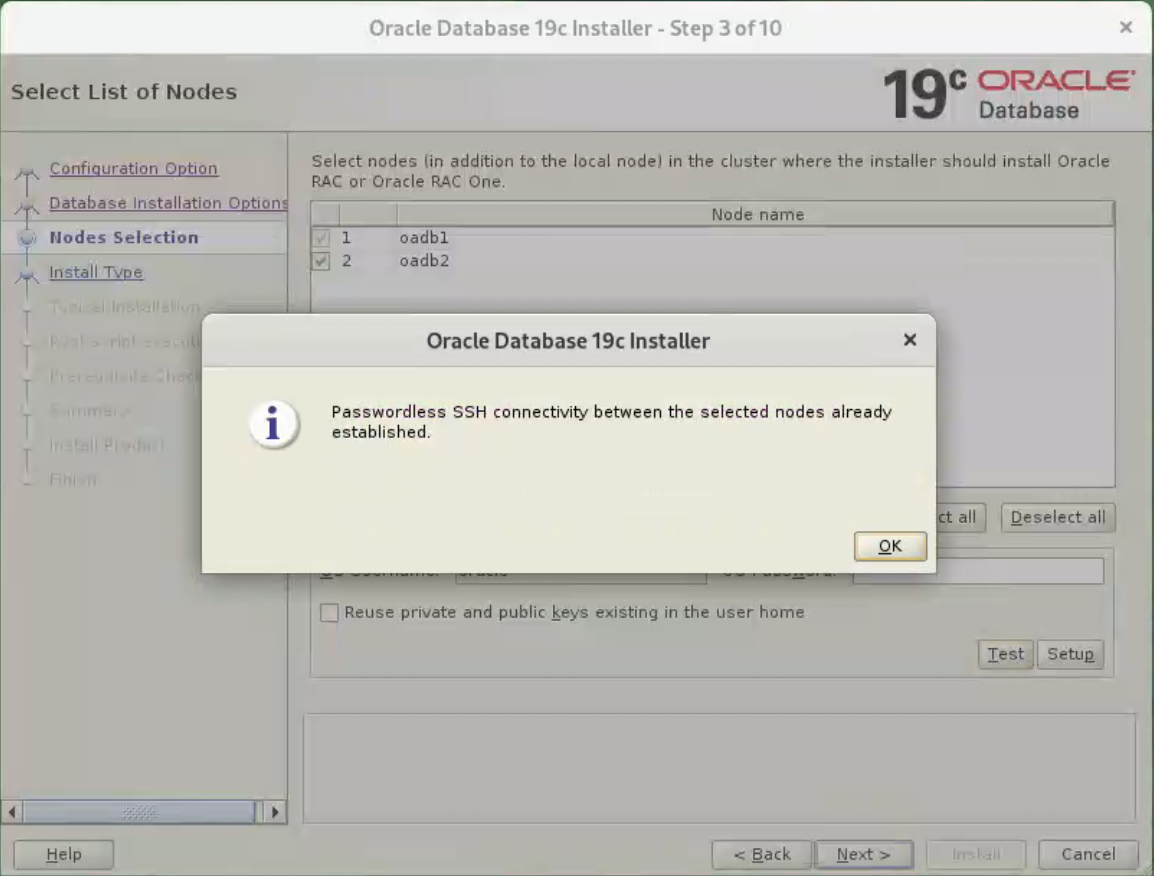
Select the “Enterprise Edition” option, then click the “Next” button. 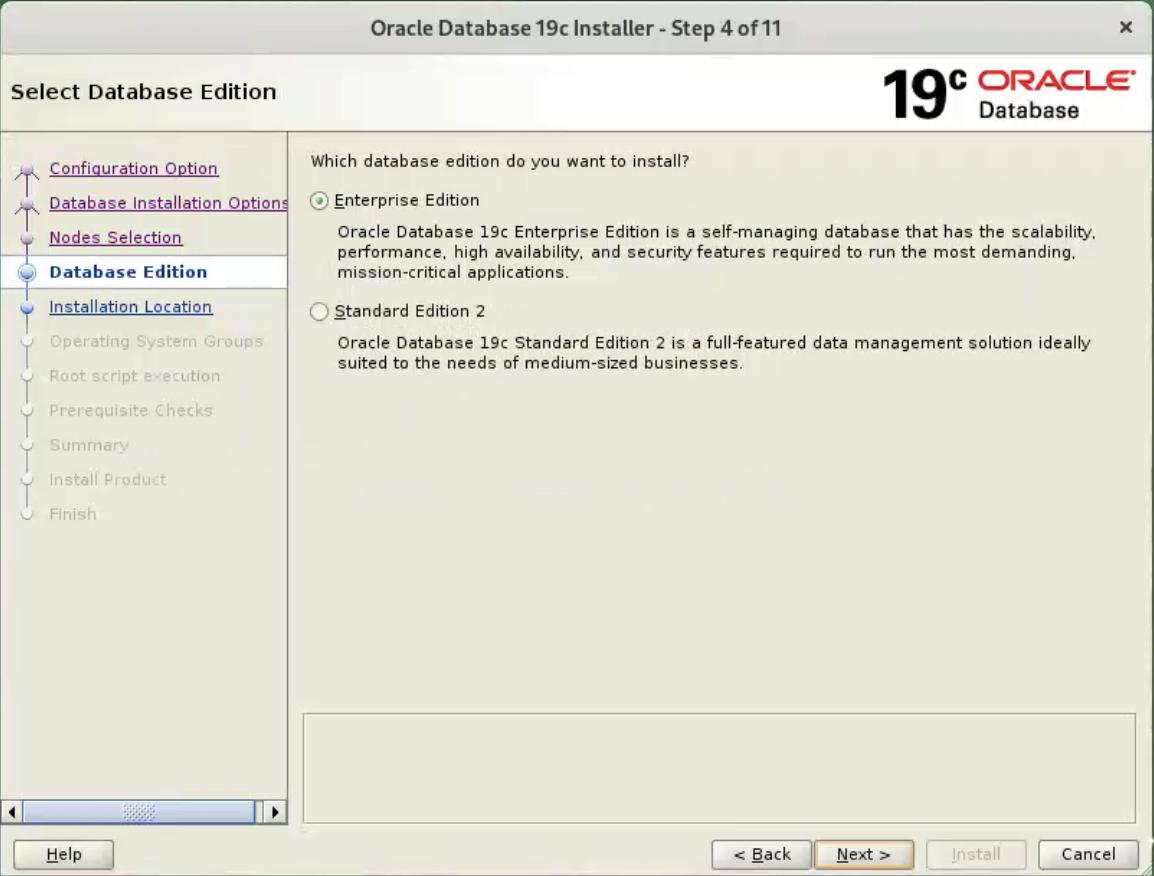 Enter “/u01/app/oracle” as the Oracle base, then click the “Next” button.
Enter “/u01/app/oracle” as the Oracle base, then click the “Next” button. 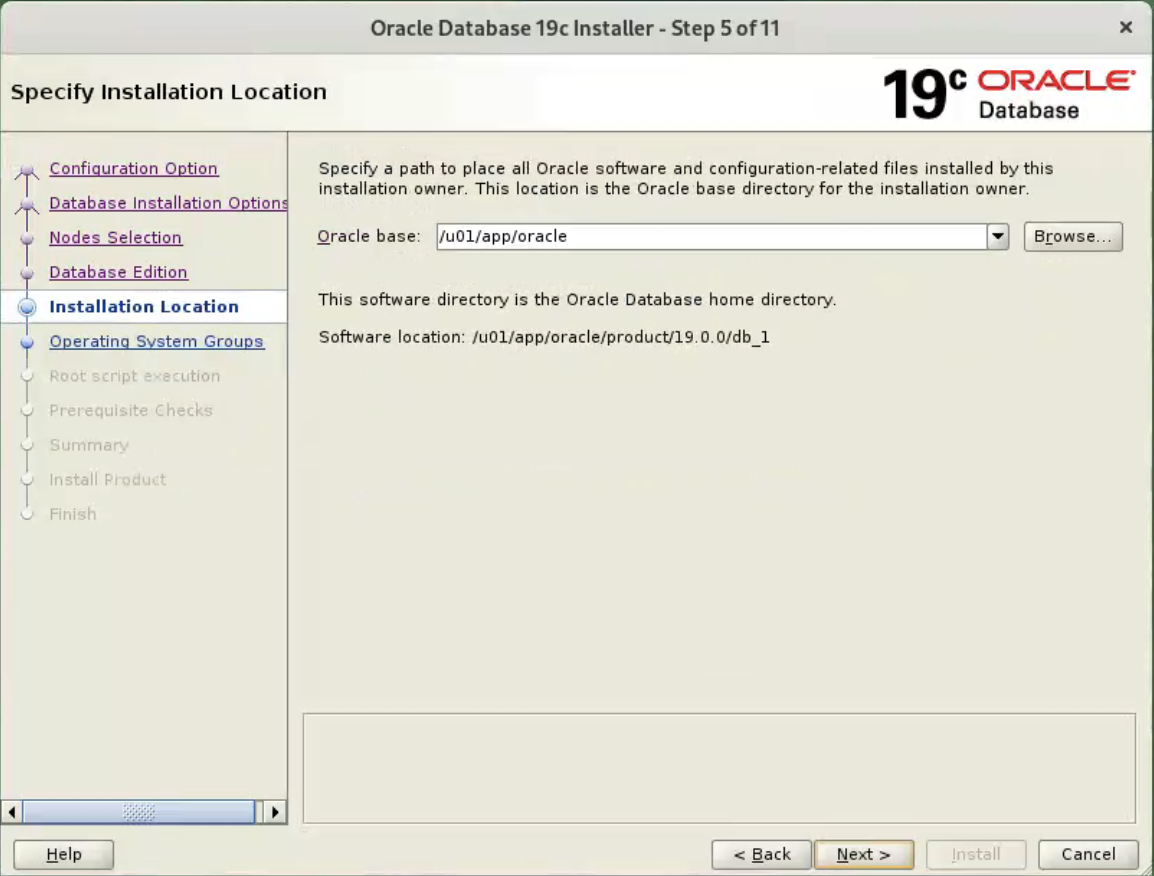 Select the desired operating system groups, then click the “Next” button. In this case we are only using the “dba” group.
Select the desired operating system groups, then click the “Next” button. In this case we are only using the “dba” group. 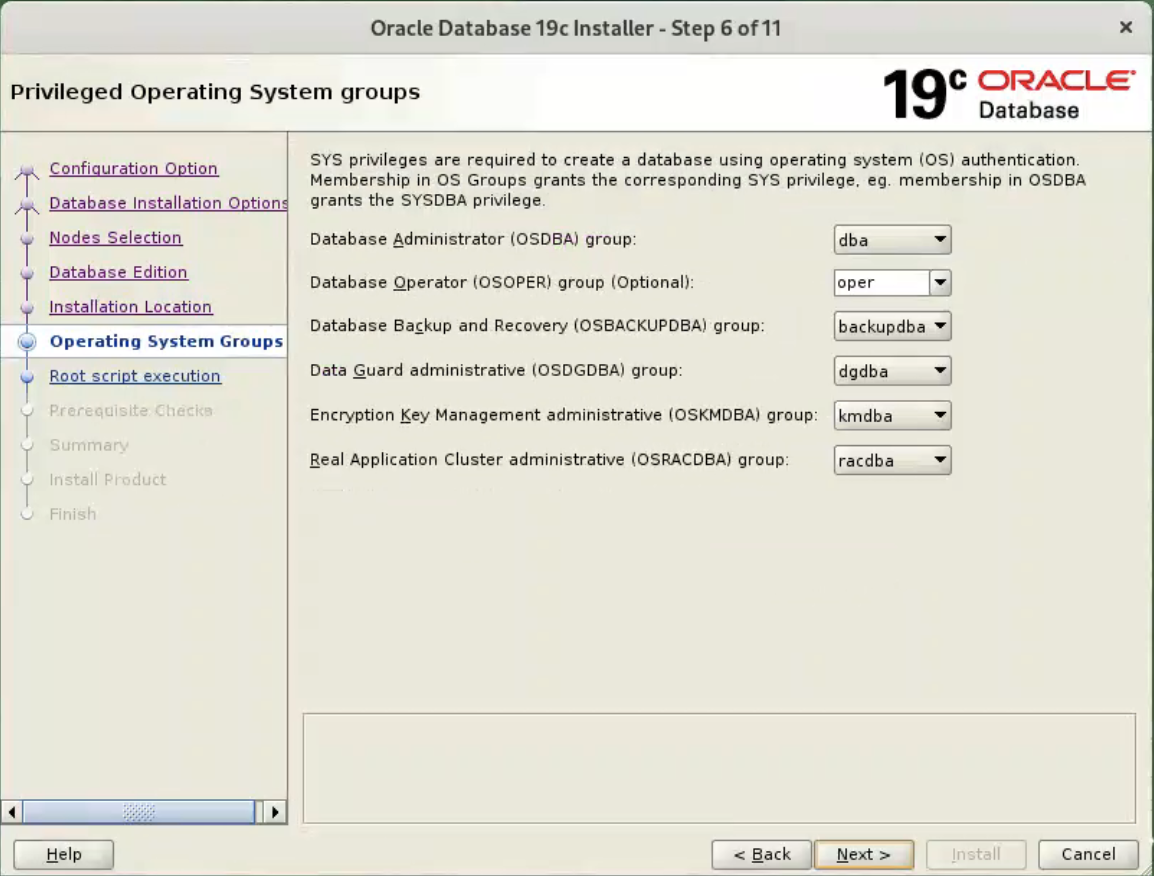 Accept the default options, and click “Next” button.
Accept the default options, and click “Next” button.  Wait for the prerequisite check to complete. If there are any problems either click the “Fix & Check Again” button, or check the “Ignore All” checkbox and click the “Next” button.
Wait for the prerequisite check to complete. If there are any problems either click the “Fix & Check Again” button, or check the “Ignore All” checkbox and click the “Next” button. 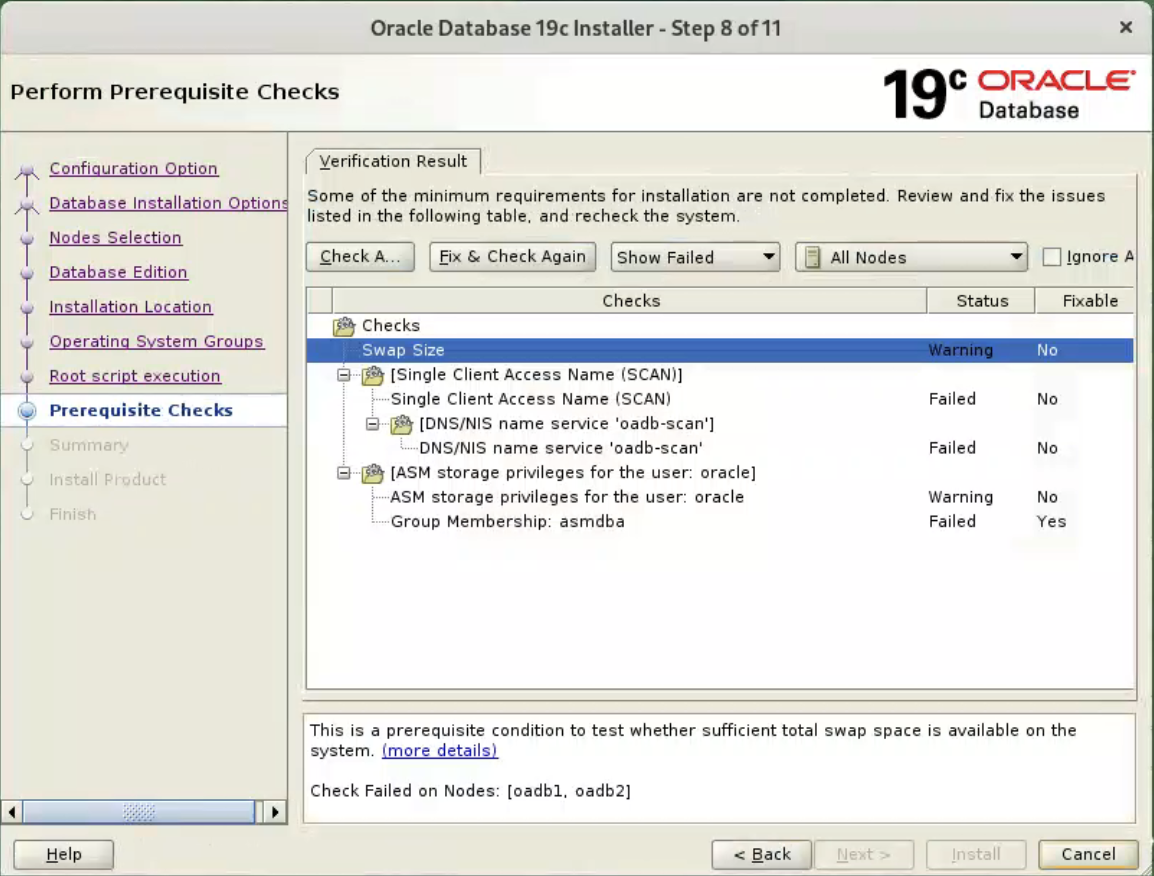
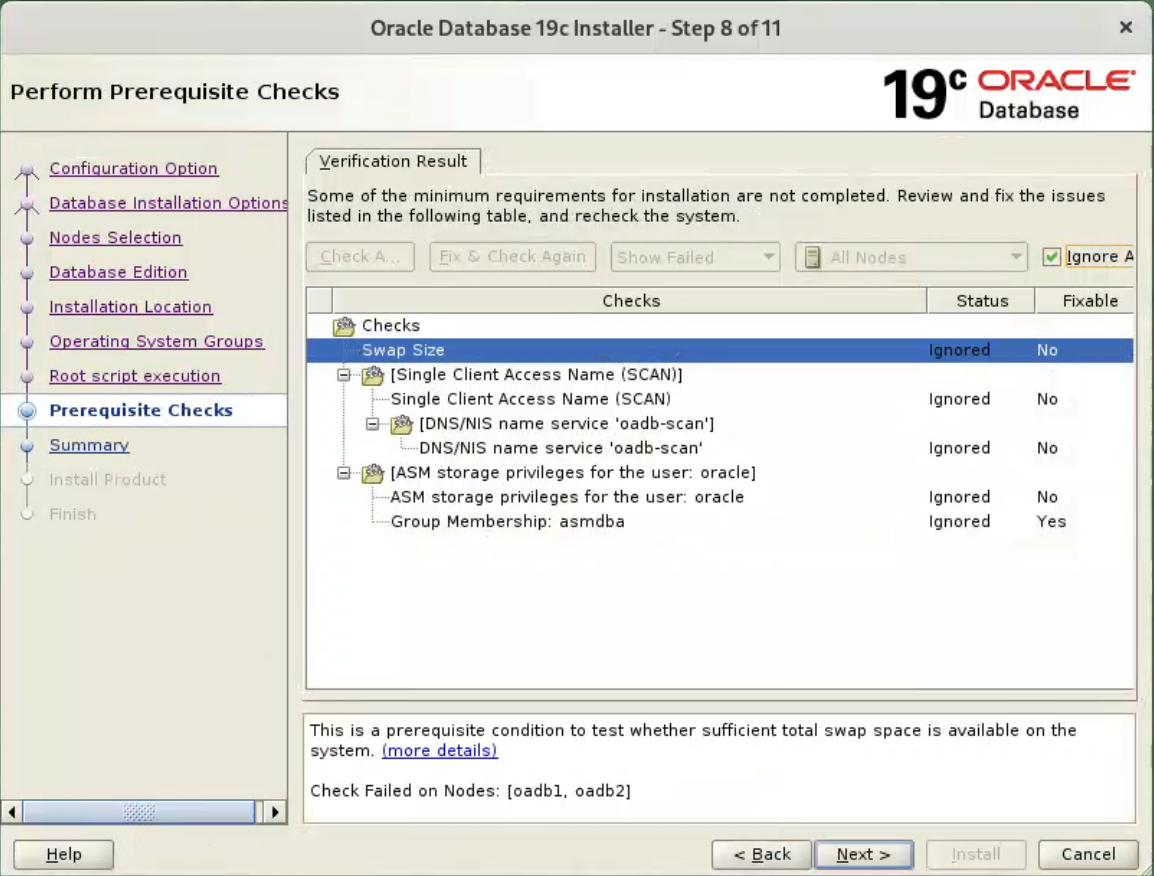 If you are happy with the summary information, click the “Install” button.
If you are happy with the summary information, click the “Install” button. 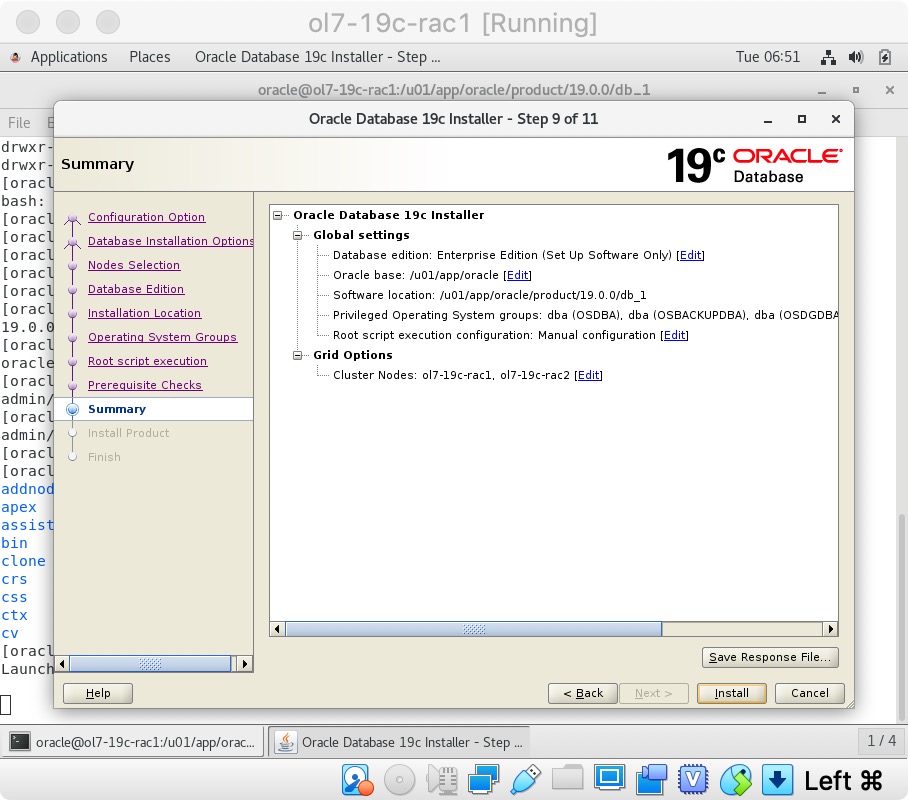 Wait while the installation takes place.
Wait while the installation takes place. 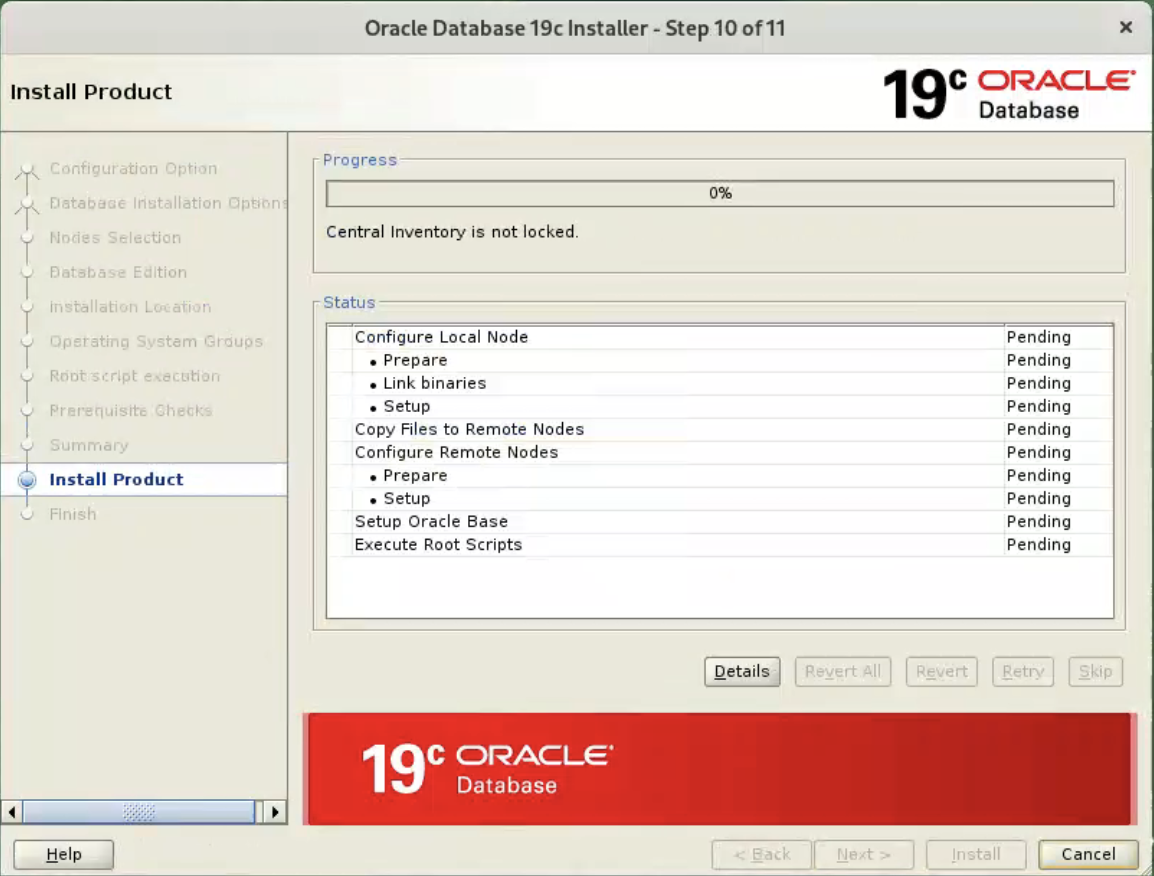 When prompted, run the configuration script on each node. When the scripts have been run on each node, click the “OK” button.
When prompted, run the configuration script on each node. When the scripts have been run on each node, click the “OK” button. 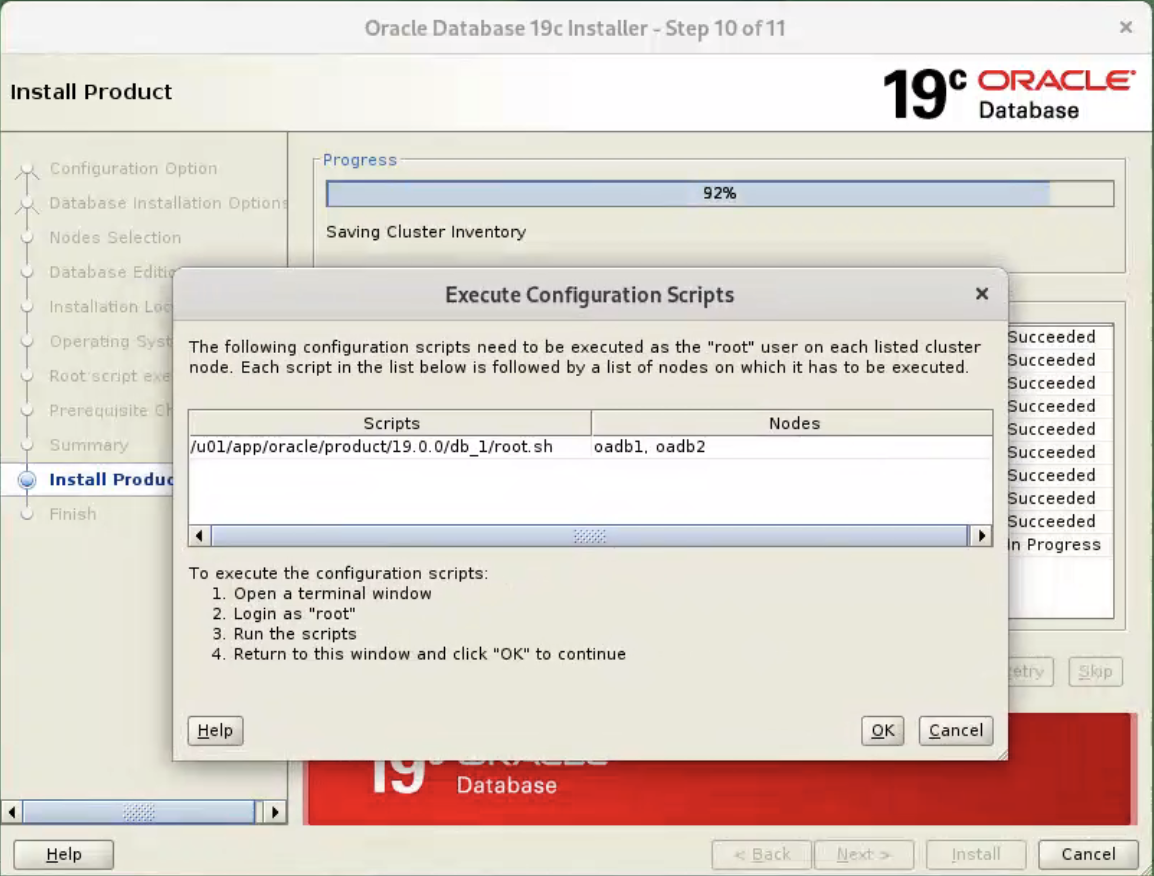
Click the “Close” button to exit the installer. 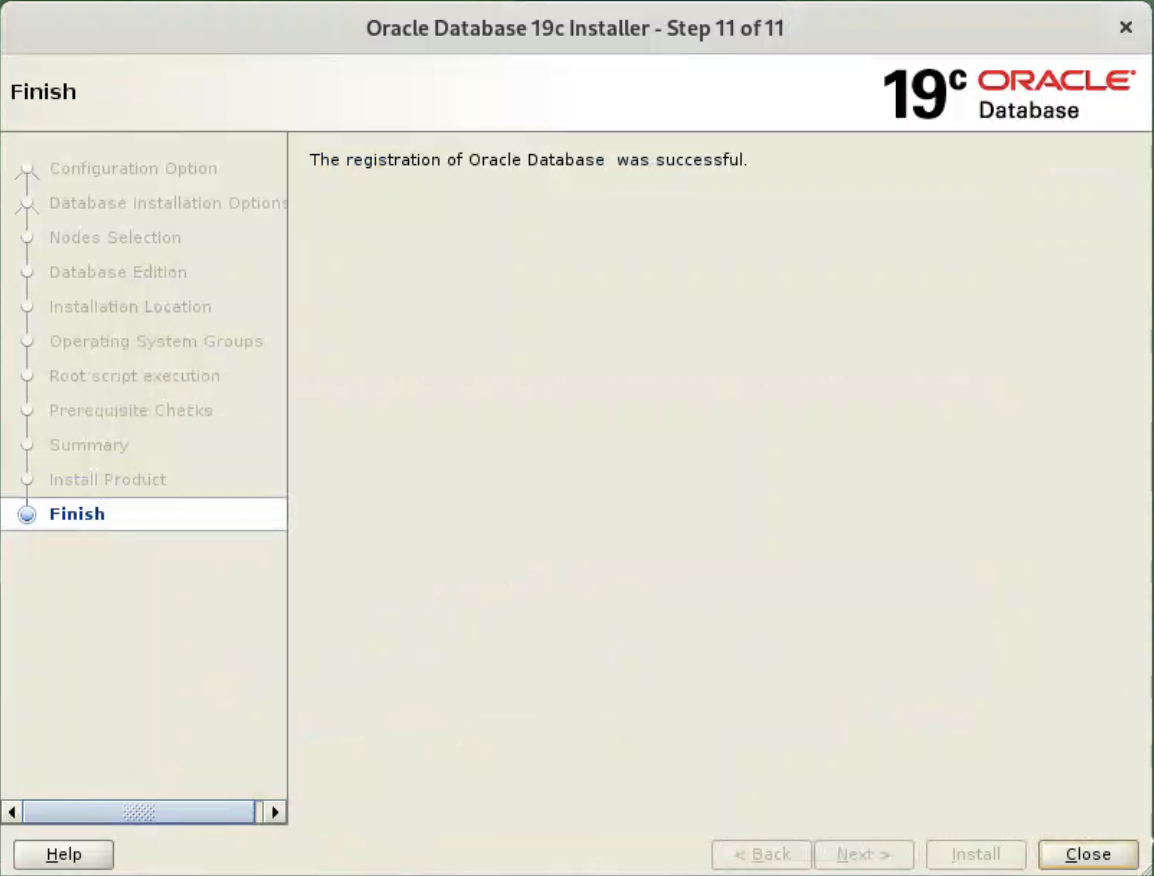
Check patches installed on database home.
oracle@oadb1[cdb1]:/home/oracle$ opatch lspatches
35926646;OJVM RELEASE UPDATE: 19.22.0.0.240116 (35926646)
35967489;OCW RELEASE UPDATE 19.22.0.0.0 (35967489)
35943157;Database Release Update : 19.22.0.0.240116 (35943157)
OPatch succeeded.
oracle@oadb1[cdb1]:/home/oracle$
oracle@oadb2[cdb2]:/home/oracle$ opatch lspatches
35926646;OJVM RELEASE UPDATE: 19.22.0.0.240116 (35926646)
35967489;OCW RELEASE UPDATE 19.22.0.0.0 (35967489)
35943157;Database Release Update : 19.22.0.0.240116 (35943157)
OPatch succeeded.
Log in as the “grid” user and add the following lines at the end of the “/home/grud/.bash_profile” file.
# Oracle Settings
umask 022
export TMP=/tmp
export TMPDIR=$TMP
export ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle
export GRID_HOME=/u01/app/19.0.0/grid
export DB_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/19.0.0/db_1
export ORACLE_HOME=$GRID_HOME
export ORACLE_SID=+ASM1
export ORACLE_TERM=xterm
export BASE_PATH=/usr/sbin:$PATH
export PATH=.:$ORACLE_HOME/OPatch:$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$BASE_PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib:/lib:/usr/lib
export CLASSPATH=$ORACLE_HOME/JRE:$ORACLE_HOME/jlib:$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/jlib
#print ' '
#print '$ORACLE_SID: '$ORACLE_SID
#print '$ORACLE_HOME: '$ORACLE_HOME
#print ' '
# Set up the shell variables
set -o vi
stty erase ^h
export PS1=`whoami`@`hostname`\['$ORACLE_SID'\]':$PWD$ '
# Alias
alias oh="cd $ORACLE_HOME"
Log in as the “oracle” user and add the following lines at the end of the “/home/oracle/.bash_profile” file.
# Oracle Settings
umask 022
export TMP=/tmp
export TMPDIR=$TMP
export ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle
export GRID_HOME=/u01/app/19.0.0/grid
export DB_HOME=$ORACLE_BASE/product/19.0.0/db_1
export ORACLE_HOME=$DB_HOME
export ORACLE_SID=rac1
export ORACLE_PDB_SID=pdb1
export ORACLE_TERM=xterm
export BASE_PATH=/usr/sbin:$PATH
export PATH=.:$ORACLE_HOME/OPatch:$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$BASE_PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/lib:/lib:/usr/lib
export CLASSPATH=$ORACLE_HOME/JRE:$ORACLE_HOME/jlib:$ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/jlib
printf '\n$ORACLE_SID: '$ORACLE_SID
printf '\n$ORACLE_PDB_SID: '$ORACLE_PDB_SID
printf '\n$ORACLE_HOME: '$ORACLE_HOME
printf '\n\n'
# Set up the shell variables
set -o vi
stty erase ^h
export PS1=`whoami`@`hostname`\['$ORACLE_SID'\]':$PWD$ '
# Alias
alias ss="sqlplus / as sysdba"
alias oh="cd $ORACLE_HOME"
alias alert='cd /u01/app/oracle/diag/rdbms/rac/rac1/trace'
Shutdown both VMs and take snapshots. Remember to make a fresh zip of the ASM disks on the host machine, which you will need to restore if you revert to the post-db snapshots.
$ cd /u04/VirtualBox/ol9-19c-rac
$ zip PostDB.zip *.vdi
Create a Database
Make sure the “ol9-19c-rac1” and “ol9-19c-rac2” virtual machines are started, then login to “ol9-19c-rac1” as the oracle user and start the Database Creation Asistant (DBCA).
$ dbca
Select the “Create Database” option and click the “Next” button. 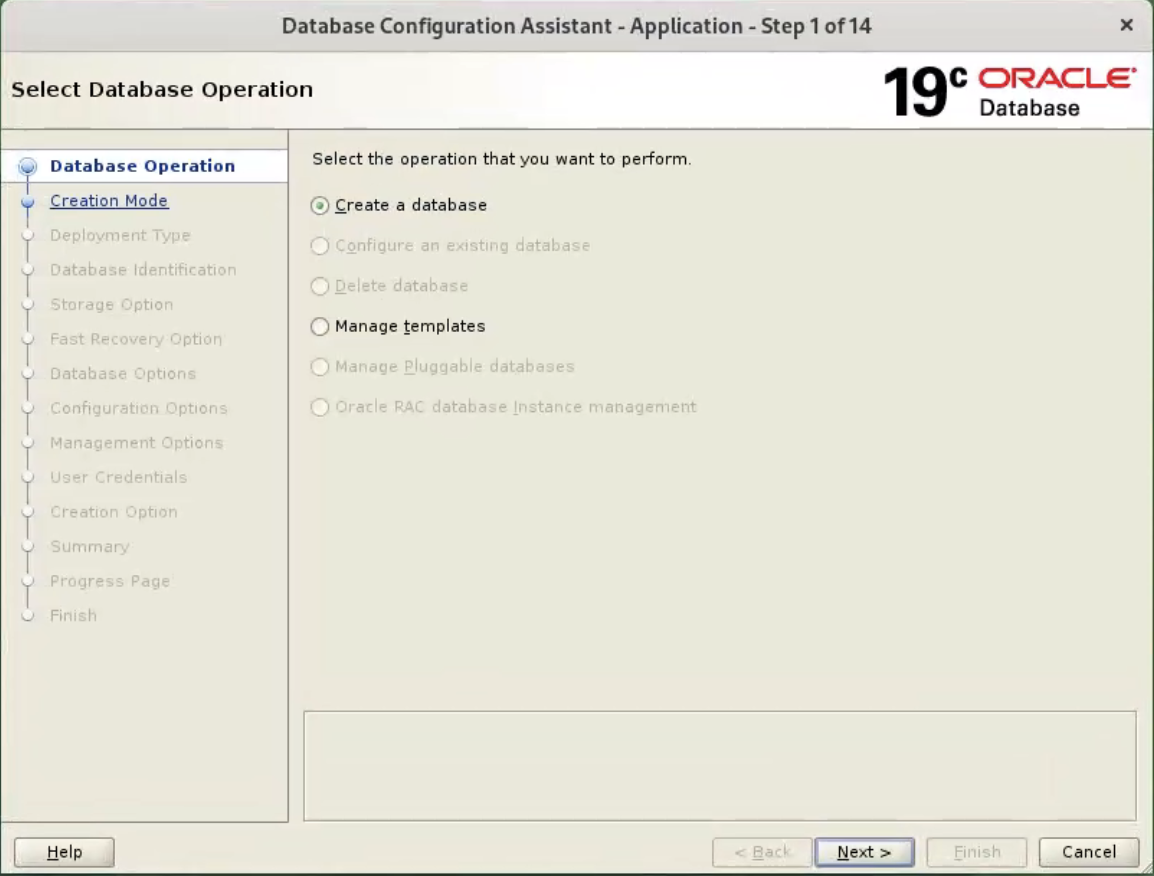 Select the “Advanced Mode” option. Click the “Next” button.
Select the “Advanced Mode” option. Click the “Next” button. 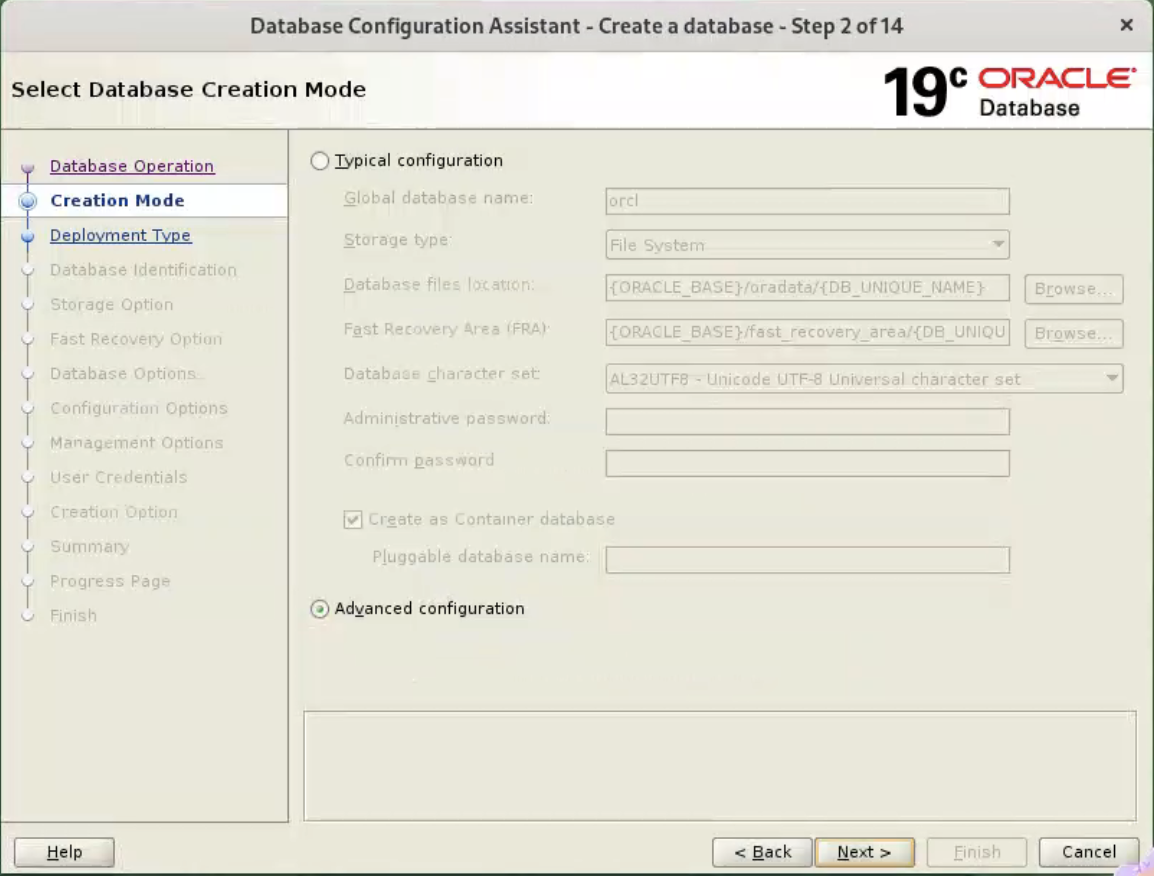 Check the “Custom Database” option and click the “Next” button.
Check the “Custom Database” option and click the “Next” button. 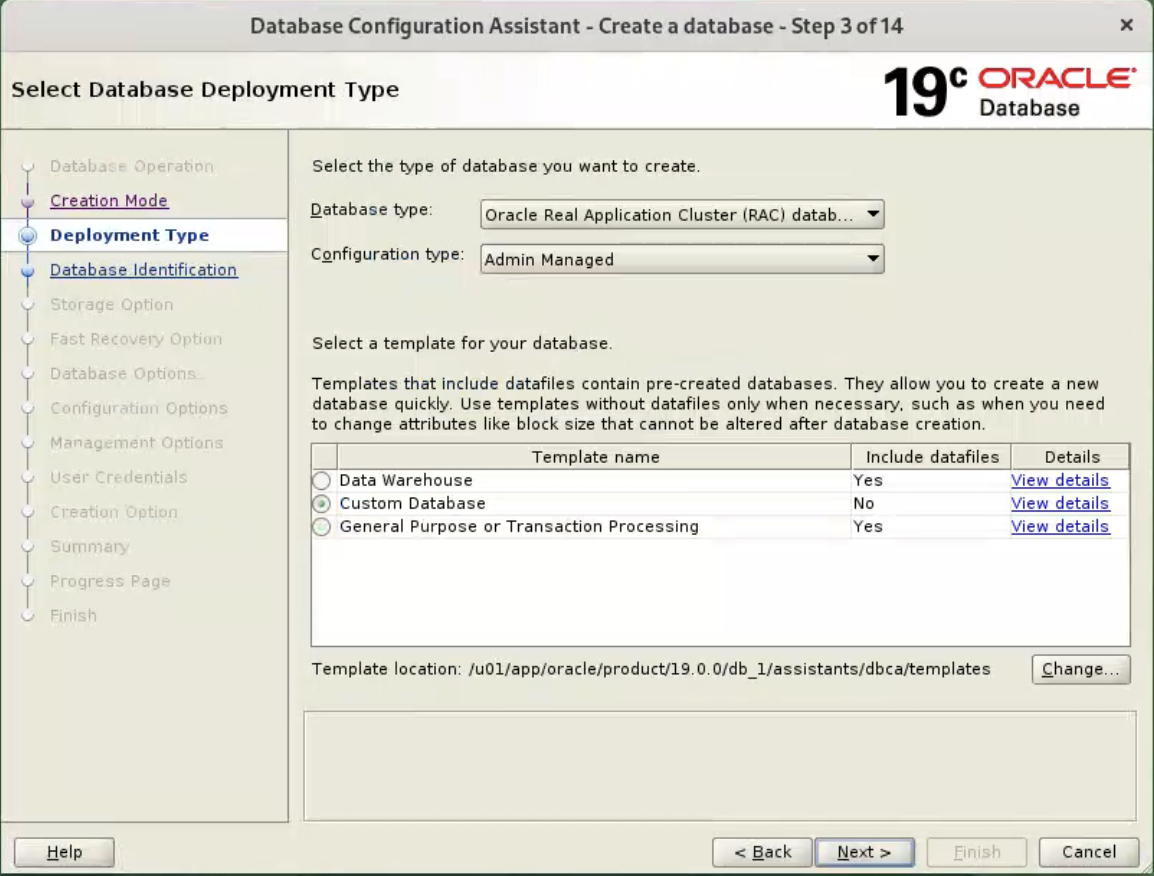 Make sure both nodes are selected, then click the “Next” button.
Make sure both nodes are selected, then click the “Next” button. 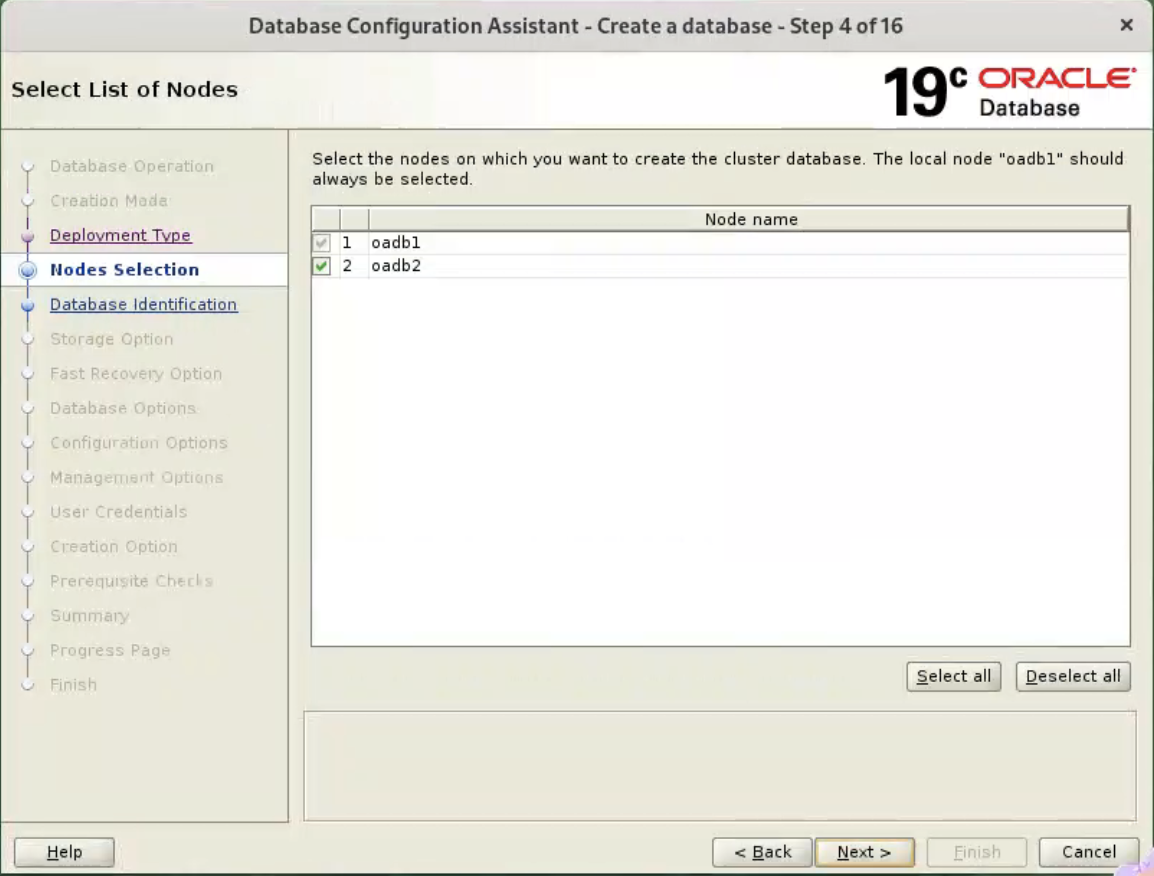 Enter the container database name (cdb), pluggable database name (pdb) and administrator password. Click the “Next” button.
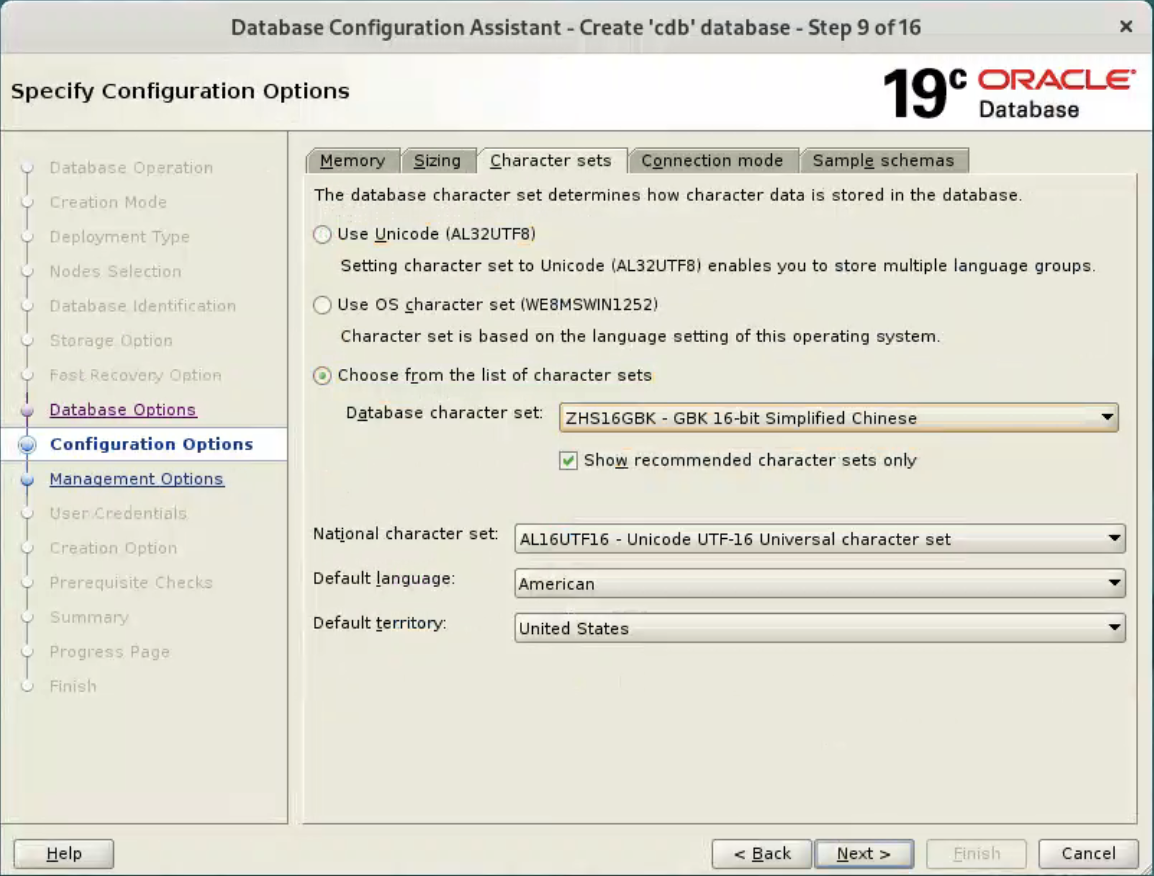
Enter the container database name (cdb), pluggable database name (pdb) and administrator password. Click the “Next” button. 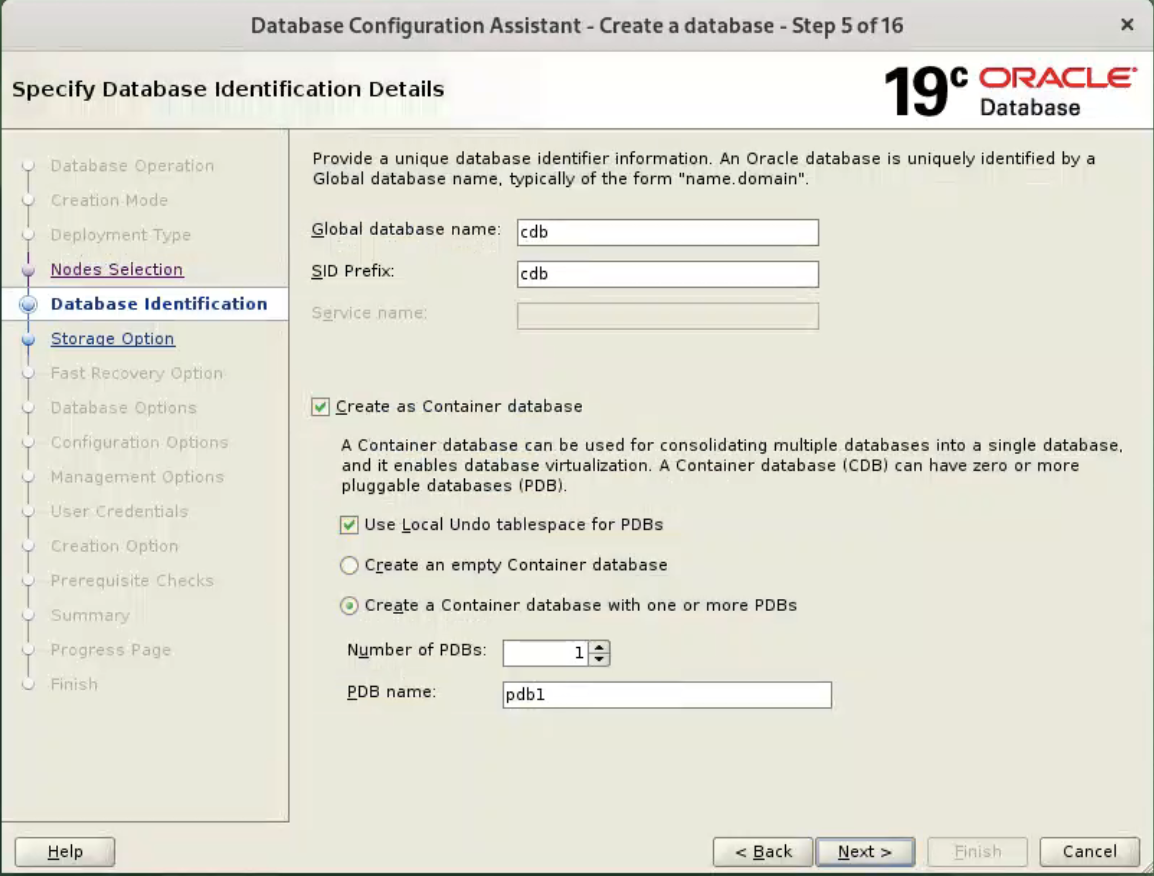 Accept the default values, and click “Next” button.
Accept the default values, and click “Next” button. 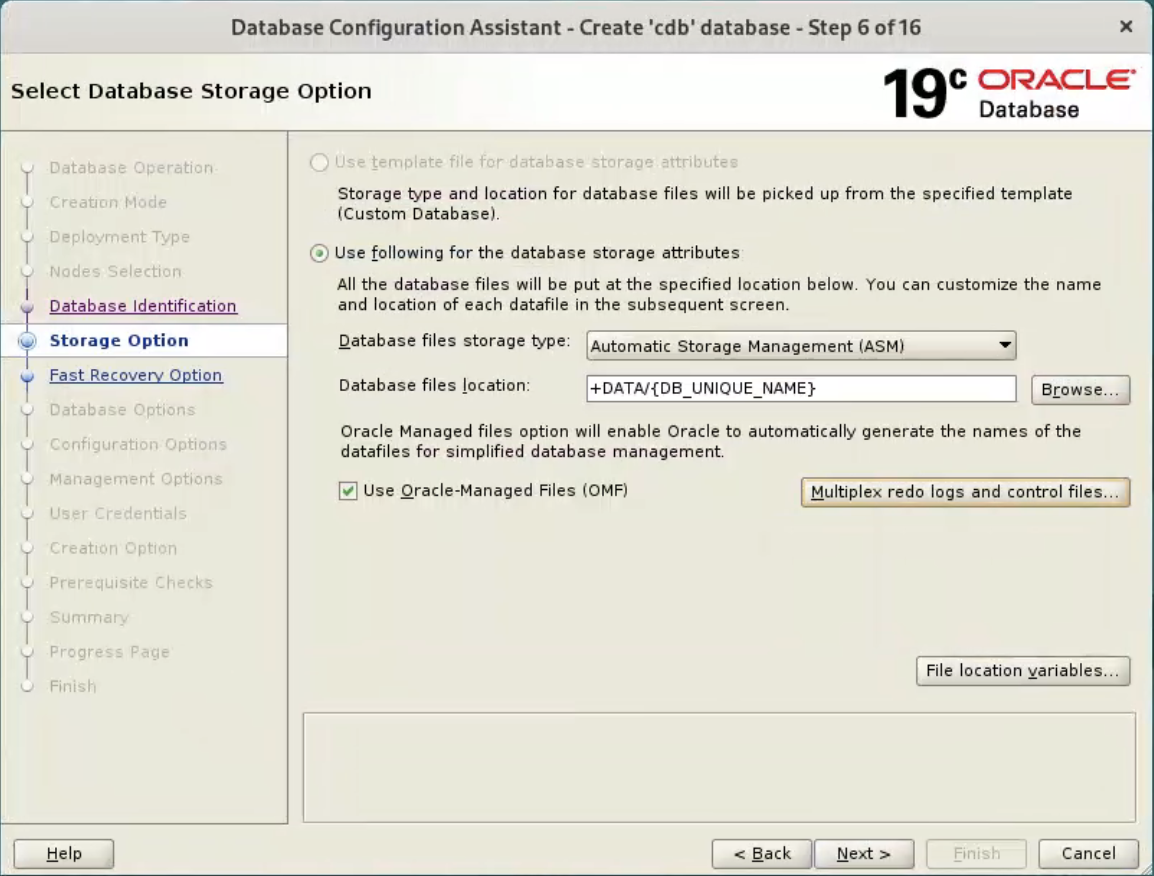 Accept the default values, and click “Next” button.
Accept the default values, and click “Next” button.  Or set your desired options.
Or set your desired options. 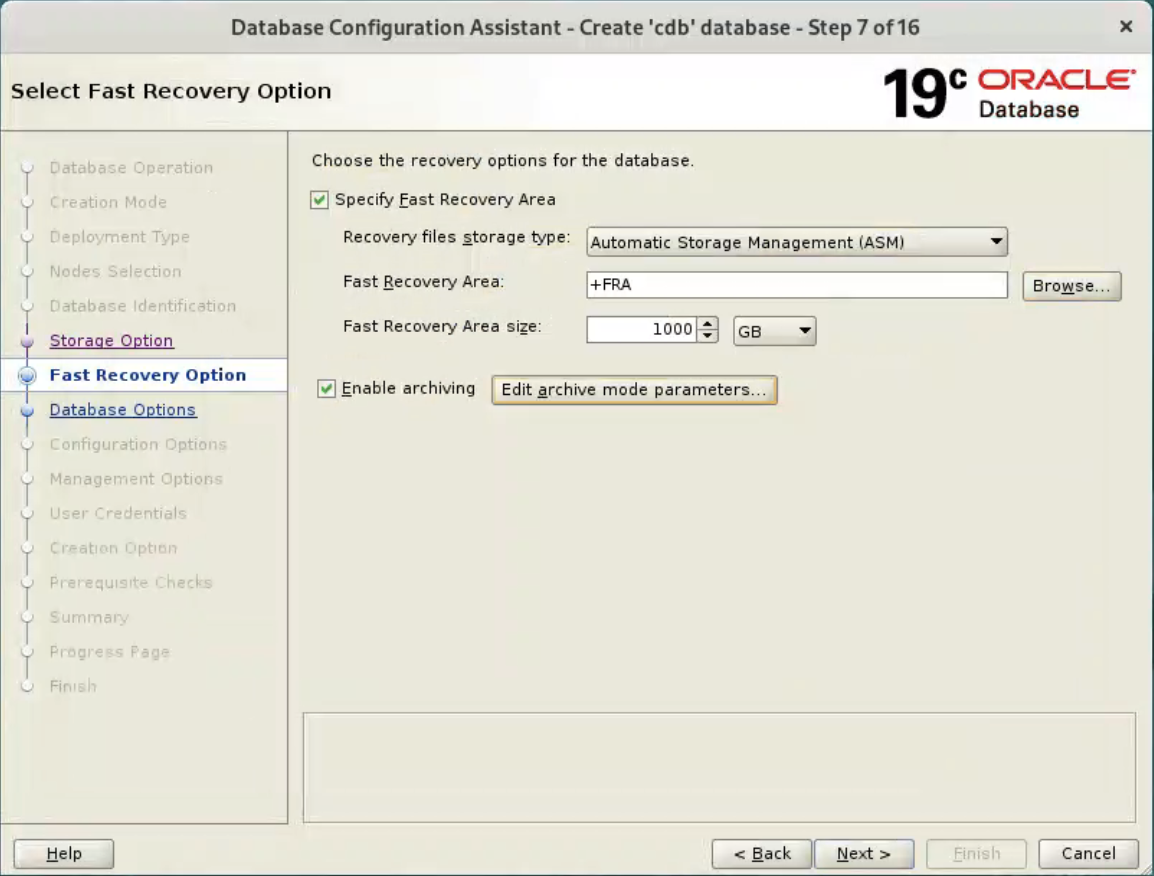
Accept the default values, and click “Next” button. 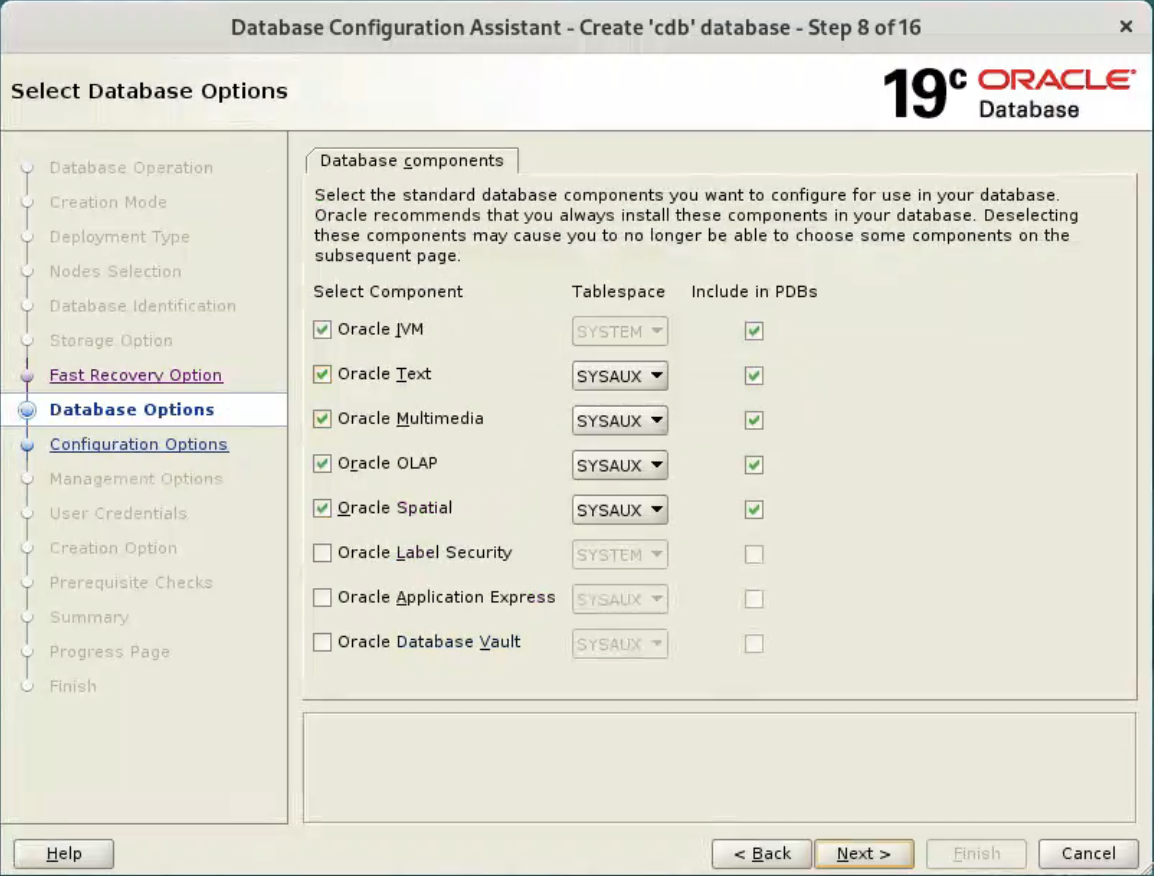 Accept the default values, and click “Next” button.
Accept the default values, and click “Next” button. 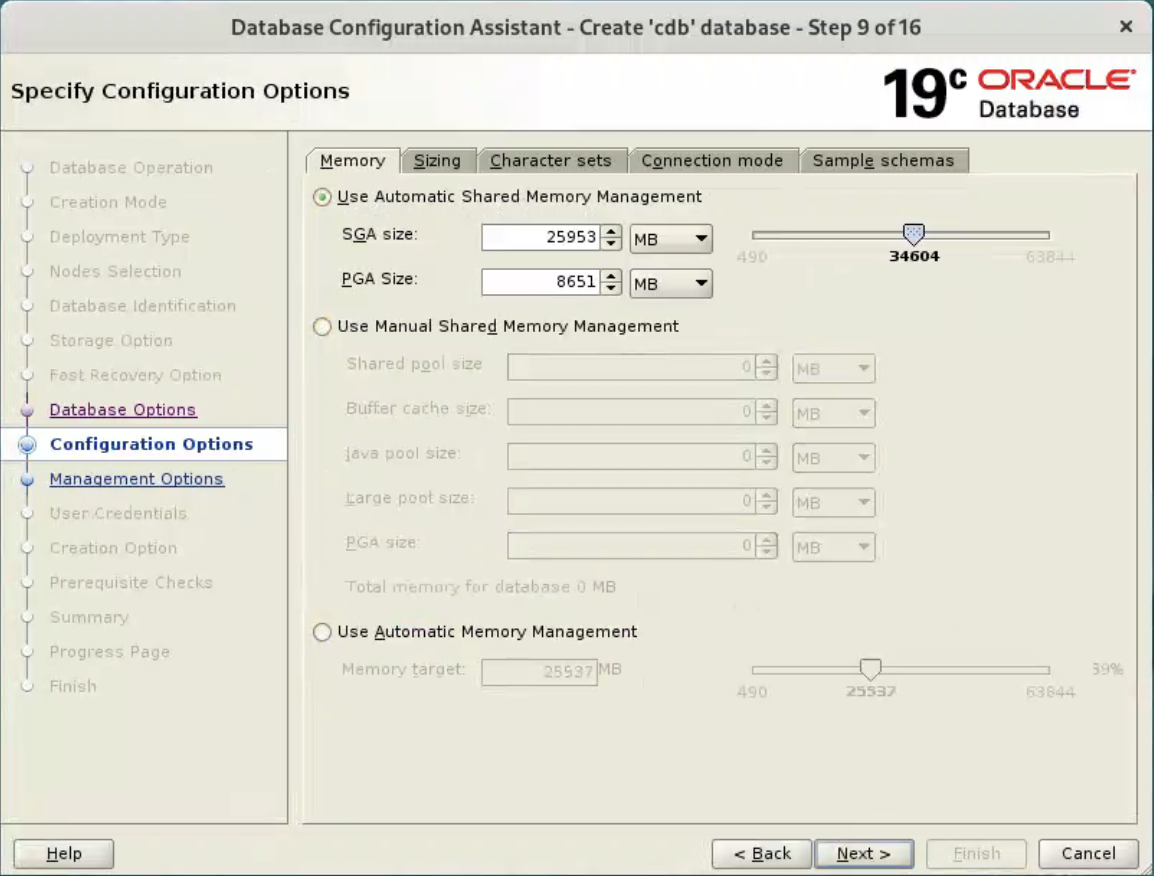
Deselect the CVU and EM options, and click “Next” button. 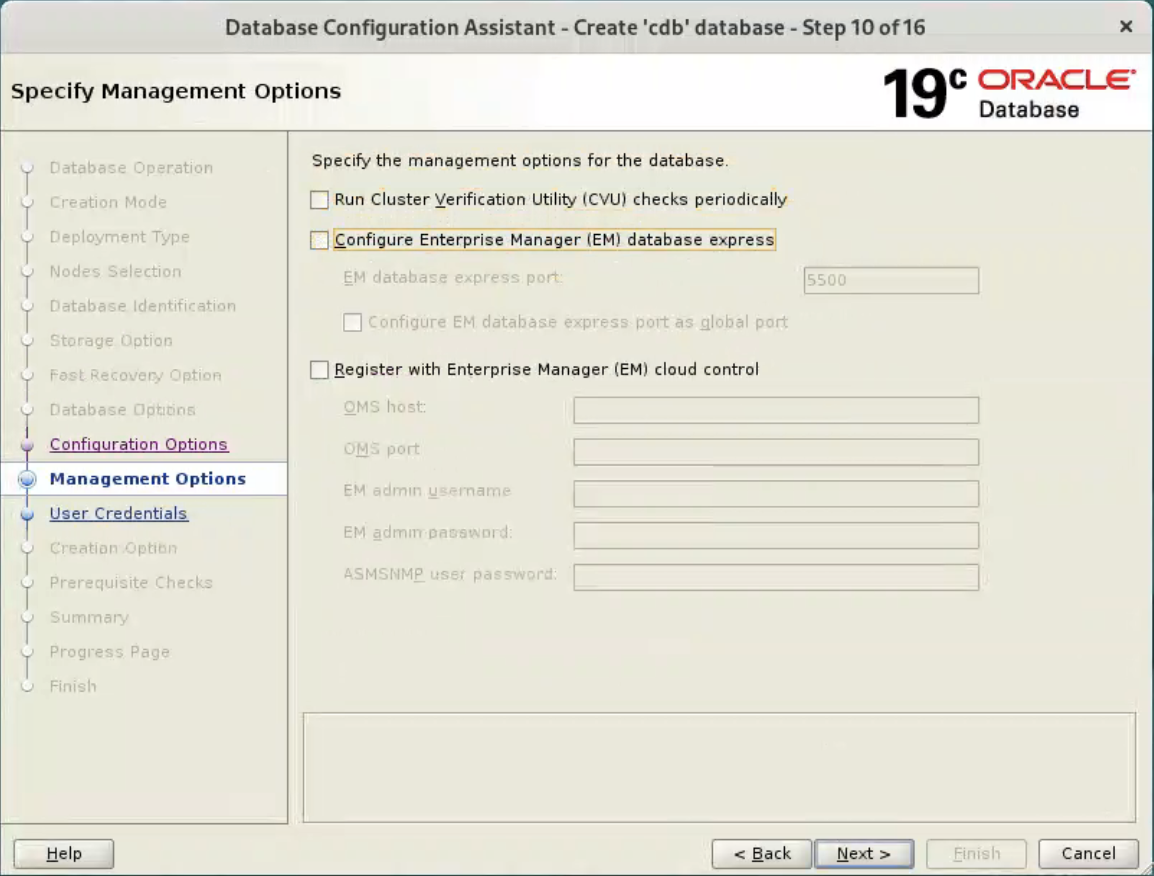 Enter dba password, and click “Next” button.
Enter dba password, and click “Next” button. 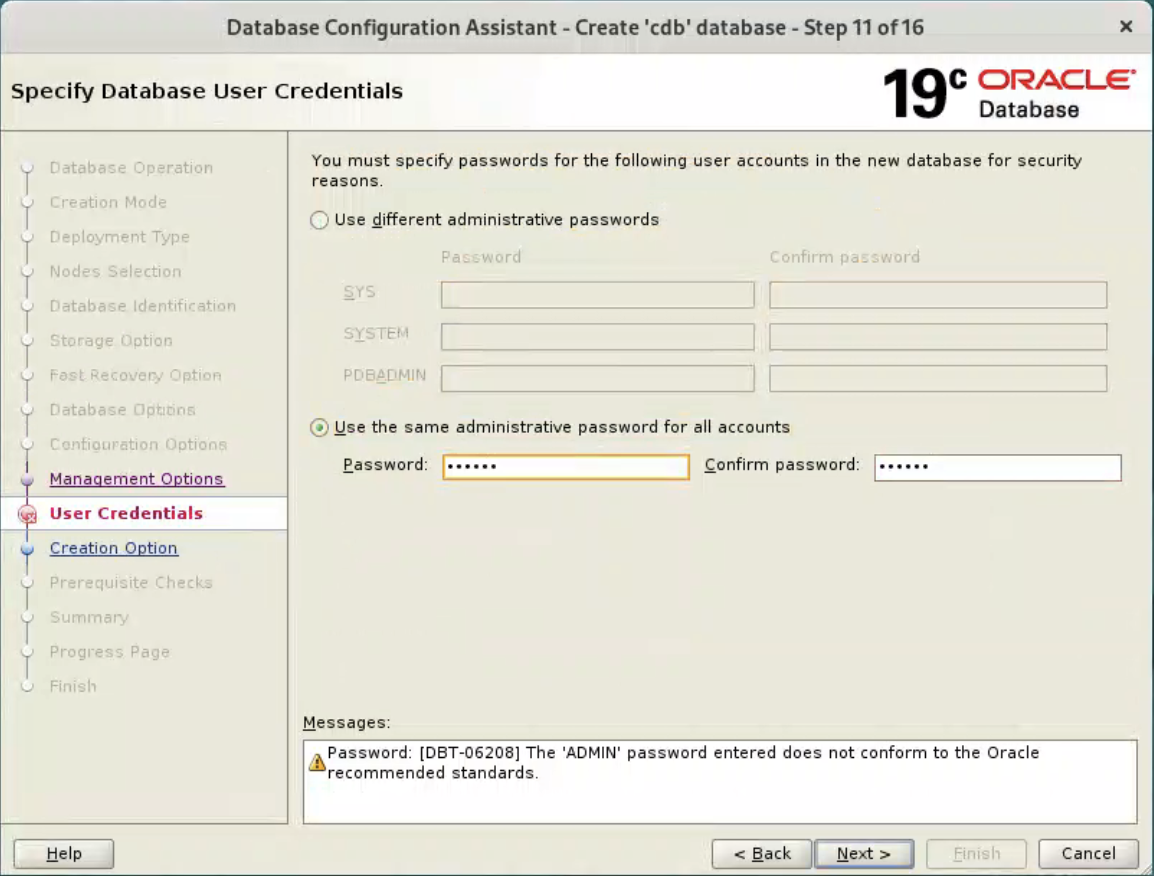
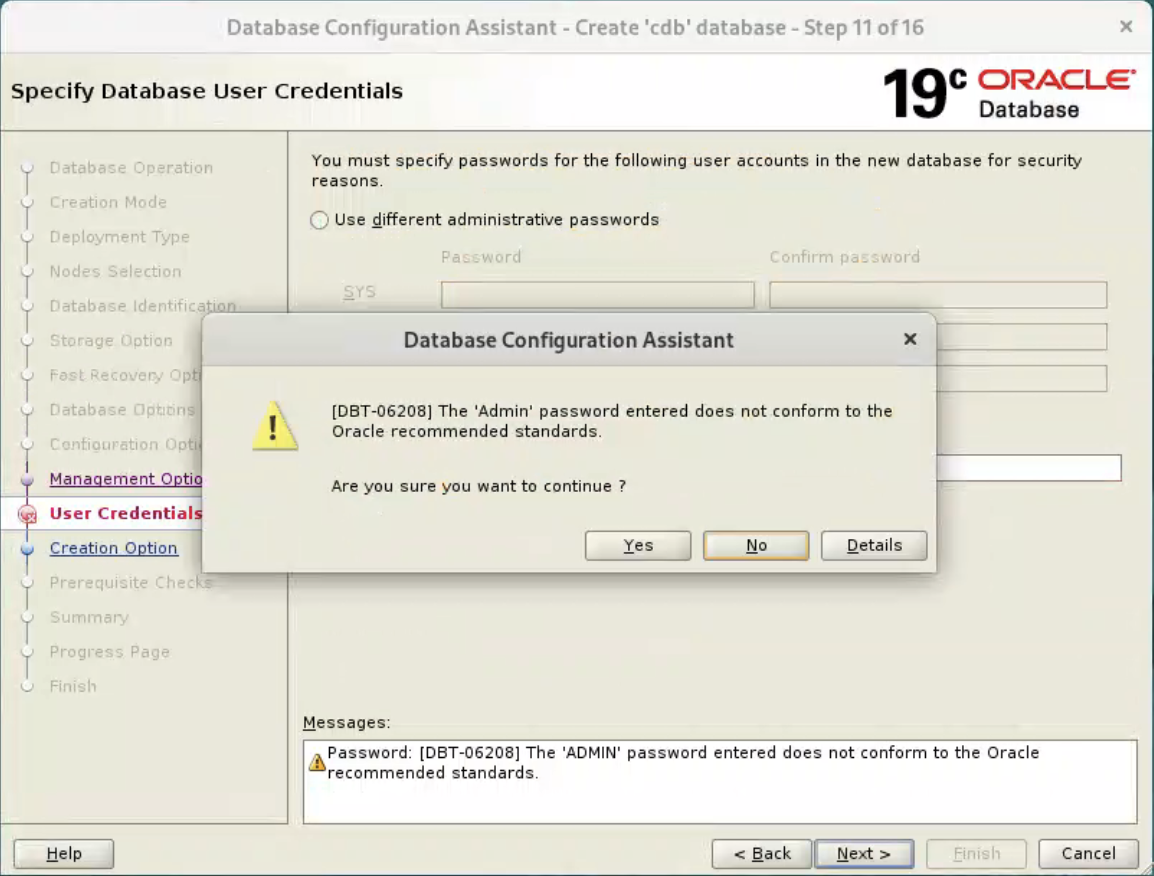
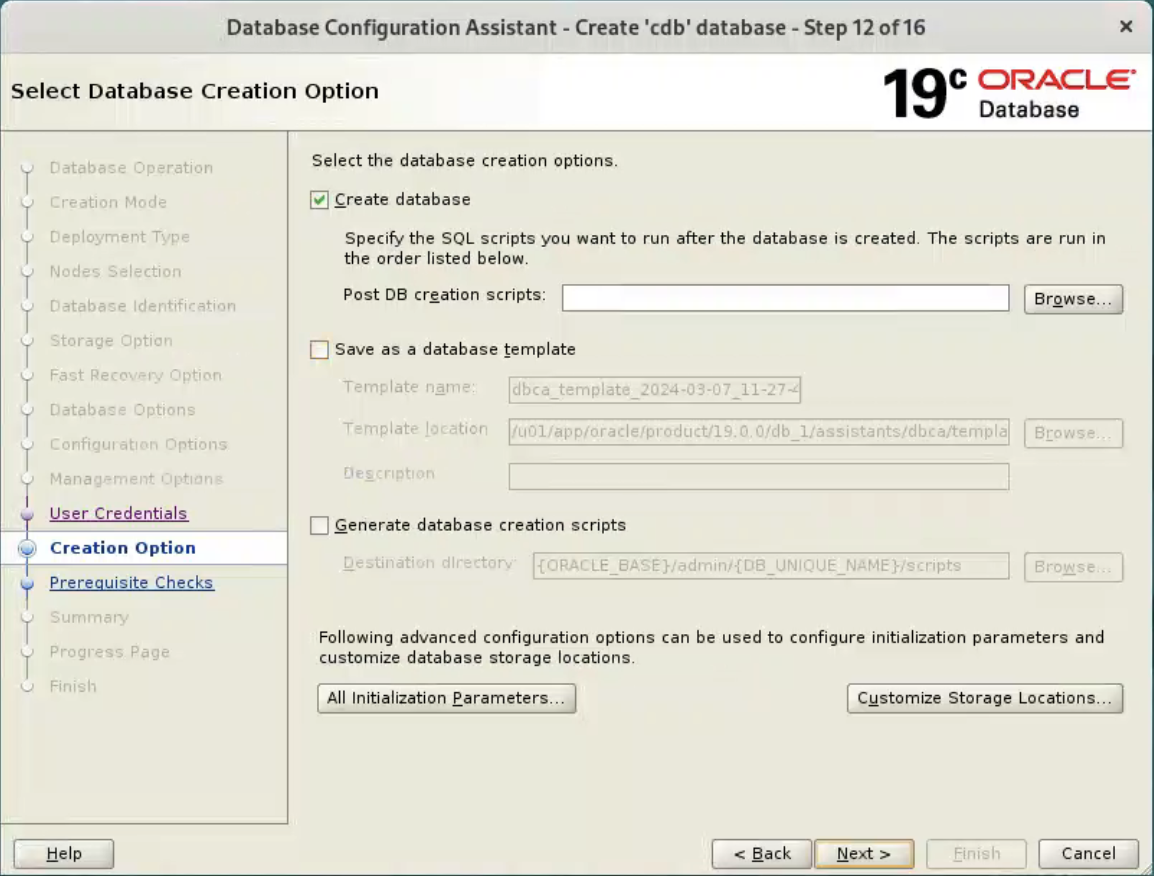
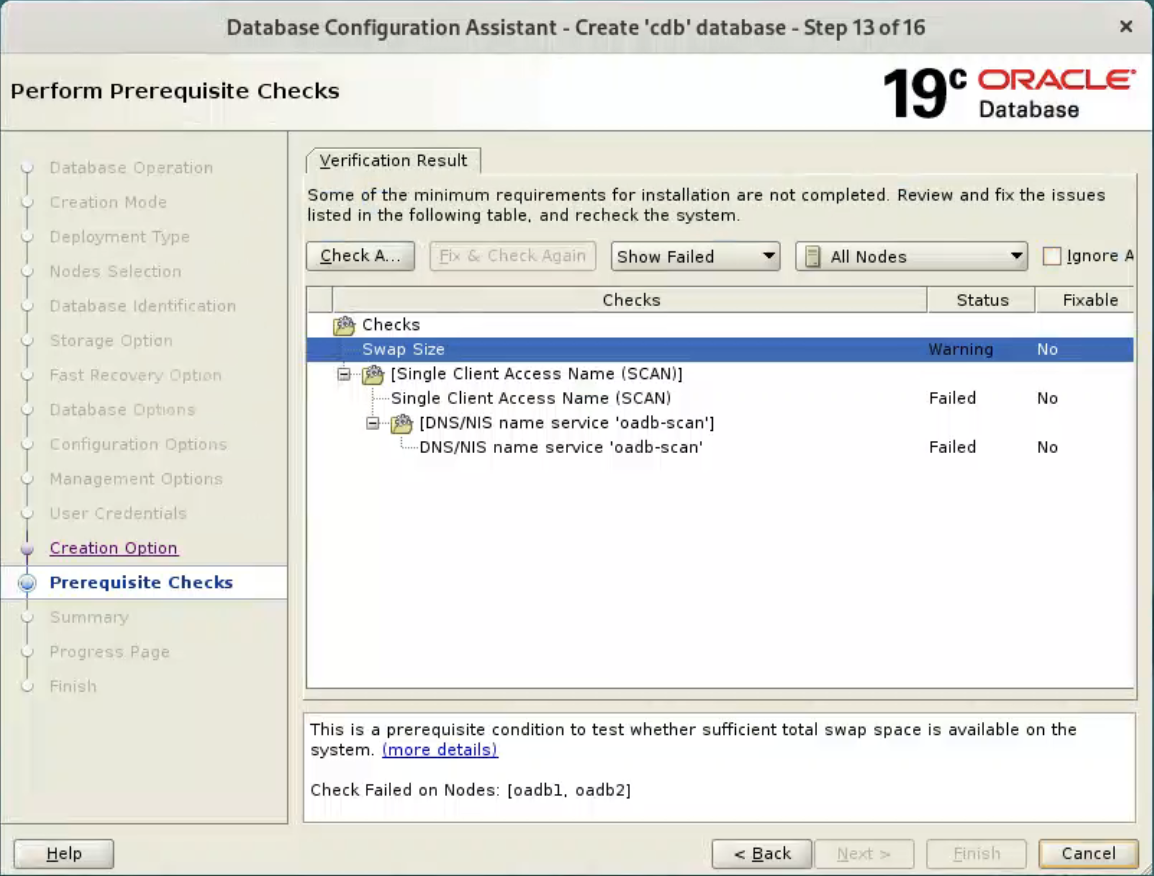
Select “Ignore All”, and click “Next” button. 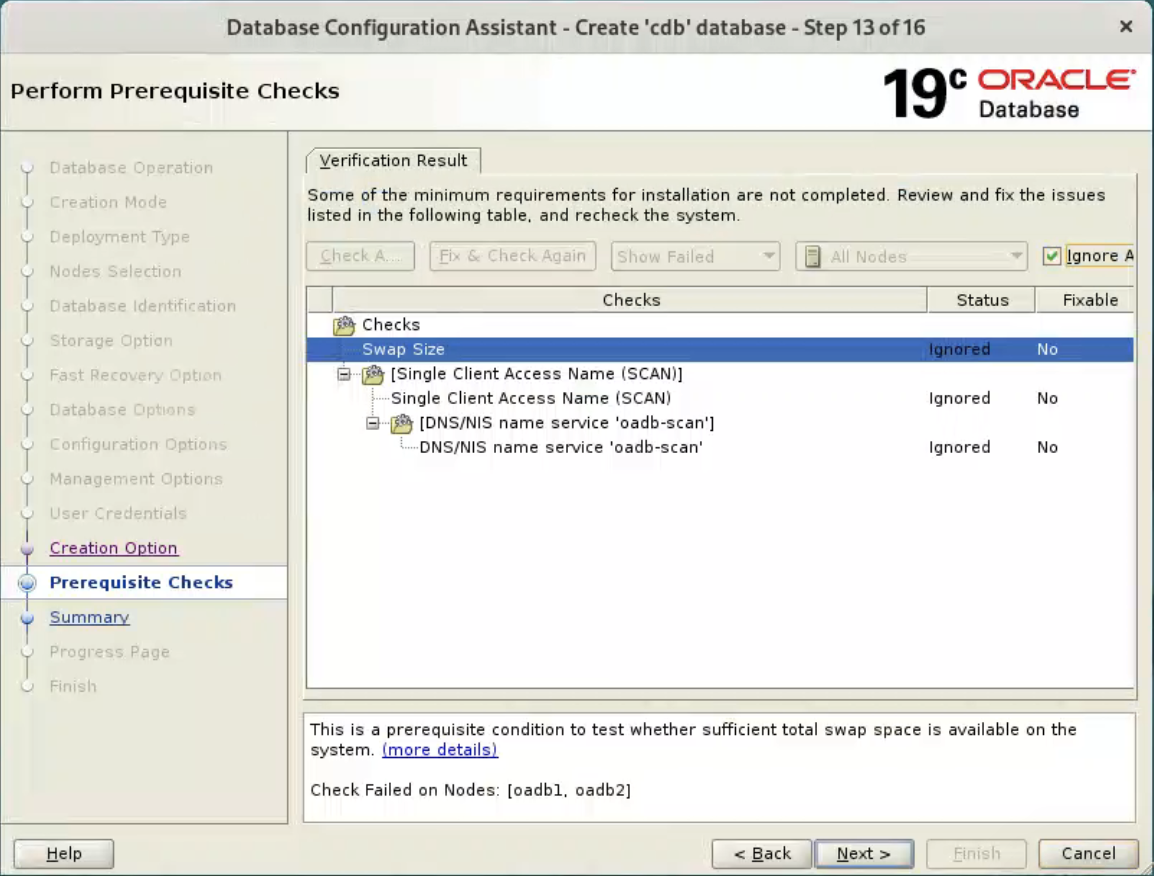 If you are happy with the summary information, click the “Finish” button.
If you are happy with the summary information, click the “Finish” button. 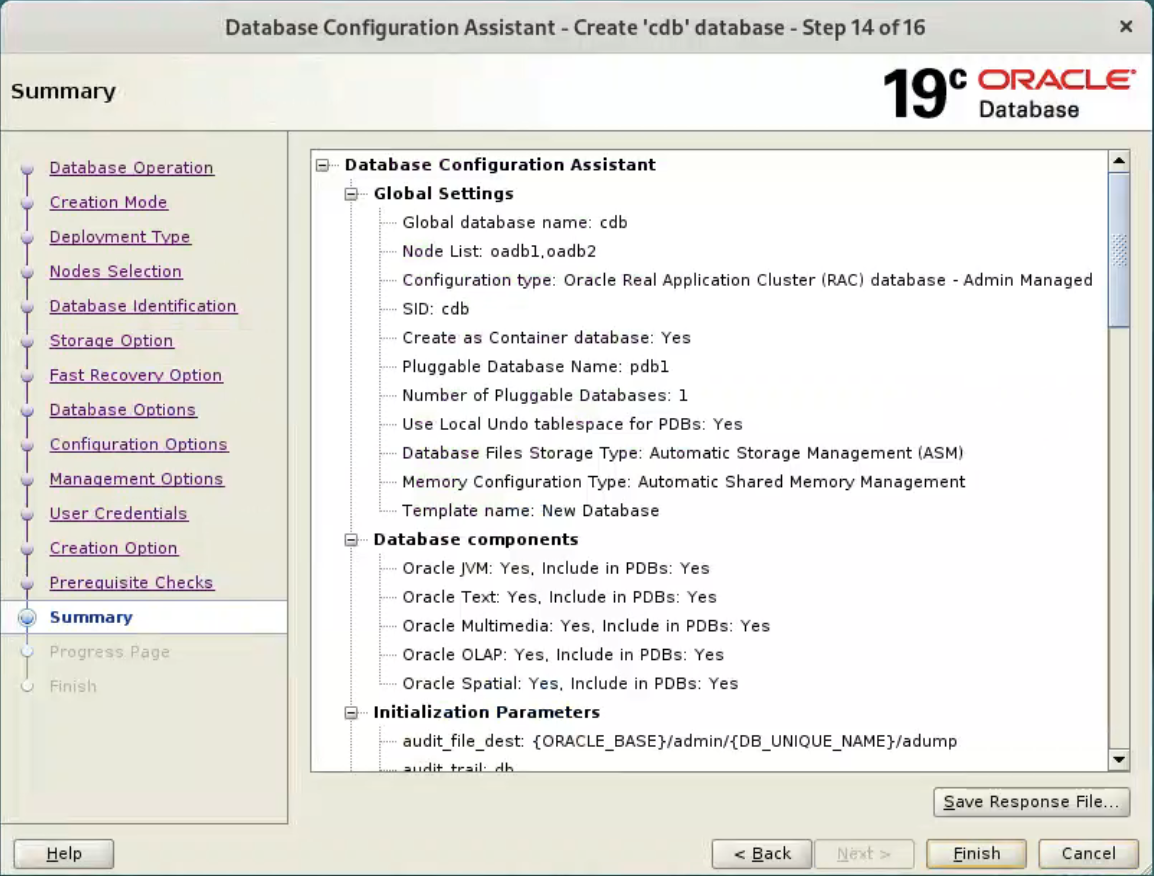 Wait while the database creation takes place.
Wait while the database creation takes place.  If you want to modify passwords, click the “Password Management” button. When finished, click the “Close” button.
If you want to modify passwords, click the “Password Management” button. When finished, click the “Close” button. 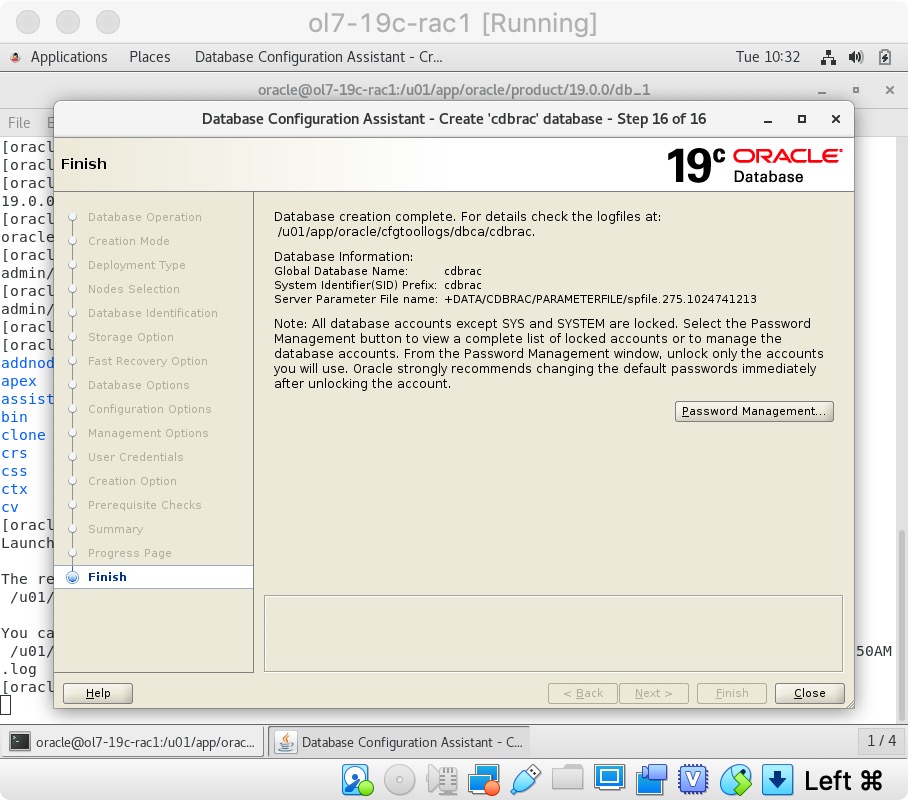 The RAC database creation is now complete.
The RAC database creation is now complete.
Check the Status of the RAC
There are several ways to check the status of the RAC. The srvctl utility shows the current configuration and status of the RAC database.
grid@oadb1[+ASM1]:/home/grid$ crsctl stat res -t
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Name Target State Server State details
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Local Resources
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ora.LISTENER.lsnr
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.chad
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.net1.network
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.ons
ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cluster Resources
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
ora.ASMNET1LSNR_ASM.lsnr(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.DATA.dg(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.FRA.dg(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.LISTENER_SCAN1.lsnr
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.asm(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 Started,STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 Started,STABLE
ora.asmnet1.asmnetwork(ora.asmgroup)
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.cvu
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.oadb1.vip
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 STABLE
ora.oadb2.vip
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.qosmserver
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
ora.rac.db
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb1 Open,HOME=/u01/app/o
racle/product/19.0.0
/db_1,STABLE
2 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 Open,HOME=/u01/app/o
racle/product/19.0.0
/db_1,STABLE
ora.scan1.vip
1 ONLINE ONLINE oadb2 STABLE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
grid@oadb1[+ASM1]:/home/grid$
[oracle@ol9-19c-rac1 rac]$ grid_env
[oracle@ol9-19c-rac1 rac]$ srvctl config database -d rac
Database unique name: rac
Database name: rac
Oracle home: /u01/app/oracle/product/19.0.0/db_1
Oracle user: oracle
Spfile: +DATA/RAC/PARAMETERFILE/spfile.285.1163931523
Password file: +DATA/RAC/PASSWORD/pwdrac.264.1163928547
Domain:
Start options: open
Stop options: immediate
Database role: PRIMARY
Management policy: AUTOMATIC
Server pools:
Disk Groups: DATA
Mount point paths:
Services:
Type: RAC
Start concurrency:
Stop concurrency:
OSDBA group: dba
OSOPER group: oper
Database instances: rac1,rac2
Configured nodes: oadb1,oadb2
CSS critical: no
CPU count: 0
Memory target: 0
Maximum memory: 0
Default network number for database services:
Database is administrator managed
[oracle@ol9-19c-rac1 rac]$
The V$ACTIVE_INSTANCES view can also display the current status of the instances.
[oracle@ol9-19c-rac1 rac]$ sqlplus / as sysdba
SQL*Plus: Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production on Tue Nov 19 10:34:25 2019
Version 19.22.0.0.0
Copyright (c) 1982, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Connected to:
Oracle Database 19c Enterprise Edition Release 19.0.0.0.0 - Production
Version 19.22.0.0.0
SQL> SELECT inst_name FROM v$active_instances;
INST_NAME
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
oadb1:rac1
oadb2:rac2
SQL>
Reference
For more information see:
- Grid Infrastructure Installation and Upgrade Guide for Linux
- Database Installation Guide for Linux
- Oracle Database 12c Release 2 (12.2) RAC On Oracle Linux 7 Using VirtualBox
End.